Cloud Computing - 初识4 cyber security
Useful site
Fundamentals
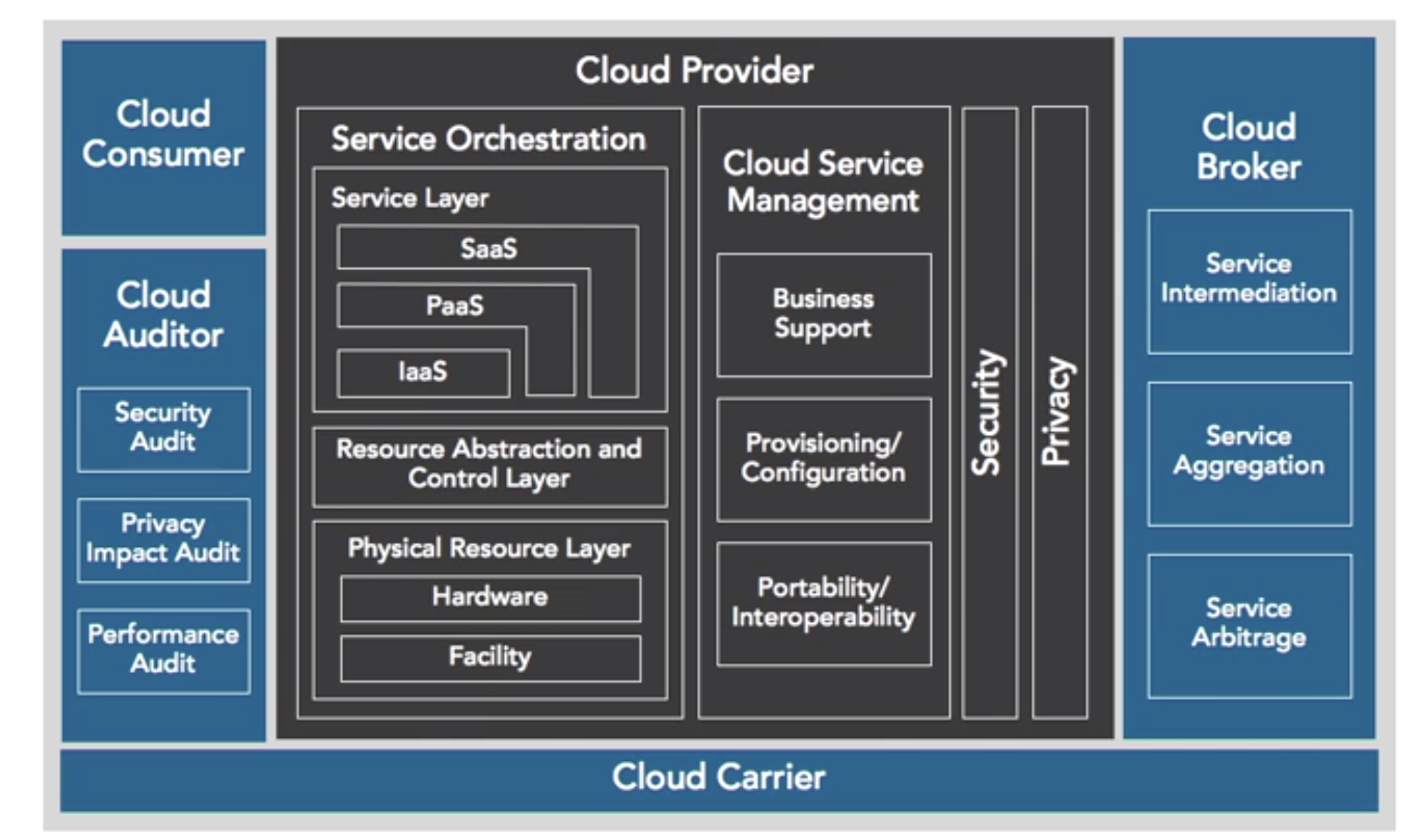
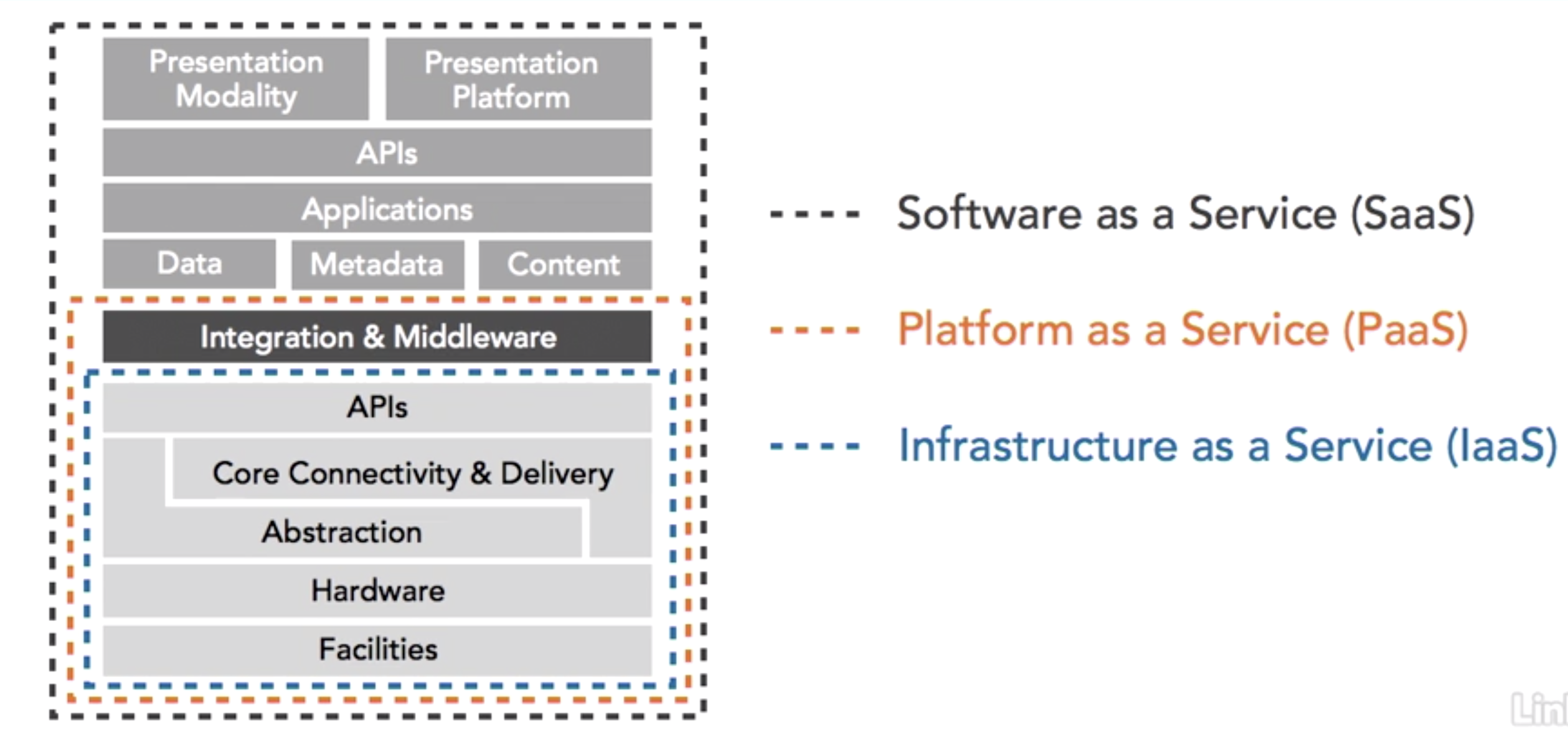
- Models
Anatomy of a service failure
- eg1: EBS nodes are served by 2 networks, primary (high bandwidth) and replication(low handwidth) network
- Amazon Cloud 12:47 am on April 21st 2011
- a network change was implemented to upgrade the capacity of the primary, this is a standard operation known as a traffic shift
- in this inicident, the traffic incorrectly routed to the low-bandwidth network, causing node to lose replica connections
- solution: roll back, but the damage had been down
- many nodes were trying to re-mirror, the free space was quickly consumed
- solution: stop API calls and block all access between the degraded cluster and the control plane
- eg2: Codespaces.com was a code-hosting and pm services provider, runnint its complete IT infra in Amazon cloud
- June the 17th, 2014, came under a distributed denial-of-service attack. The intruders had obtained the login credentials to the company’s Amazon EC2 management console
- the intruders had permanently deleted everything, the recovery has hopeless
- the incident highlight some of the key risks when using cloud
- eg1: EBS nodes are served by 2 networks, primary (high bandwidth) and replication(low handwidth) network
DSI-07, Certification or Self-Assessment
- Models
Guidance
- indentify governance and risk
- corporate governance is the set processes, technologies, culture and external mandates that effect the way in which an enterprise is directed and controlled
- governance model adhere to 5 basice principles:
- auditing supply chains
- board/management structrue
- corporate responsibility
- transparency and disclosure
- exercising control
- risk strategies:
- avoidance
- reduction
- transfer
- acceptance
- assessment of 3rd pary
- incident management
- business continuity
- DR
- comply legal and audit requirements
- data sovereignty
- cloud user want to know where their data is stored
- if personal info is involved
- ensure cloud electronic docs are discoverable
- especially around the legal implications of who has possession, custody and control of docs
- SLA
- check for compliance issues before 签合同?
- what obligations affect this service
- who is responsible for compliance?
- can the cloud provider demonstrate compliance?
- what controls are required?
- data sovereignty
- manage info and data security
- data dispersion (IDA: info dispersion algorithm)
- 6 key elements of info governments:
- info classification
- info management policies
- location and jurisdictinal policies
- authorizations
- ownership
- custodianship
- provide portability and interoperability
- physical security
- eg: DC location选址很重要
- understand DC operations
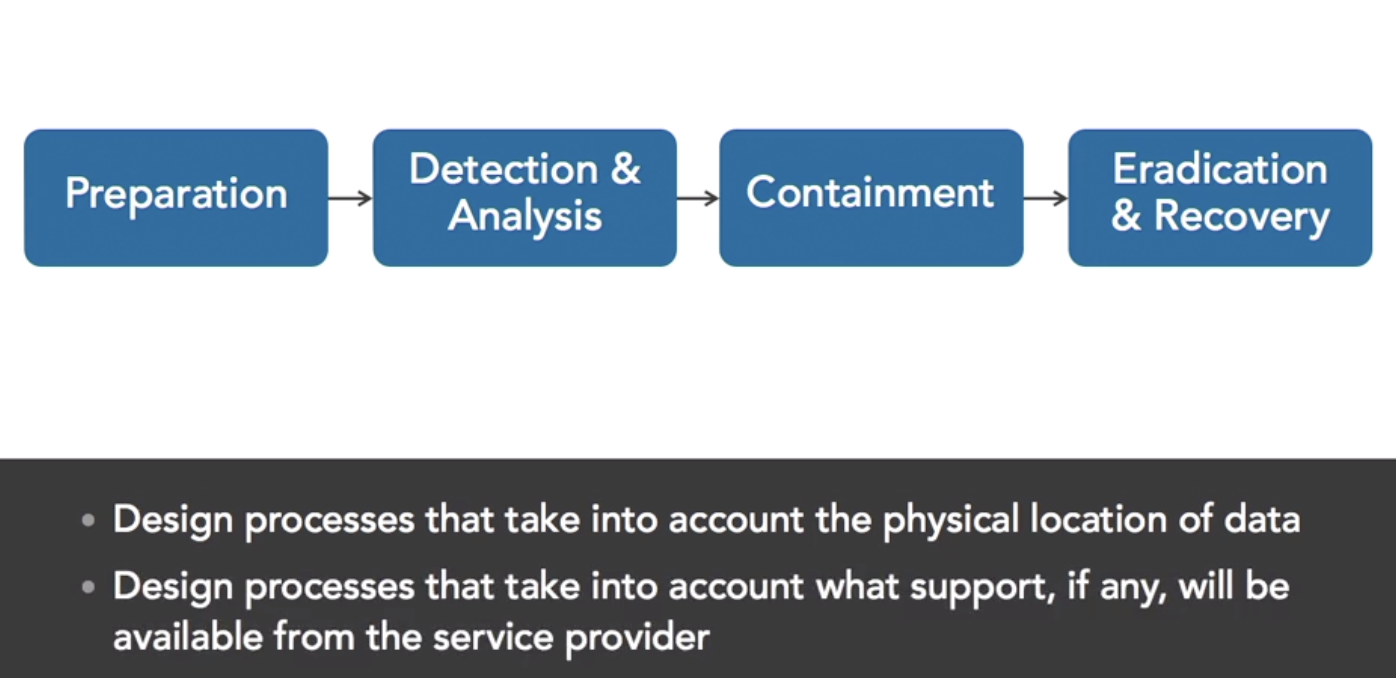
- mange incident response
- NIST SP800-61
- max apps security
- secure SDLC
- physical security
- incompatibility
- access to logs
- fail-over mechanisms
- compliance
- maturity models
- building security in BSIMM2(maturity model version 2)
- software assurance (SAMM)
- systems security engineering capability (SSE-CMM)
- assurance programme
- verification
- construction
- risks
- secure SDLC
- test and monitor apps
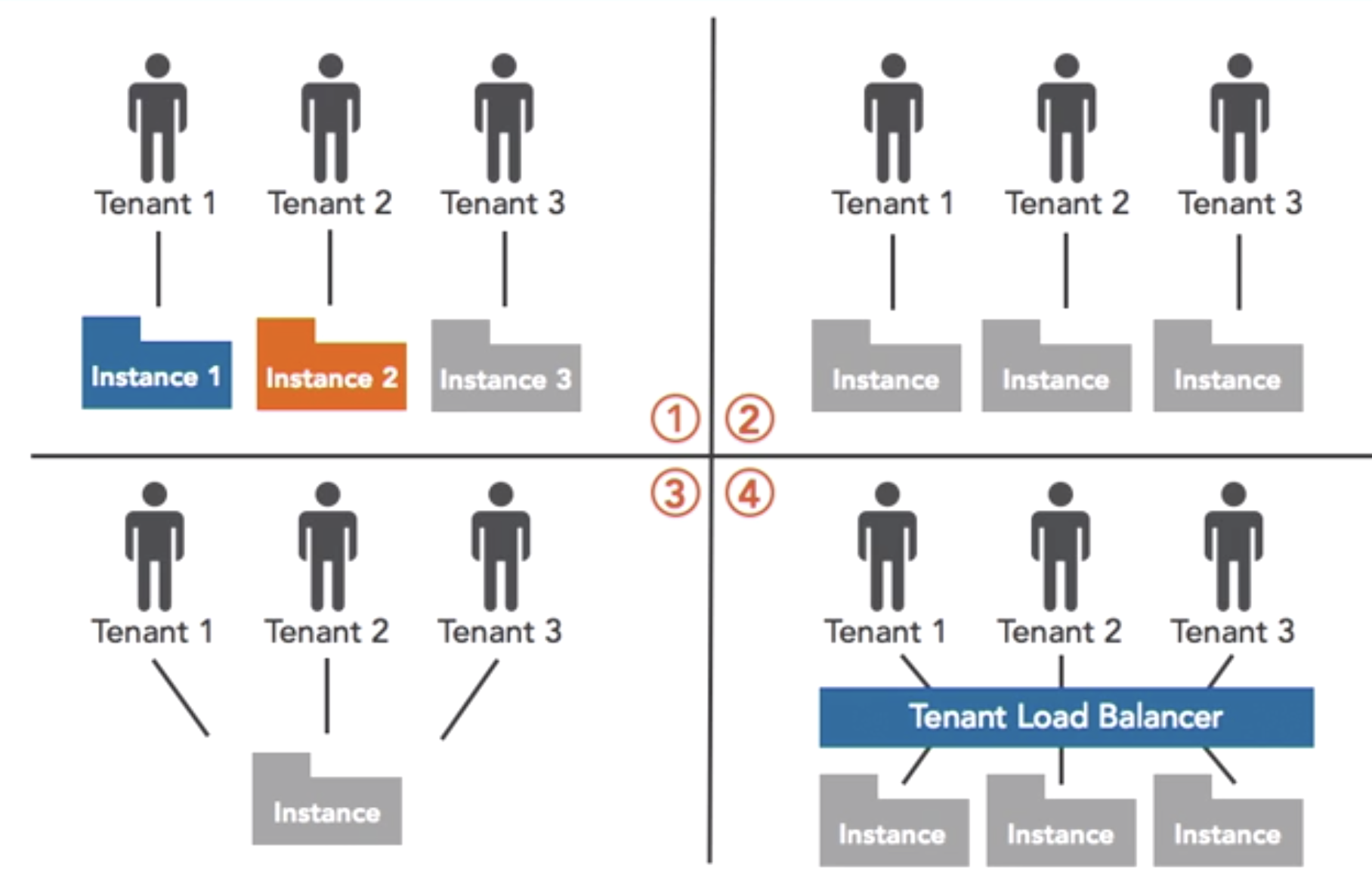
- Multi-tenancy test
- MT testing addresses the threat of one tenant accessing the data of another tenant on the same platform throught web layer vulnerabilities
- Inter-VM test
- Vm testing addresses the deficiencies in virtalization security such as improper implementation of vm zoning and segregation isssues leading to vm attachk across multiple infra tenants
- Monitor
- Logs
- performance
- malicious use
- compromise
- policy violations
- Multi-tenancy test
- manage encrytion and keys
- content aware encryption
- apply the encryption algorithm to Plain Text data to produce an unstructrued glob of ciphertext
- format perserving encryption
- apply the encryption algorithm in such a way that the ciphertext refelect the structure of the original Plain Text
- MD5
- key management
- have a cryptographic engine in which each user is registered in keys associated with their identity are used to automatically encrypt and edcrypt data
- content aware encryption
- verify indentity in the cloud
- control cloud access
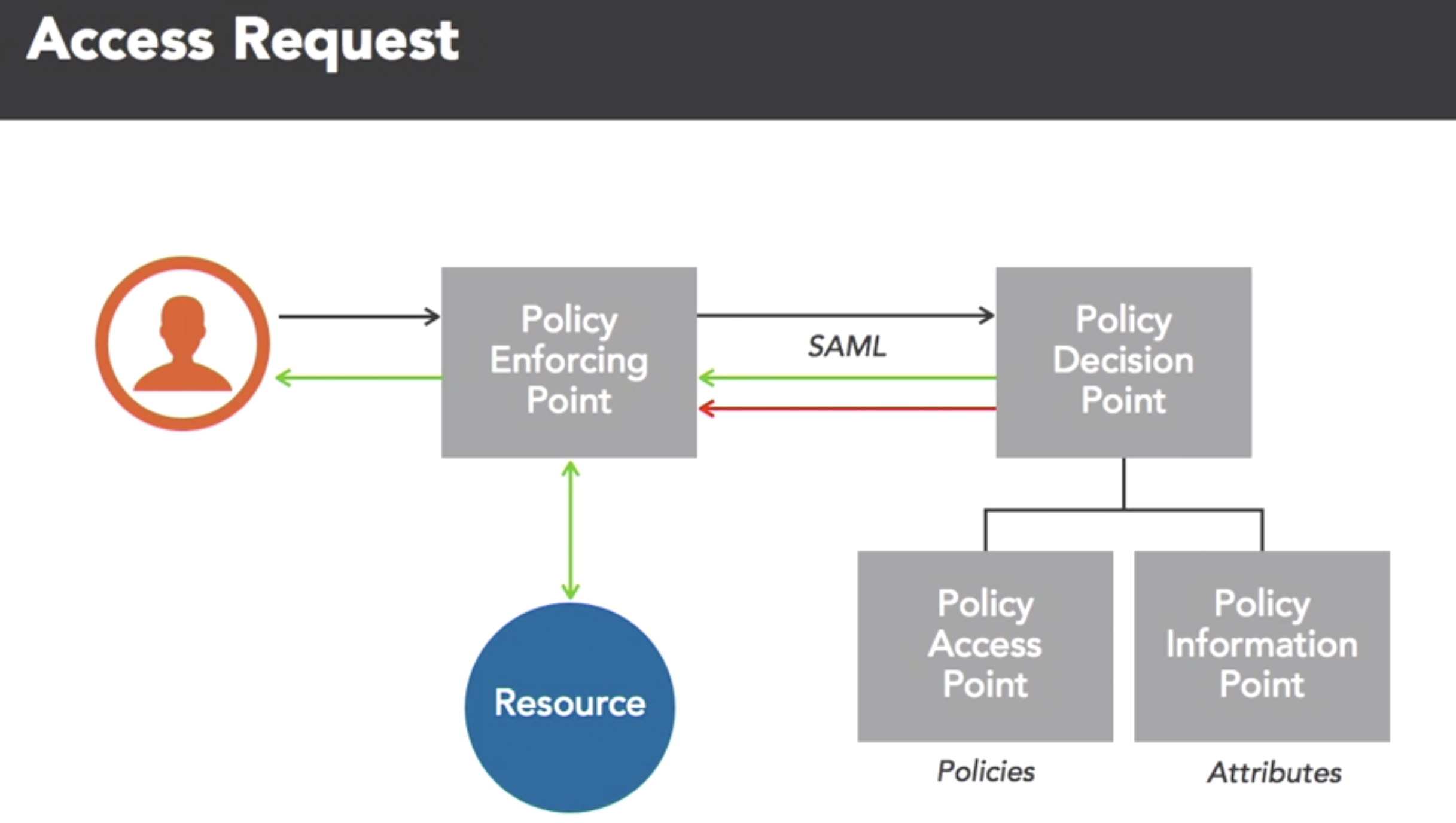
- Authorrization Models: rule based, role based
- SAML alternatives:
- SWRL
- XACML
- XRBAC
- KaoS
- OAUTH
- implement virtualization
- hypervisor (hardware -> OS)
- provide security as a service
- challenge & solution of cloud security (15 questions)
- non-traditional steps to move data to the cloud?
- monitor db and file activity in orcer to detect large internal data migrations
- monitor data moving to the cloud using URL filters or data loss prevention systmes
- standatds for single sign on?
- OAth
- SMAL
- 5 basic principles of corporate government?
- 3 teams for DR?
- emergency response team
- crisis management team
- incident response team
- what activity includes the cohesive app of policies, guidance and controls?
- corporate governance
- 2 reasons for data being classified as confidential and encrypted?
- regulatory compliance
- corporate secrecy
- 4 cloud deployment models?
- pubic
- private/community
- hybird
- process of stripping sensitive personal info called?
- definition of data anonymizaton
- is customer or service provider security monitoring more responsive?
- the customer will be more responseive because they’re monitoring just their own security alerts, whereas a service provider may be monitoring hundreds or thousands of systems
- 3 key concerns about security as service?
- compliance
- multi-tenancy
- vendor locking
- what form of DRM is used to protect mass audience electronic books?
- consumer digital rights management is the right answer
- enterprise digital rights management
- 3 approaches can be used to automate the publication of audit findings?
- cloud audit
- cloud trust
- CYBEX X.1500.
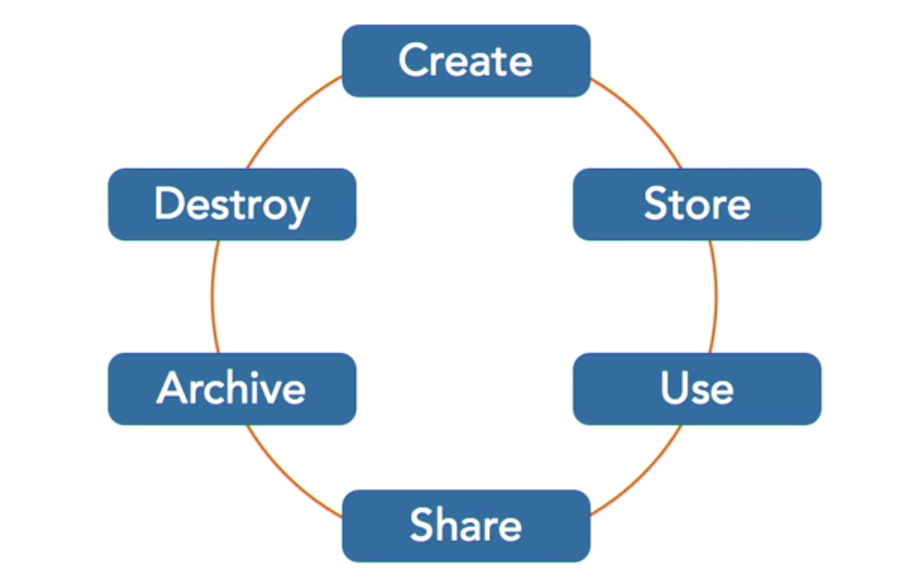
- 6 elements of data security lifecycle?
- create
- store
- use
- share
- archive
- destroy
- 5 hypervisor architecture concerns?
- vm guest hardening
- hypervisor security
- inter-VM attacks
- blind spots
- performance
- VM sprawl
- instance on gaps
- vm encryption
- data commingling
- vm data destruction
- vm image tampering
- in-motion vm
- what technique is used to remove hardware level interoperability concerns?
- virtualizaion
- non-traditional steps to move data to the cloud?
- indentify governance and risk
Architecting
- SABSA (sherwood applied business security architecture)
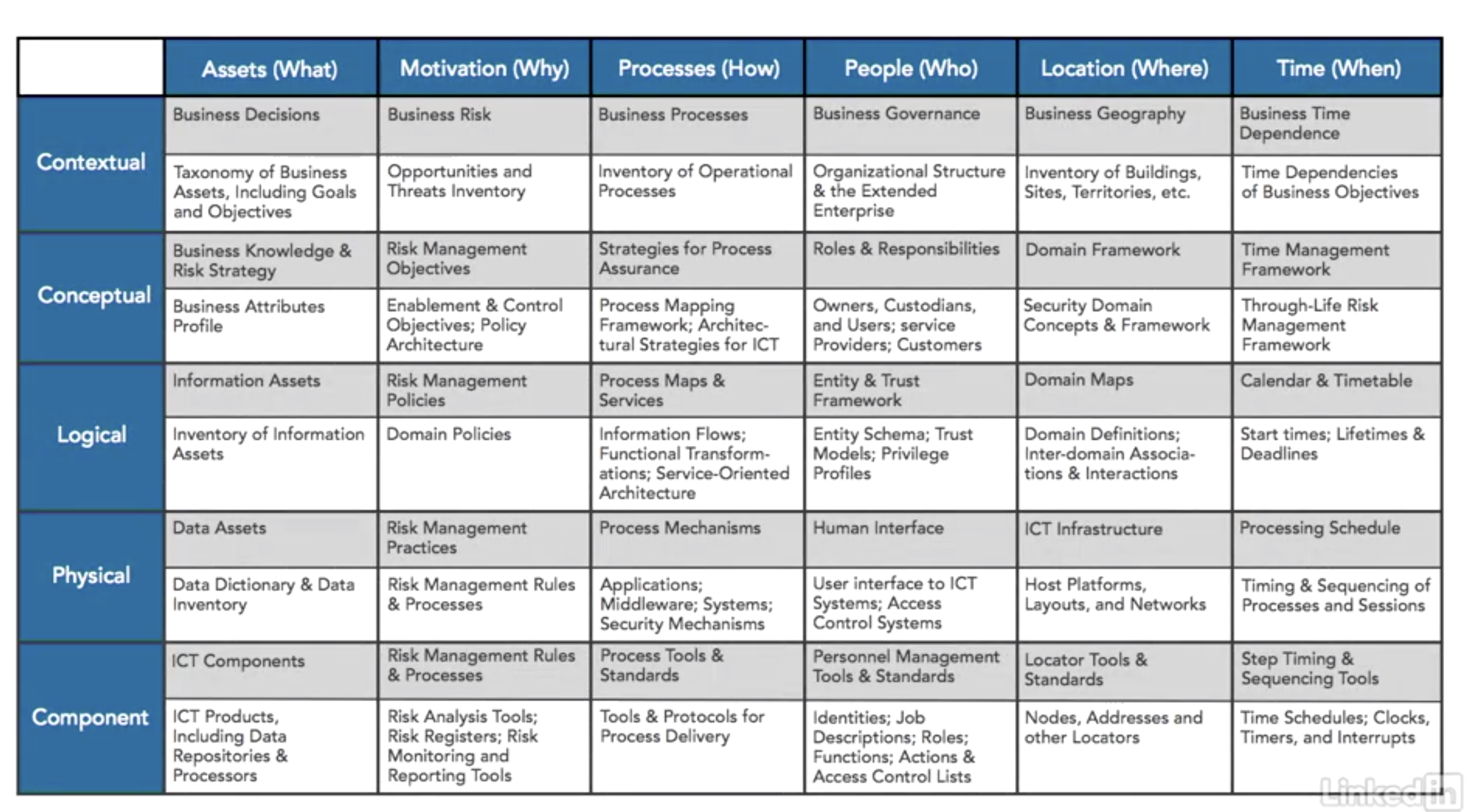
- capture business requirements and determin what security is needed to meet those requirements
- fast tracker
- a tool used a a 1st step in capturing business requirements of SABSA
- stardard: ISO 27002 AND NIST SP800-53
- attribute sets: single tier and triple tier
- a tool used a a 1st step in capturing business requirements of SABSA
- define SABSA attr
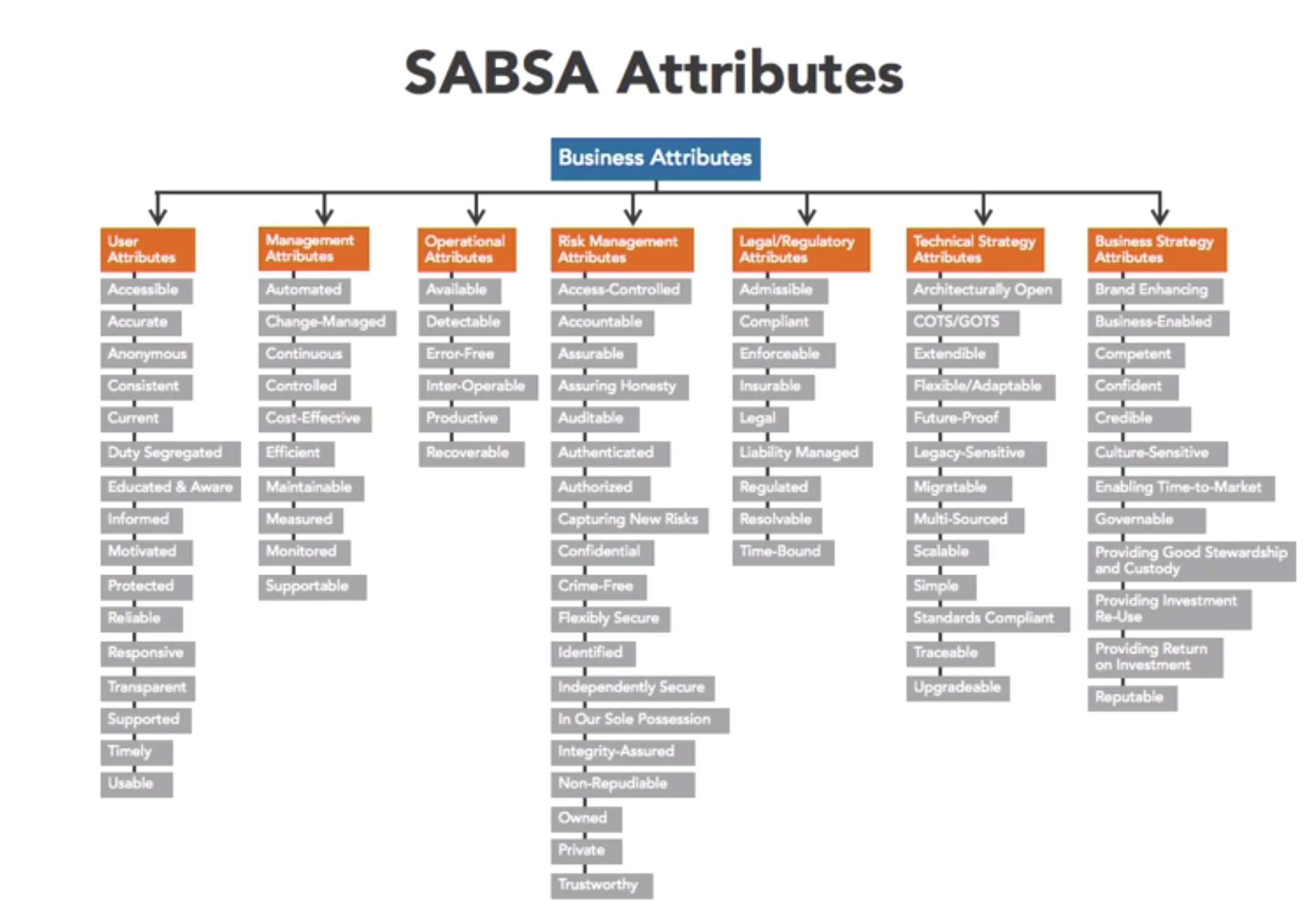
- security is often defined in terms of Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability
- SABSA defines 85 common attributes
- 6 categories: focus of the business outcome which is being protected by the attributes
- user
- management
- operatonal
- risk
- technical
- legal
- business
- the business attribute profile describes the risks of business failure and what success look like in terms of risk mitigation
- cloud attr taxonomy
- map SABSA attrs to the ENISA risks
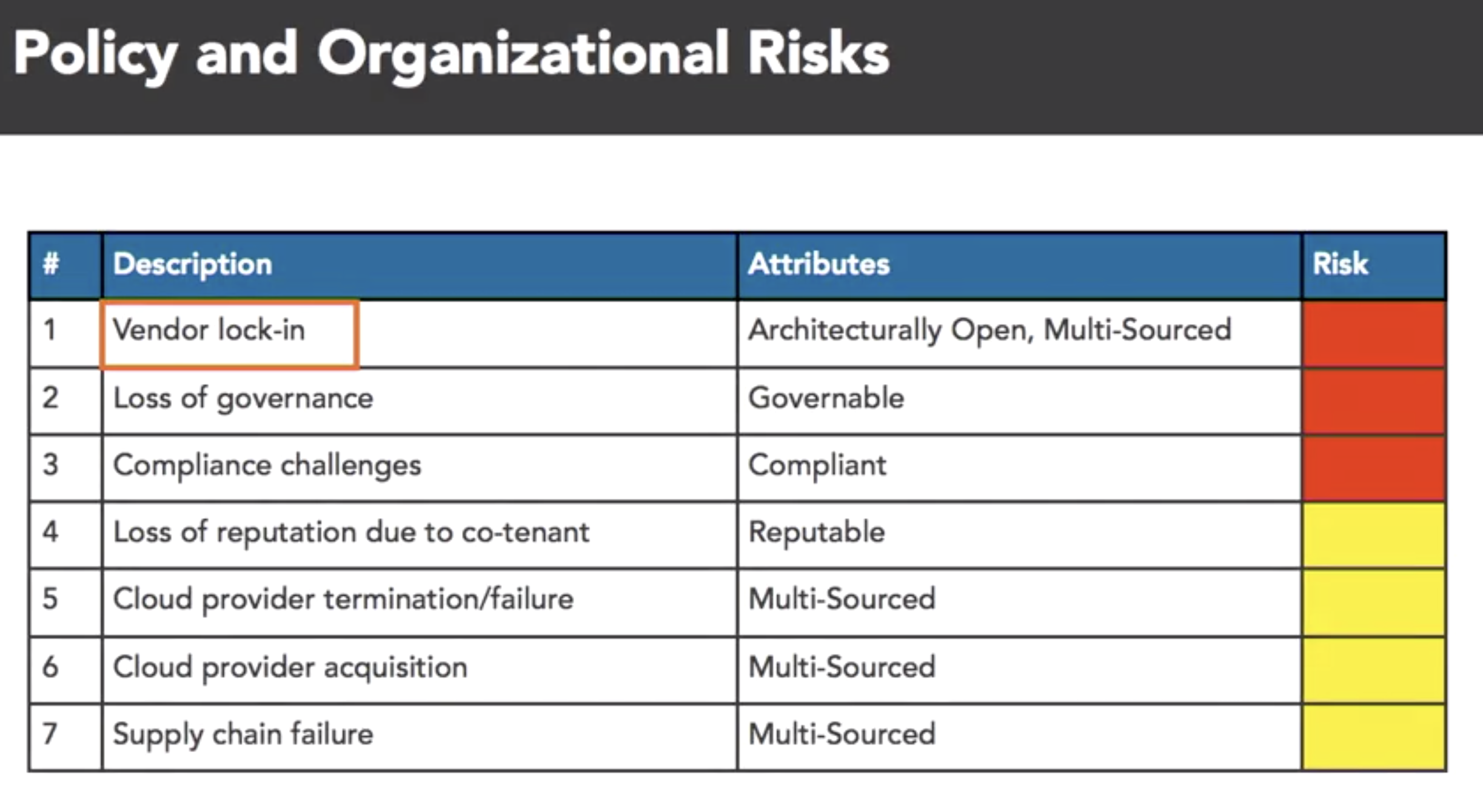
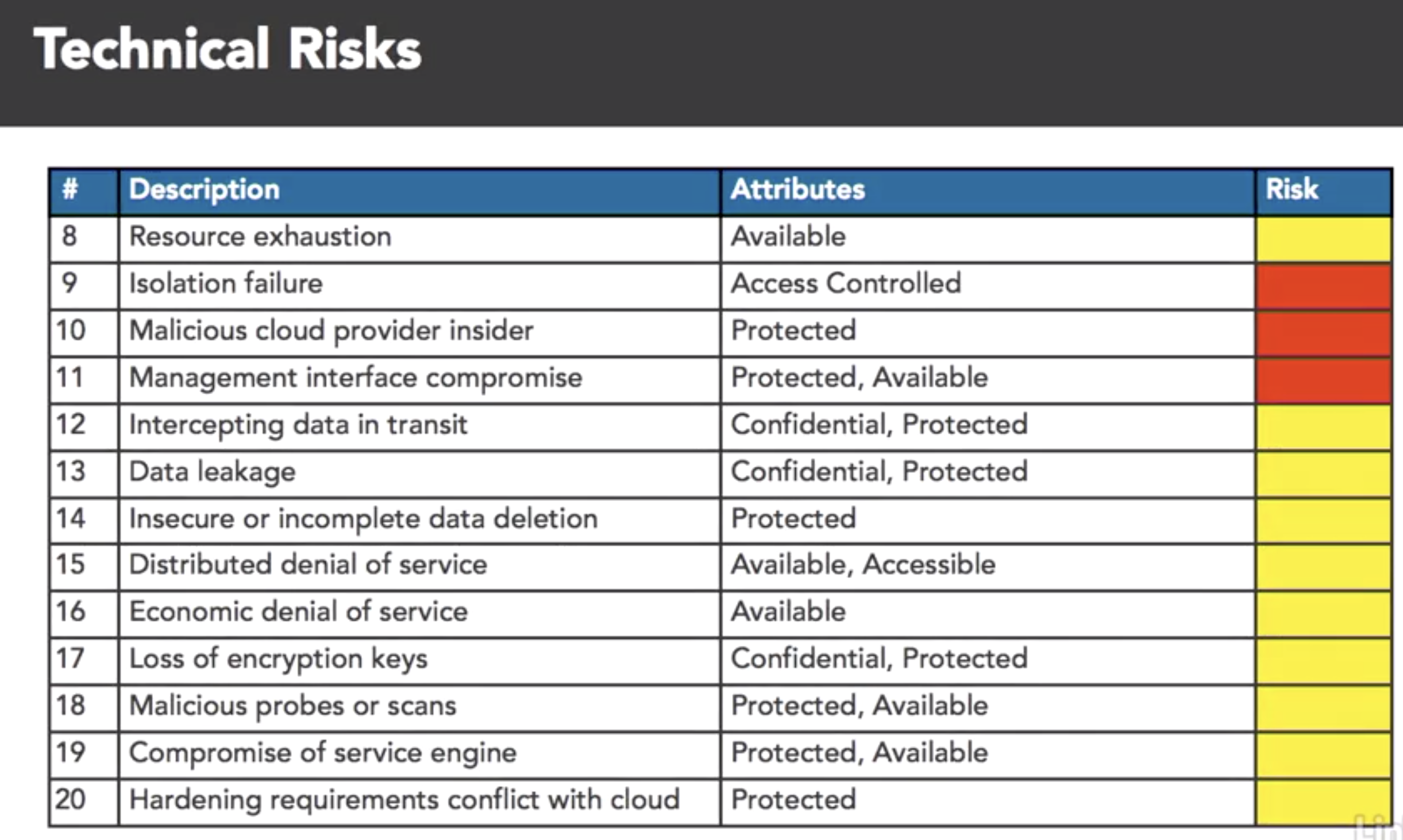
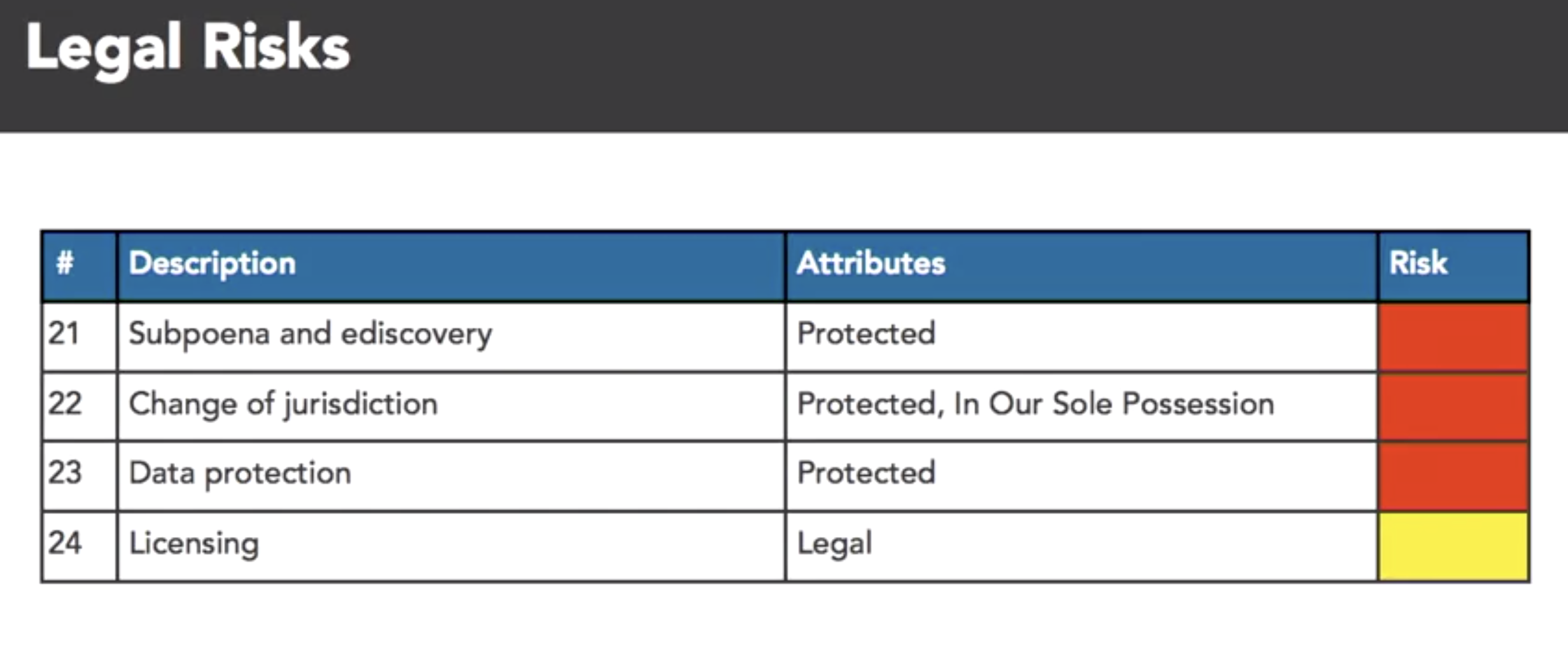
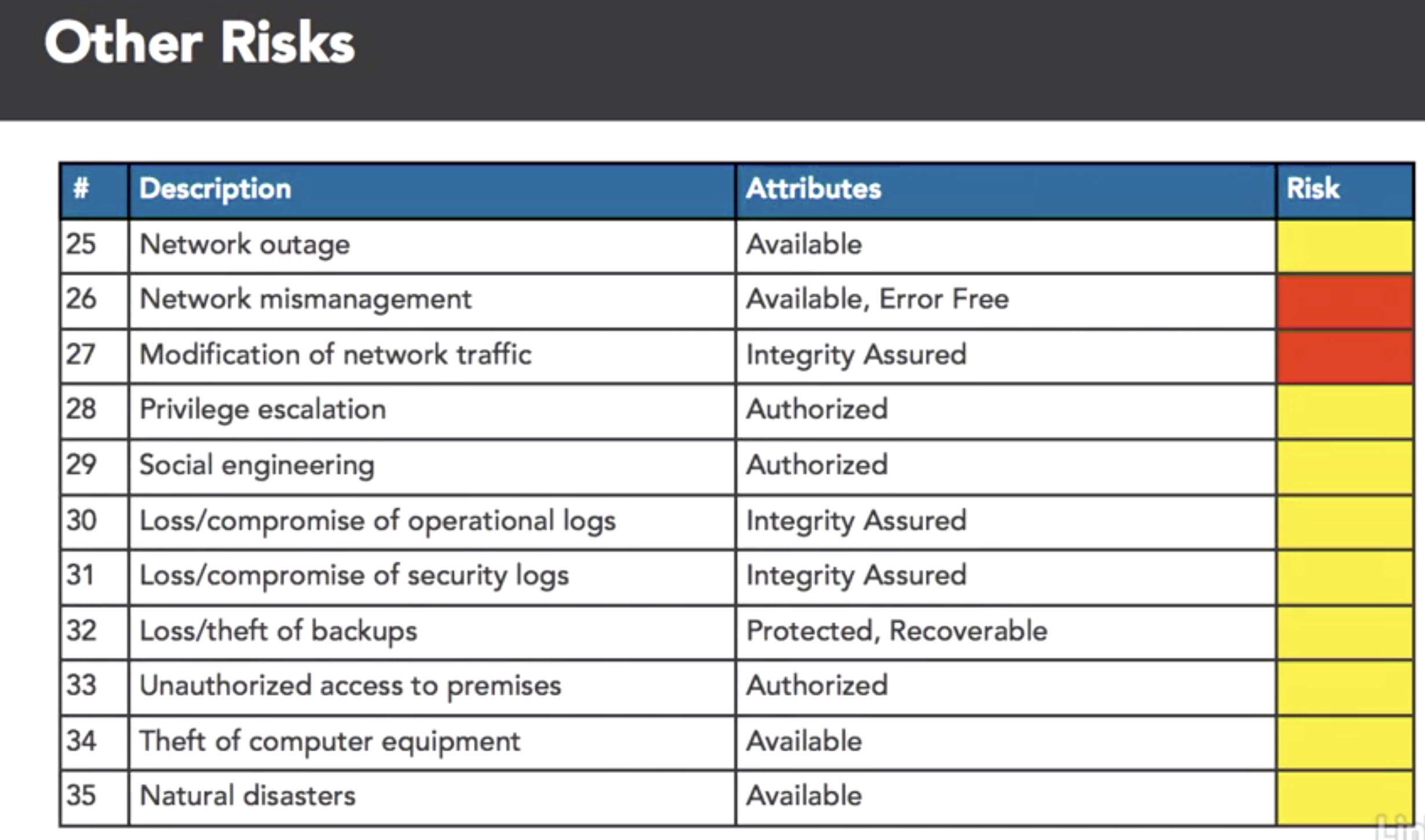
- benifit of cloud:
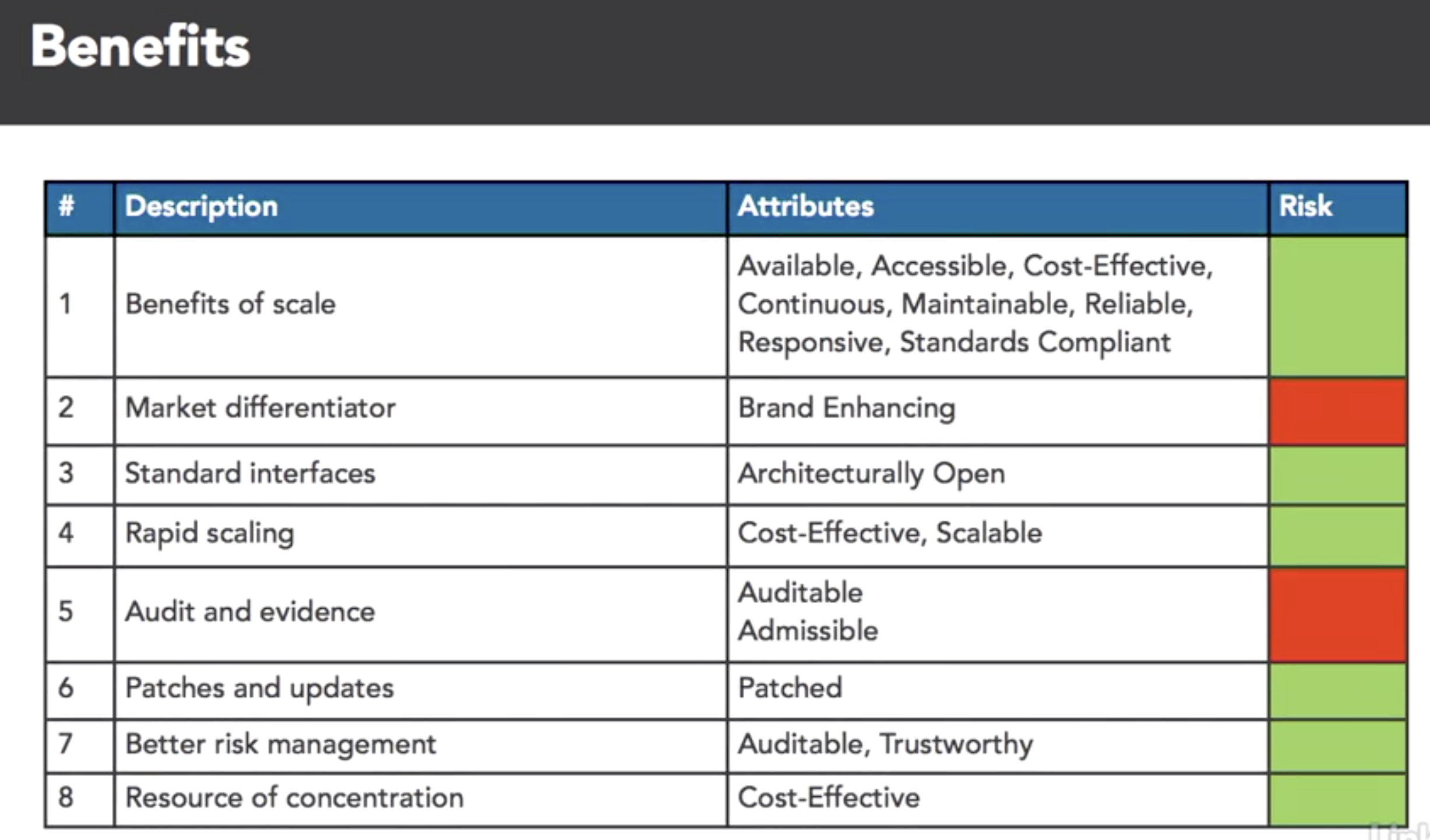
- taxonomy:
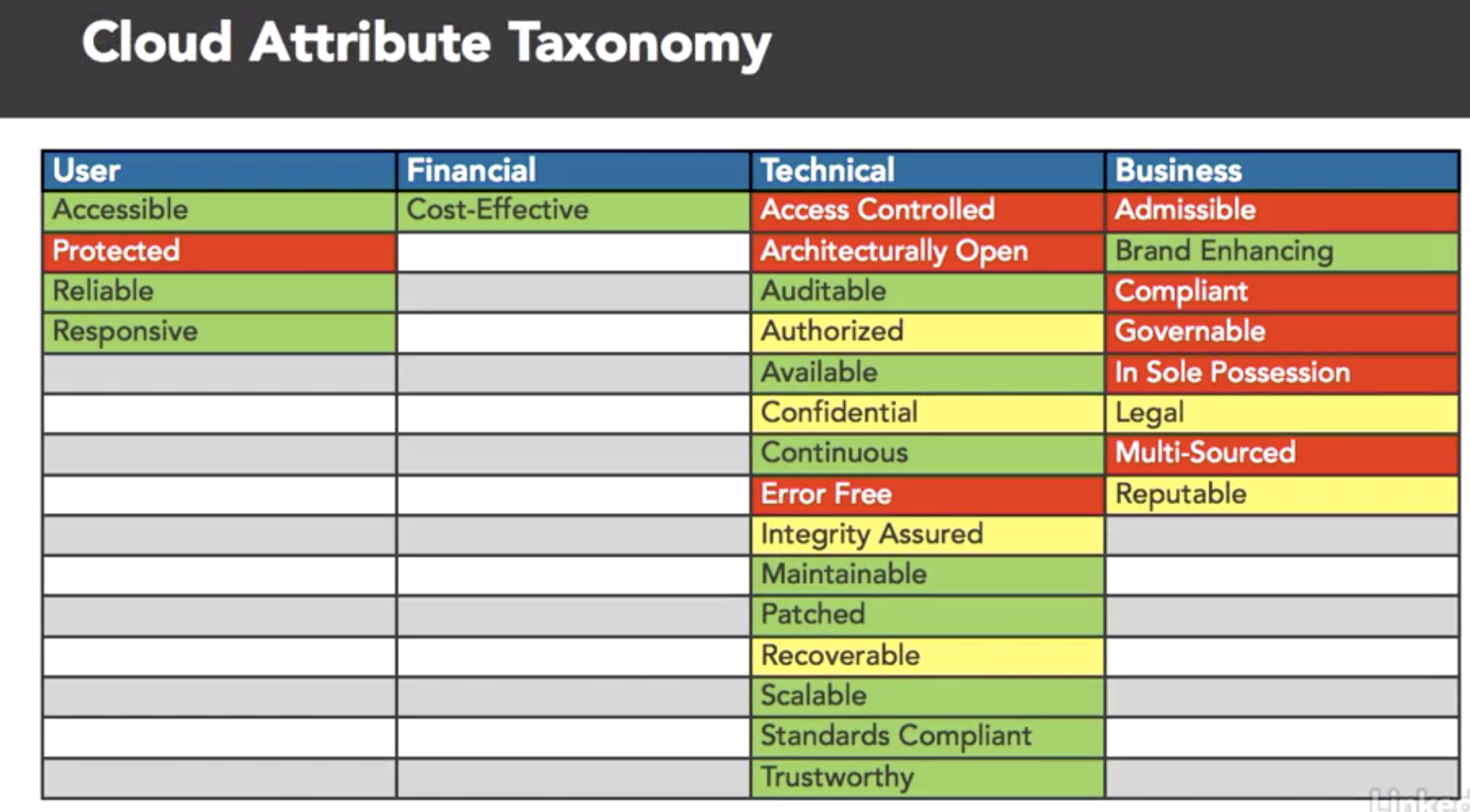
- map SABSA attrs to the ENISA risks
- SABSA (sherwood applied business security architecture)
