AWS Solutions Architect Associate2 - Data Security
- Design Concepts for Security
- Design Security with AWS services
- Design Concepts for Encryption
- Design Encryption with AWS services
- Security Scenarios and Tradeoffs
- Design for DR
Design Concepts for Security
- Data is money
- Design
- Metrics
- Monitor
- Management
- SLA
- Shared Model
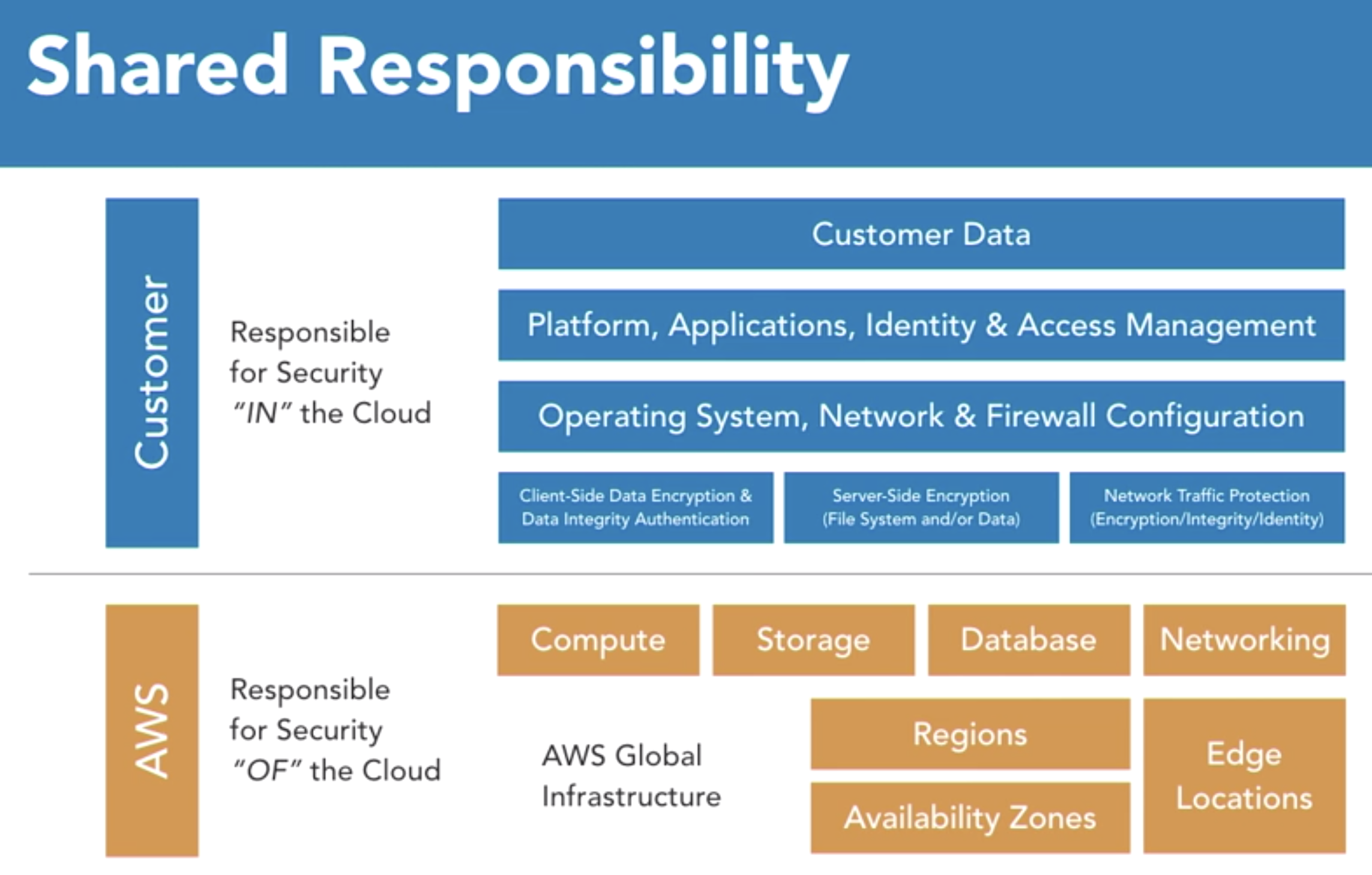
- What customer do: secures app in the aws cloud
- What AWS do:
- secures the aws cloud;
- provides patterns, checklist and whitepapers
- Devs should not own security
- Audits, aws audit guidance
- secuirty audits
- compliance audits
- internal or external auditors
- Data Flow
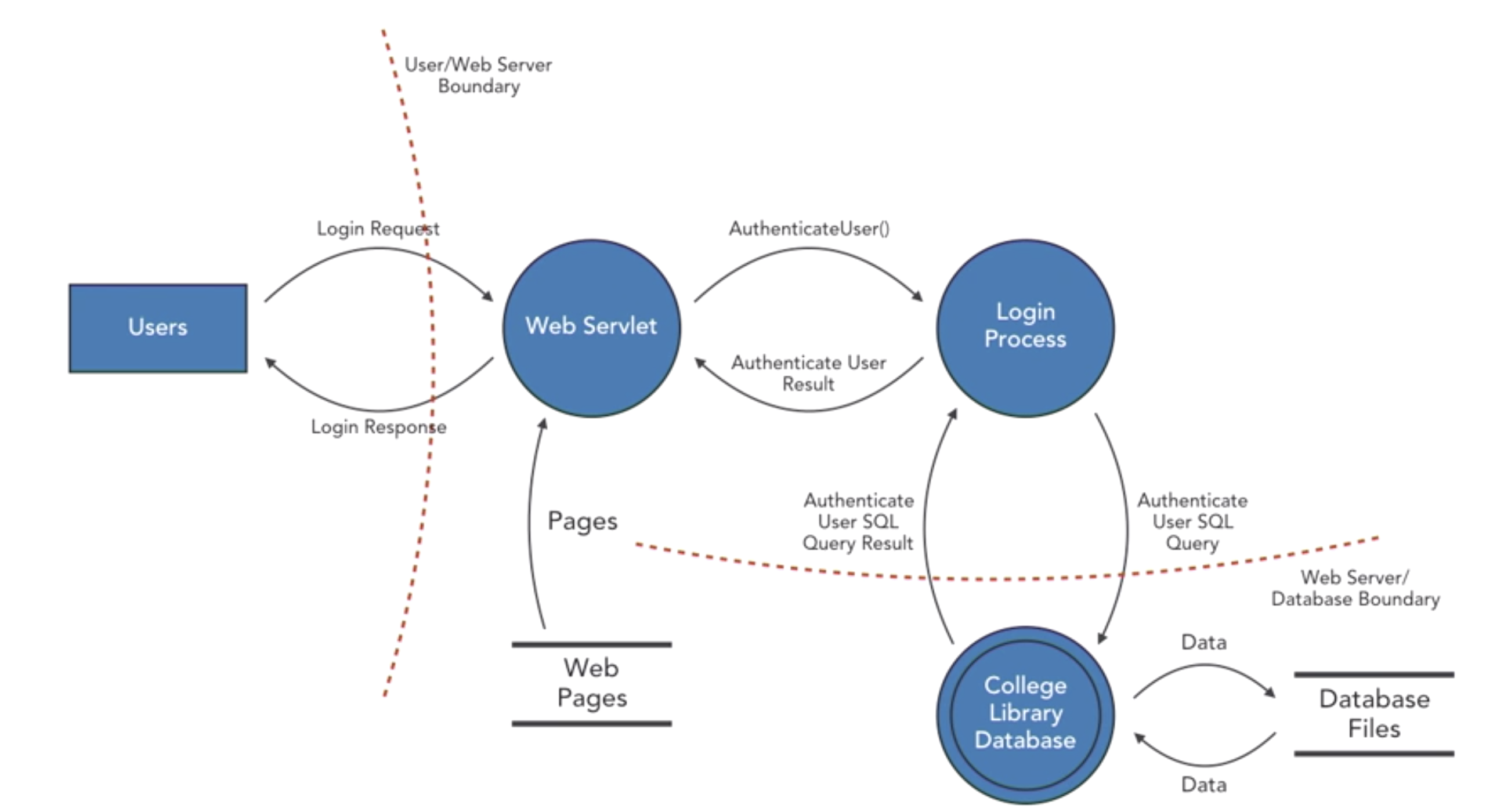
- external entities
- processes-single, multiple
- data stores
- data flows
- privilege boundaries
- Negative use cases
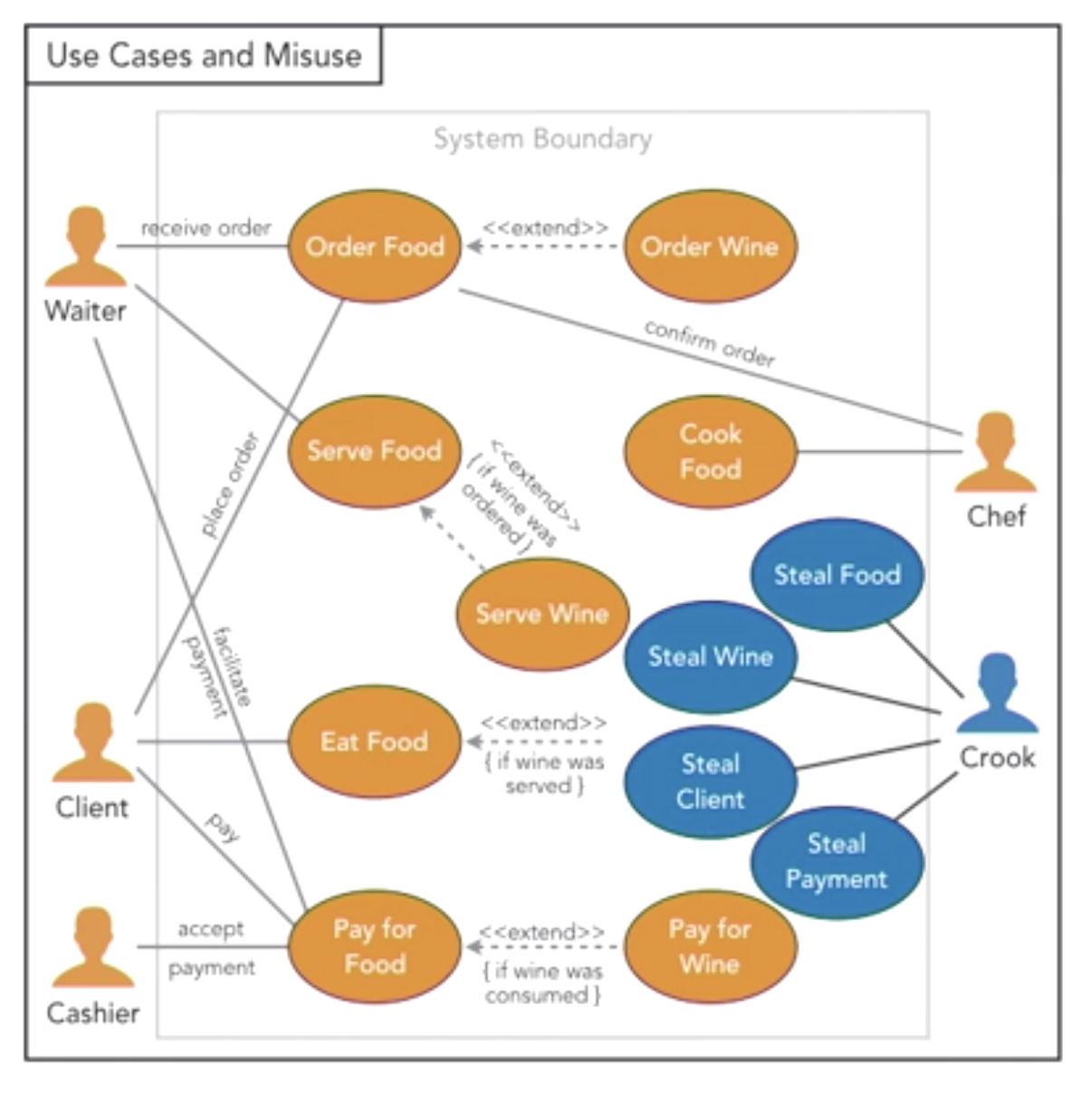
- postive path (happy path), expect pass
- negative path (err path), expect fail
- Threat Model
- ranking threats by a risk model
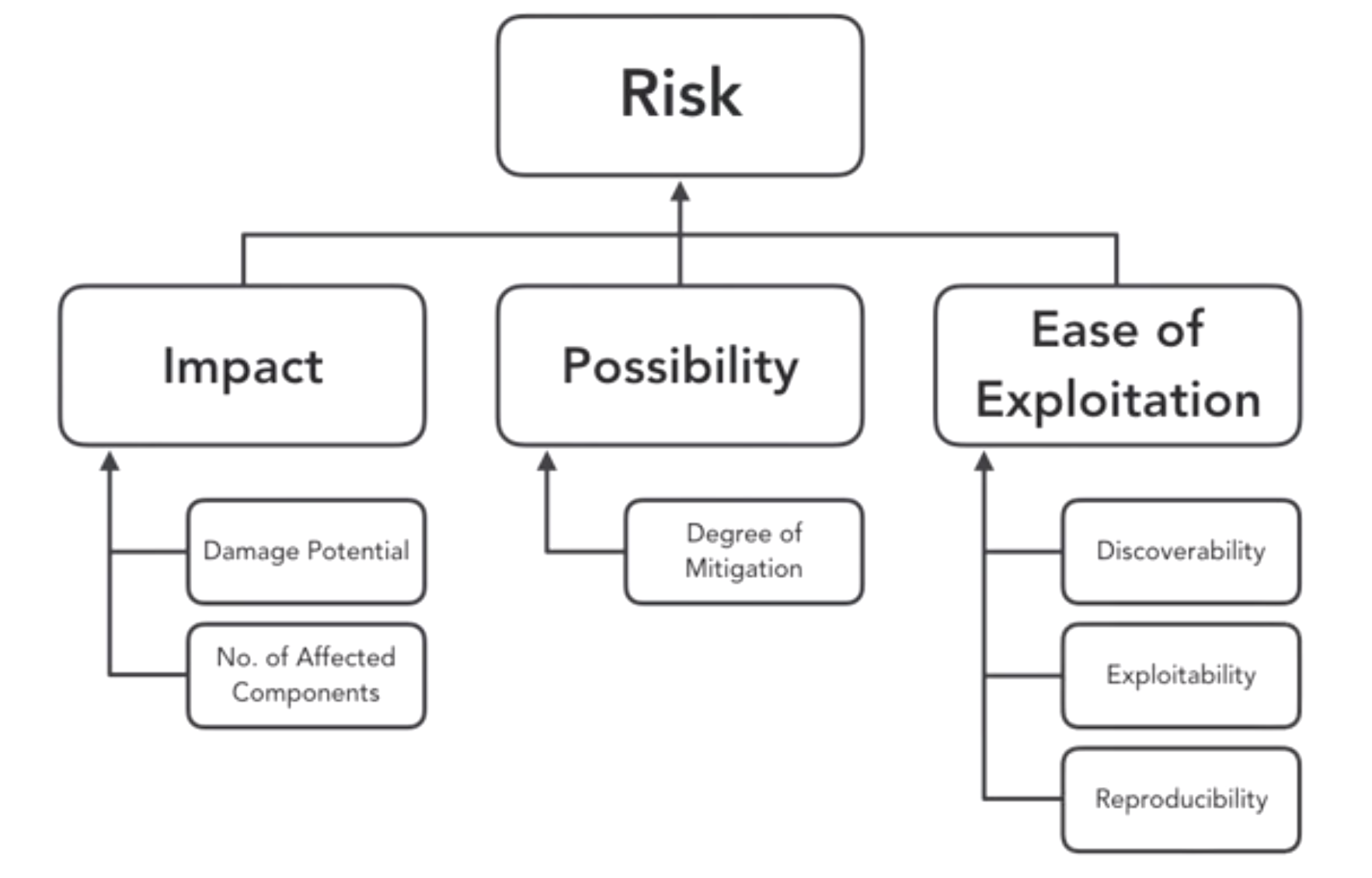
- ranking threat model
- reference
- application threat modeling
- CI Amazon web service foundations
- ranking threats by a risk model
Design Security with AWS services
- core AWS security services
- IAM
- Inspector
- Certificate Manager
- Directory service
- WAF & Shield
- Artifact
- Amazon Macie
- CloudHSM
- IAM: users and roles
- add IAM user
- access type, pwd
- create group, set police to the group
- sign in your IAM user
- customer your login URL
- create role to your IAM user
- select trust aws service,eg: EC2
- give it police
- add IAM user
- IAM: root
- one email per AWS account is root
- who set the account who get root credentials
- no one should be with root in a prod env
- aws root should use MFA
- reference: IAM Best Practices
- IAM: policies
- attach existed police
- create police
- set permissions
- ARN(amazon resource name)
- run simulation
- Logging: CloudWatch and CloudTrail
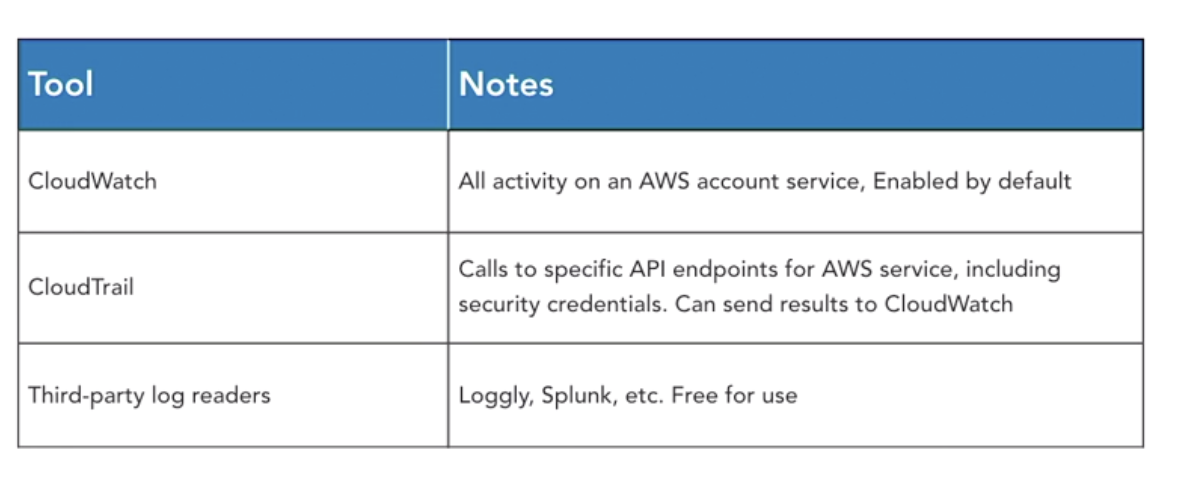
- CloudWatch: support alarm
- EC2 with inspector
- run a series of scans and provides with assessment results that you can action
- types:
- common vulnerabilities and exposures
- center for internet security (CIS) benchmarks
- security best practices
- runtime behavior ananlysis
- EC2 with WAF (web application firewall)
- for layers and middleware
- a tool can help mitigate DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks
- WAF works with lb
- WAF works with cloud front distributions for HTTP and HTTPS requests
- WAF works with Route53(DNS)
- WAF shield
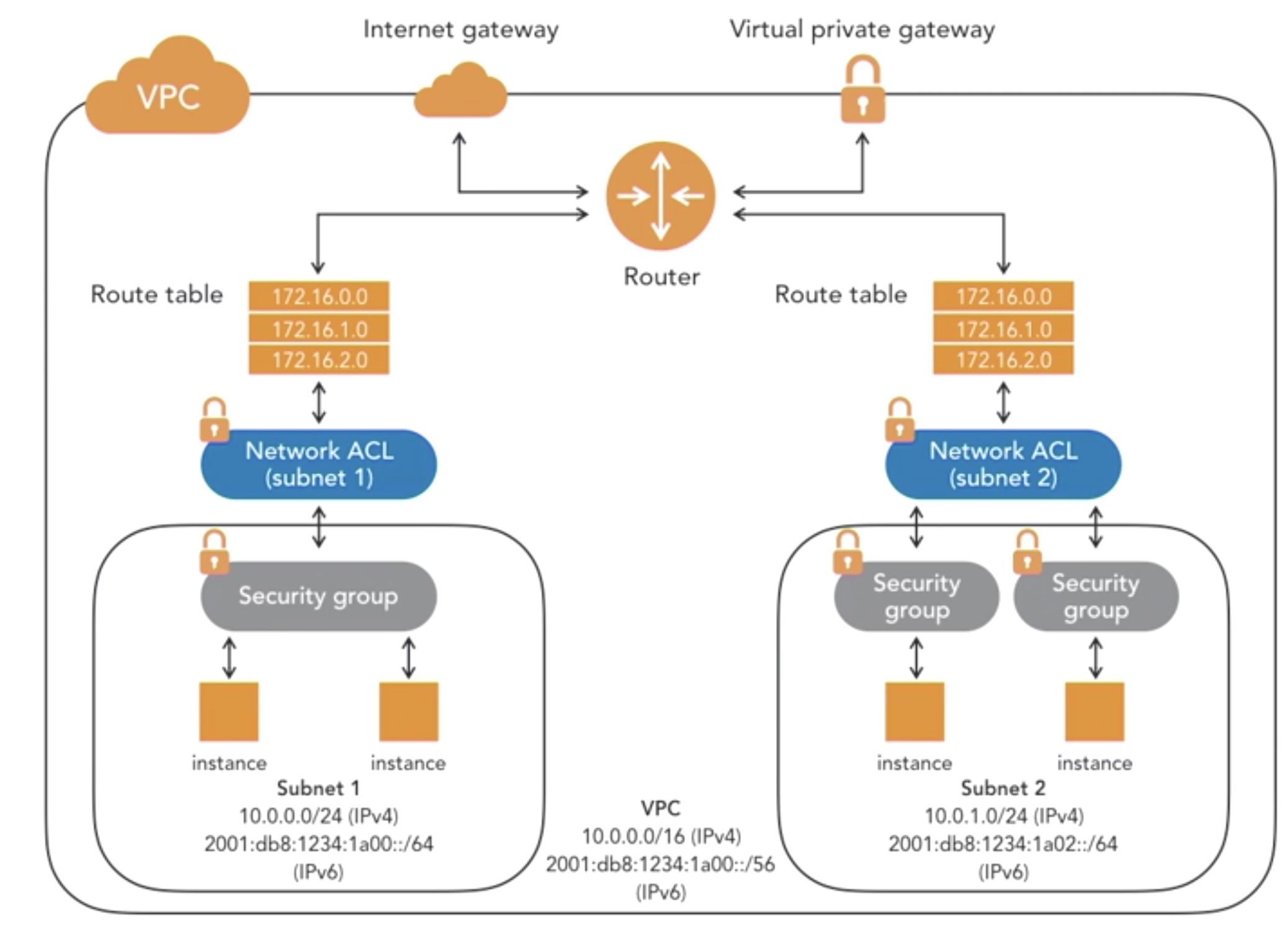
- VPC security
Design Concepts for Encryption
- what’s encryption?
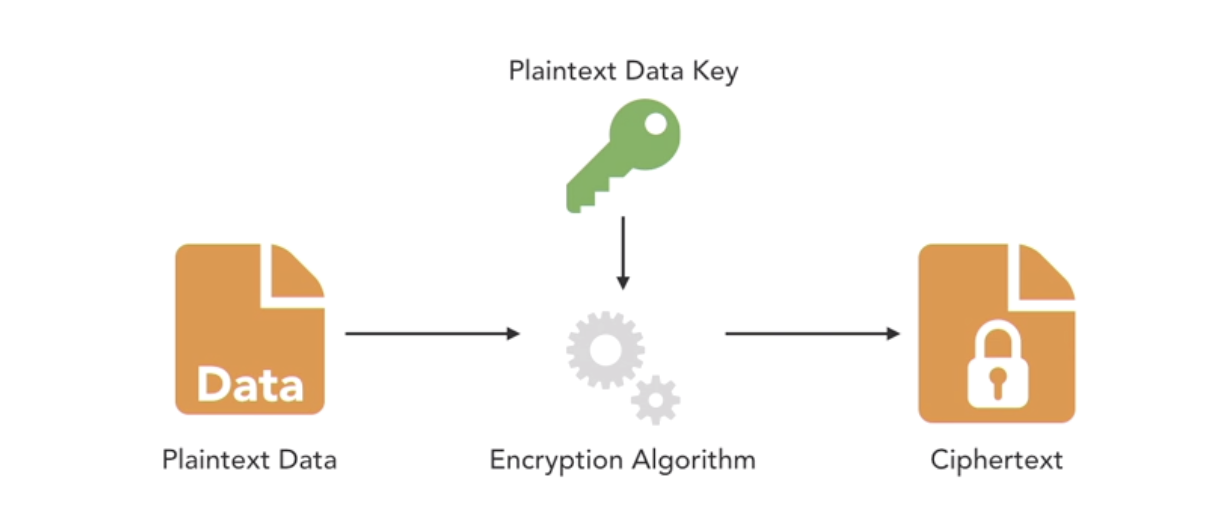
- No crypto is better than bad crypto
- How to manage you keys?
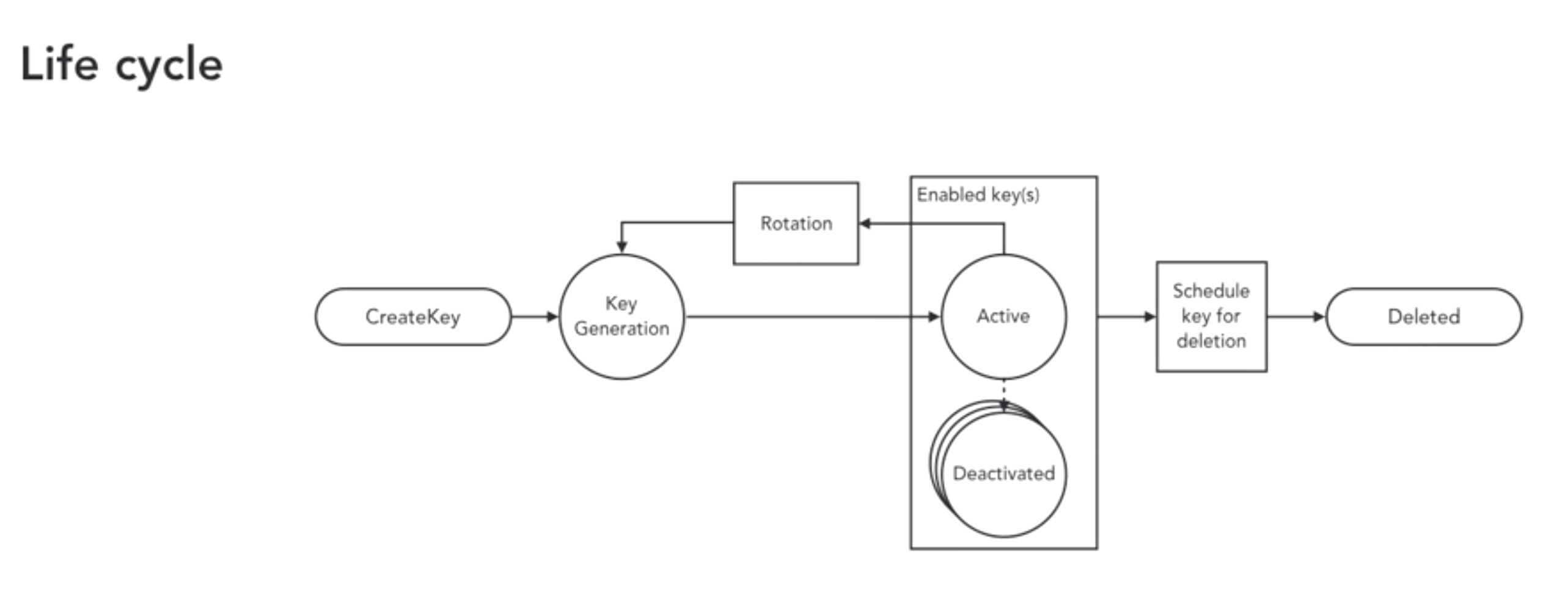
- create -> generate -> activate -> use -> rotate -> deactivate -> deactive
- encryption key managemetns choices
- data encrytion in AWS
- client-side vs server-side encrytion
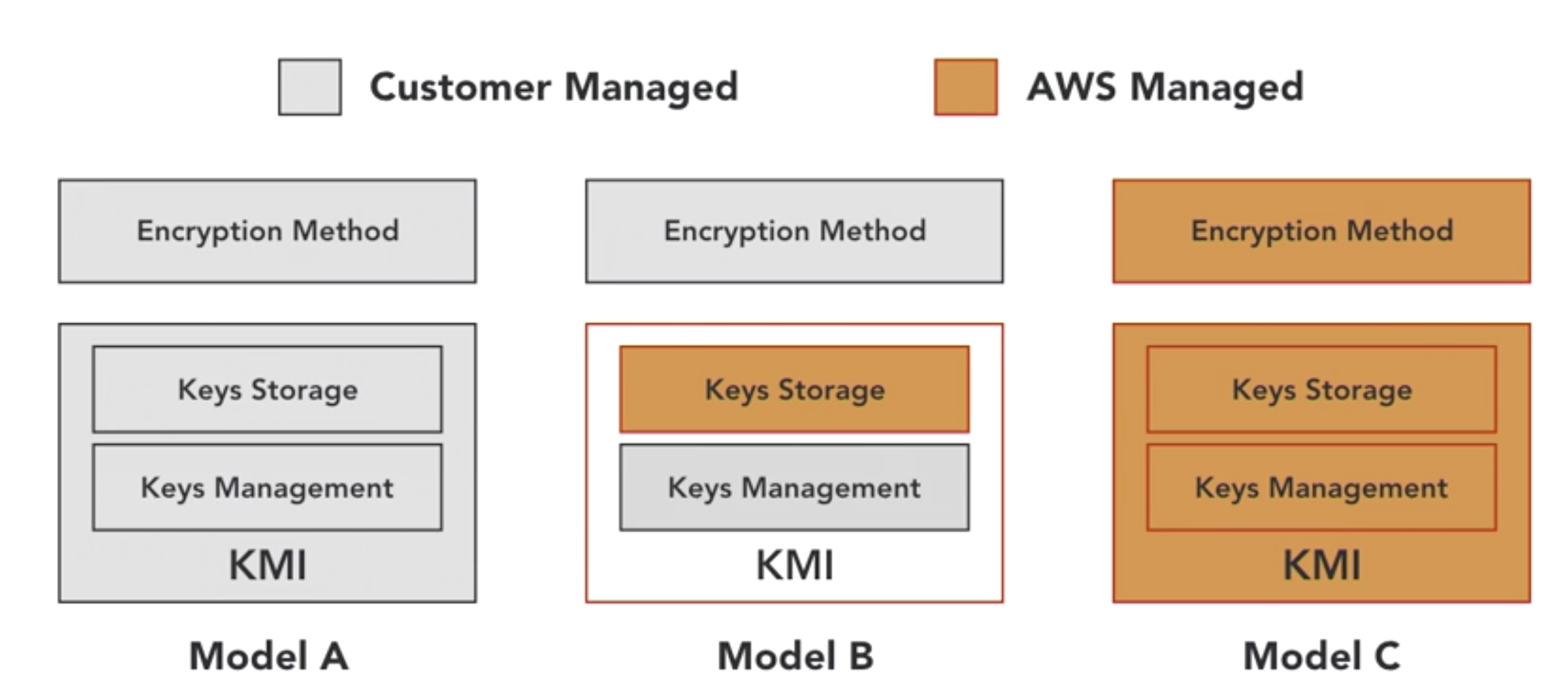
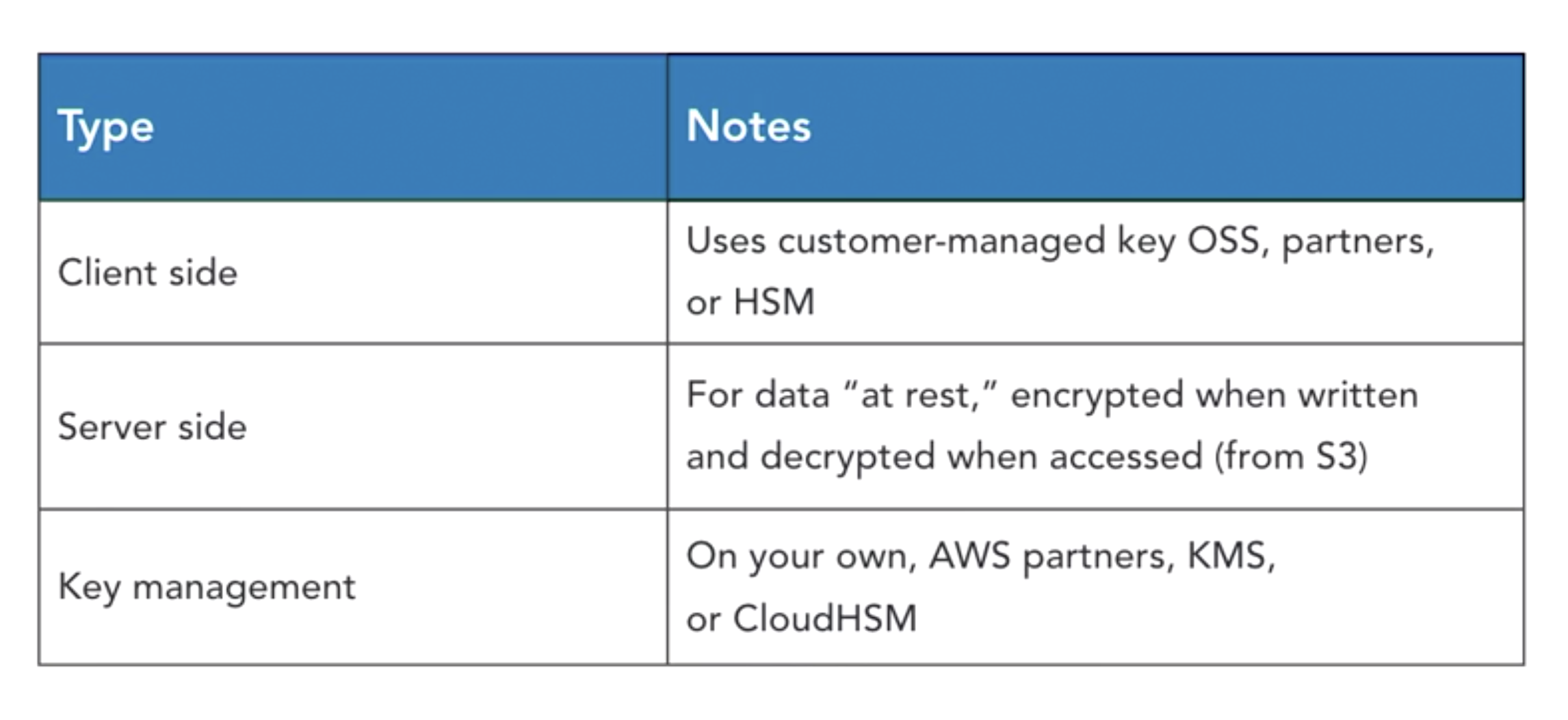
- client-side
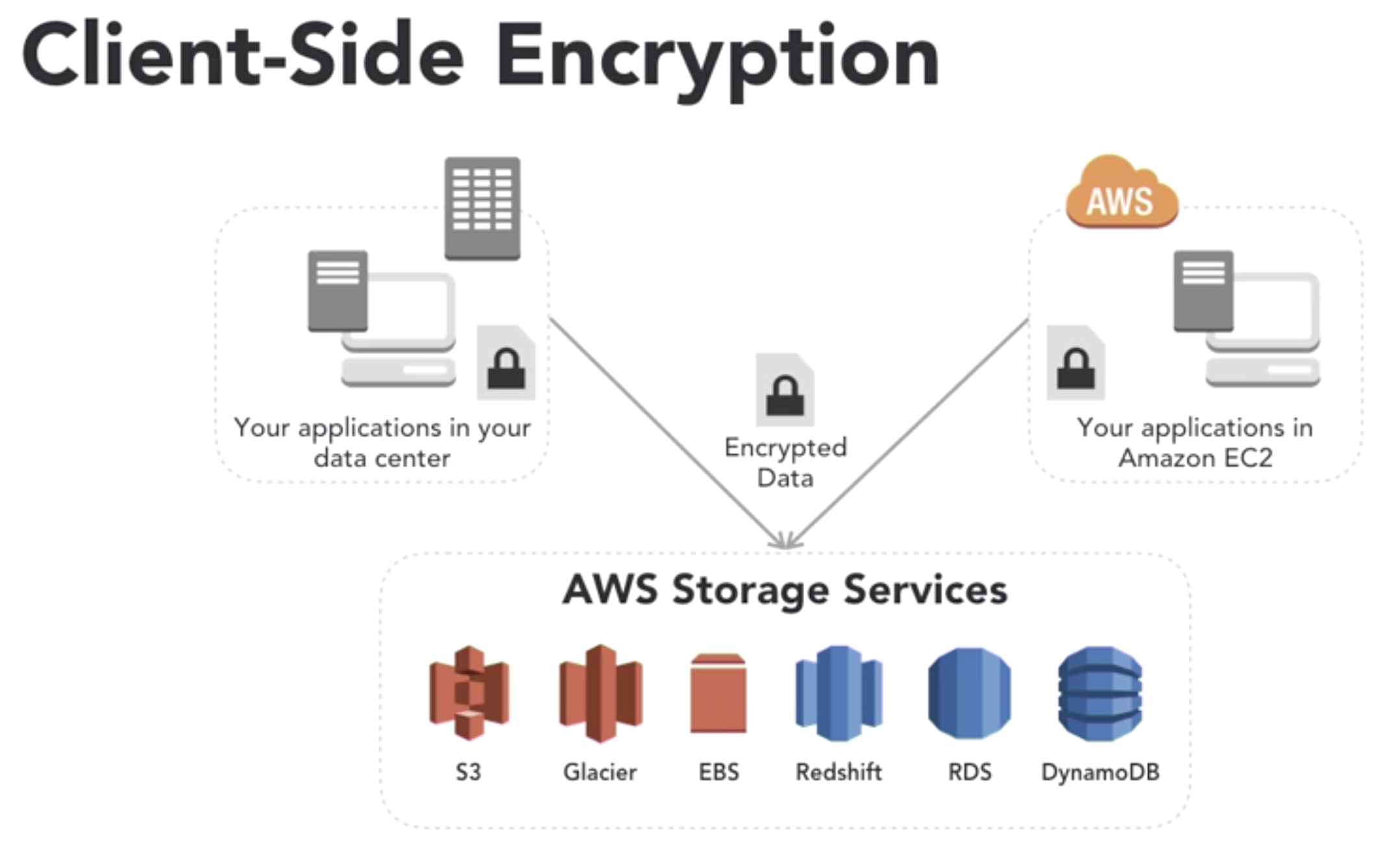
- server-side
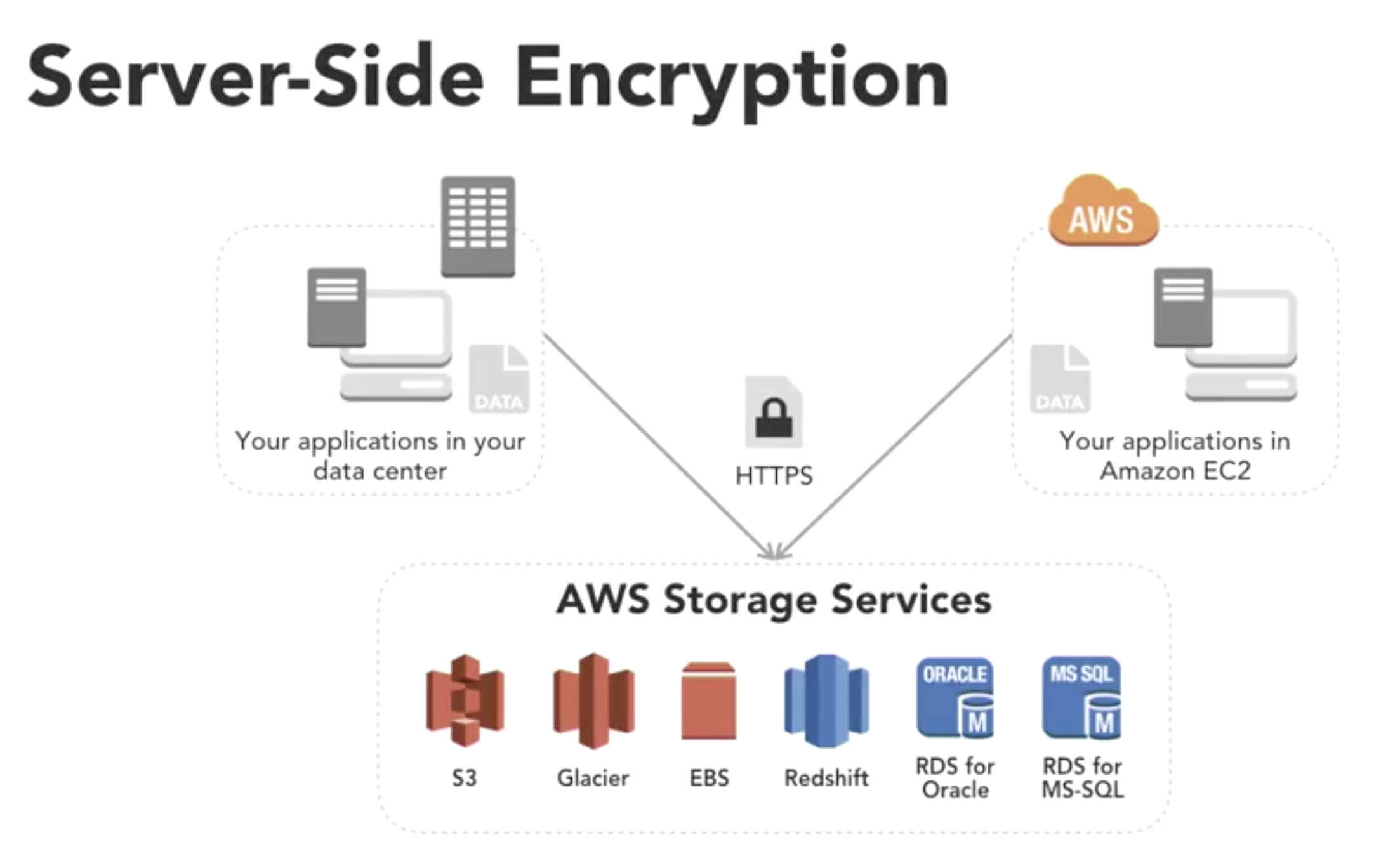
- client-side
- data protestion at rest and in transit
- at rest
- in transit
- to the edge, over the public internet
- at the edge
- within aws: no vpc between services
- within aws: vpc between sercices
- between aws regions
- design PCI DSS requriement
- payment card industry (PCI) data security standard
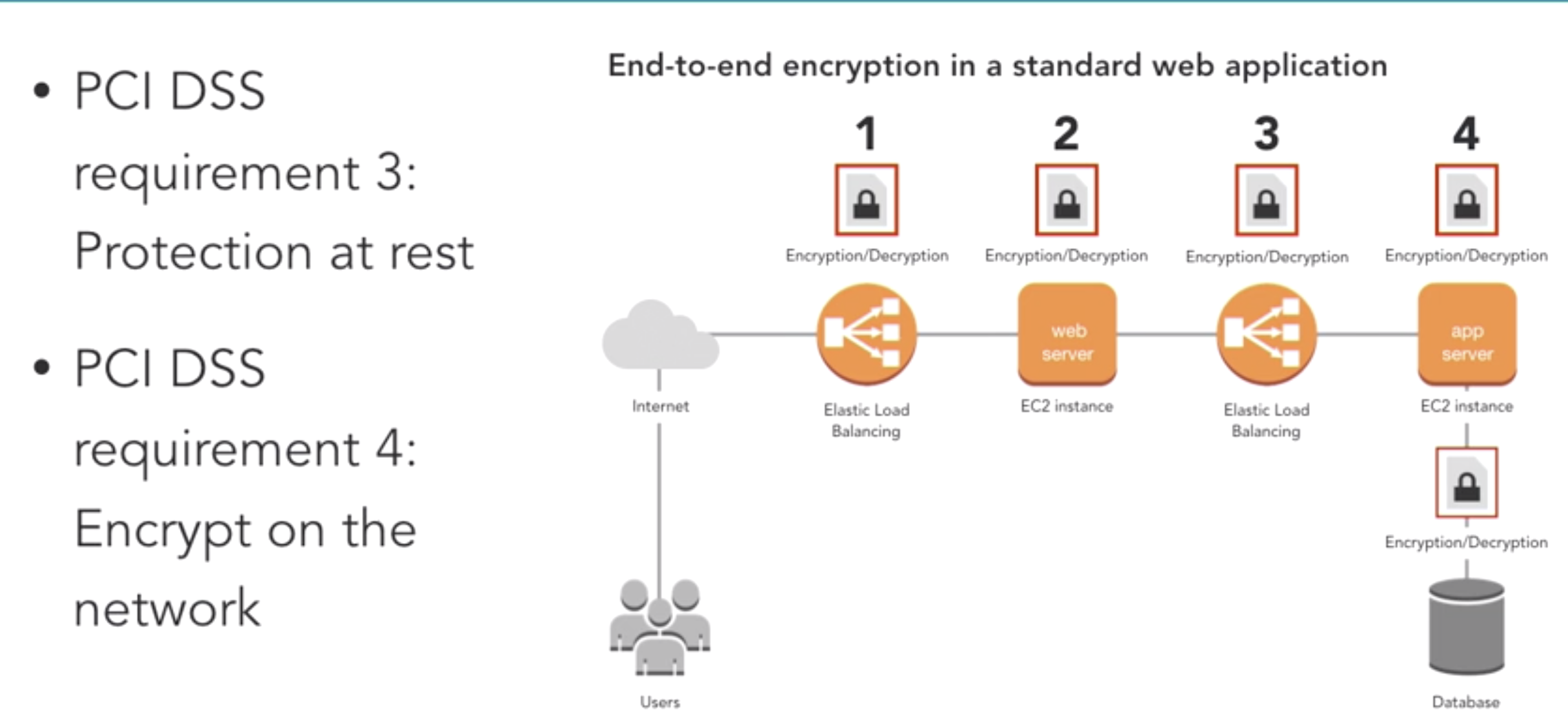
- payment card industry (PCI) data security standard
- summary
Design Encryption with AWS services
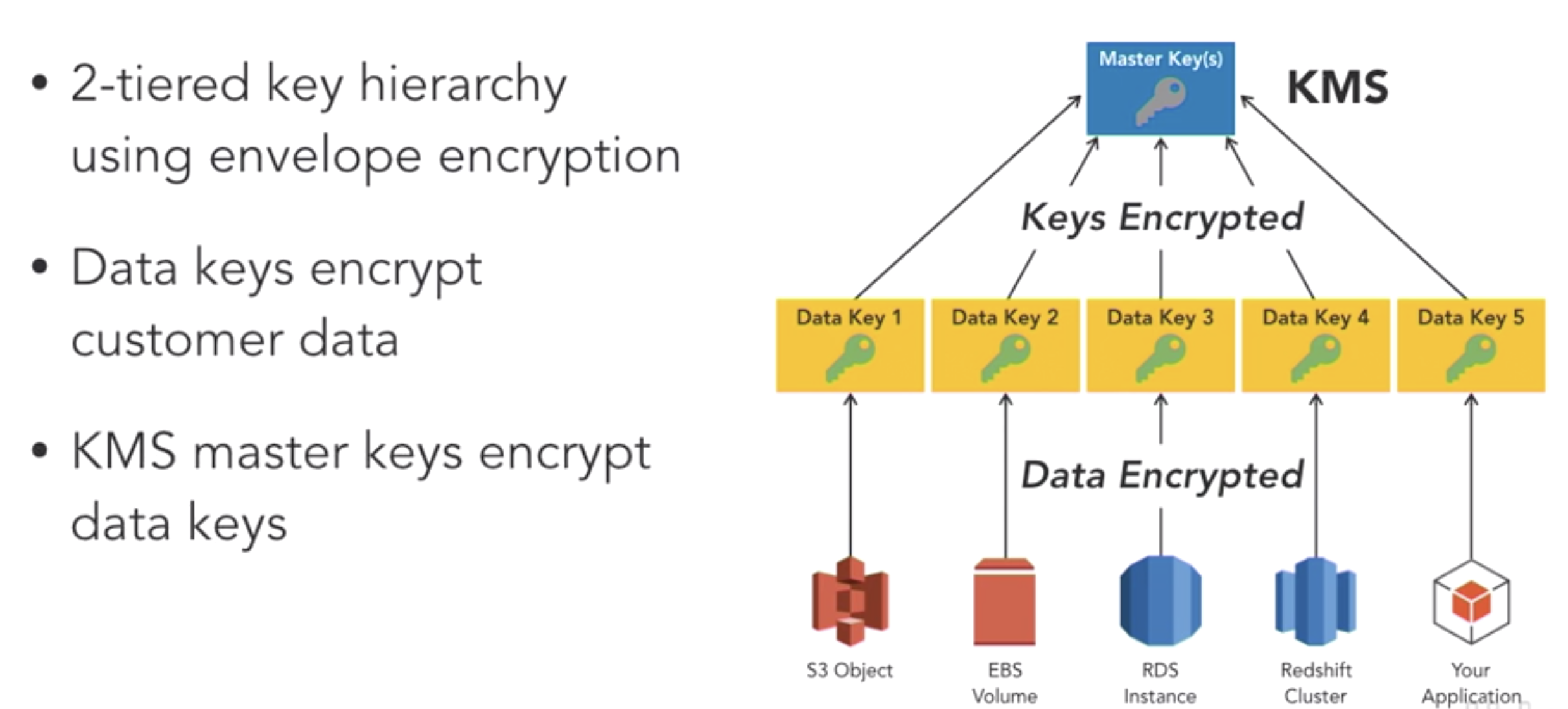
- What’s CMK (customer master key)?
- A logical key that represents the top of a customer’s key hierarchy.
- A CMK is given an Amazon Resource Name (ARN) that include a unique key identifier or key ID.
- What’s Data keys?
- Cryptographic keys generated on an HSA under a CMK
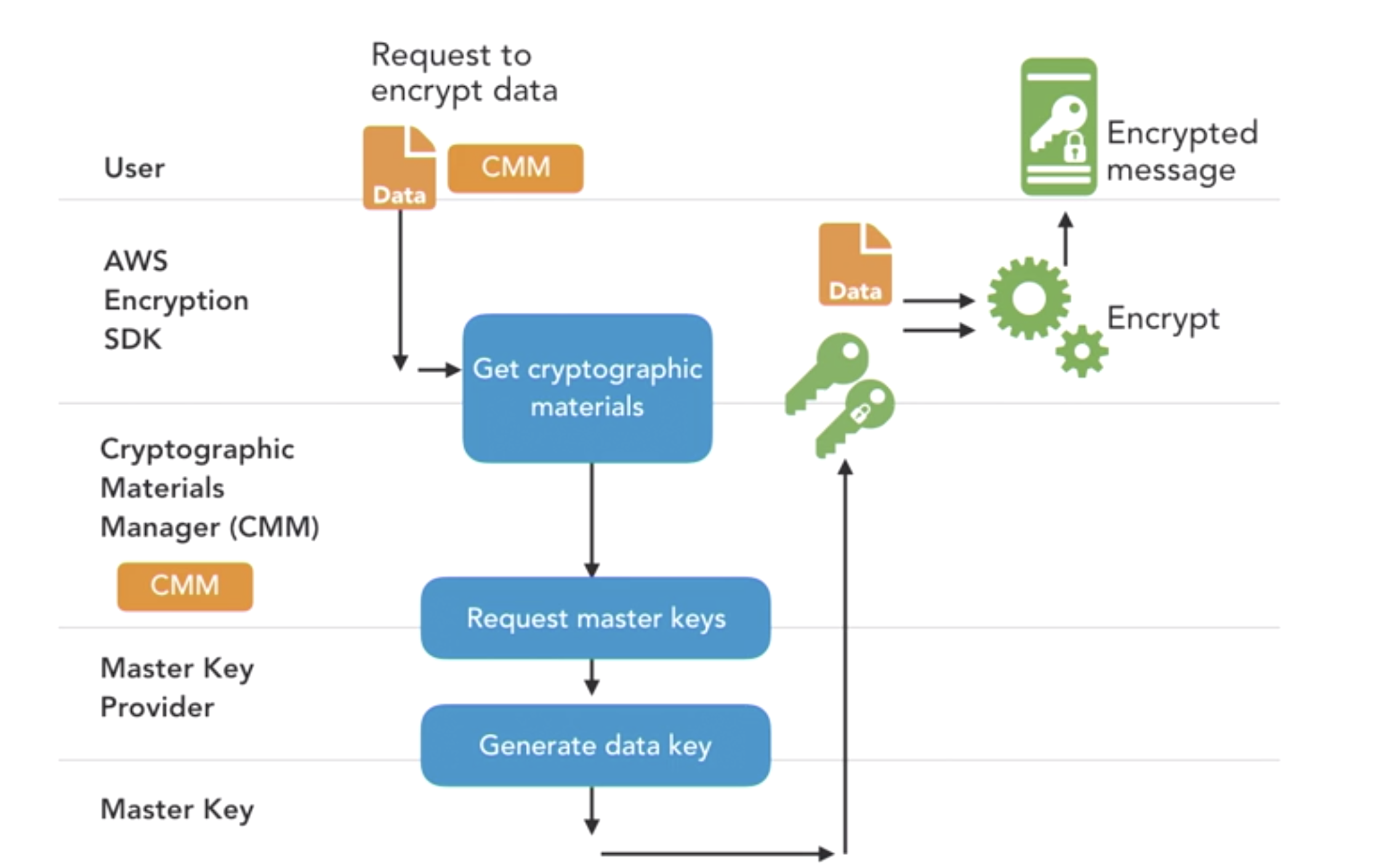
- How AWS key management service works?
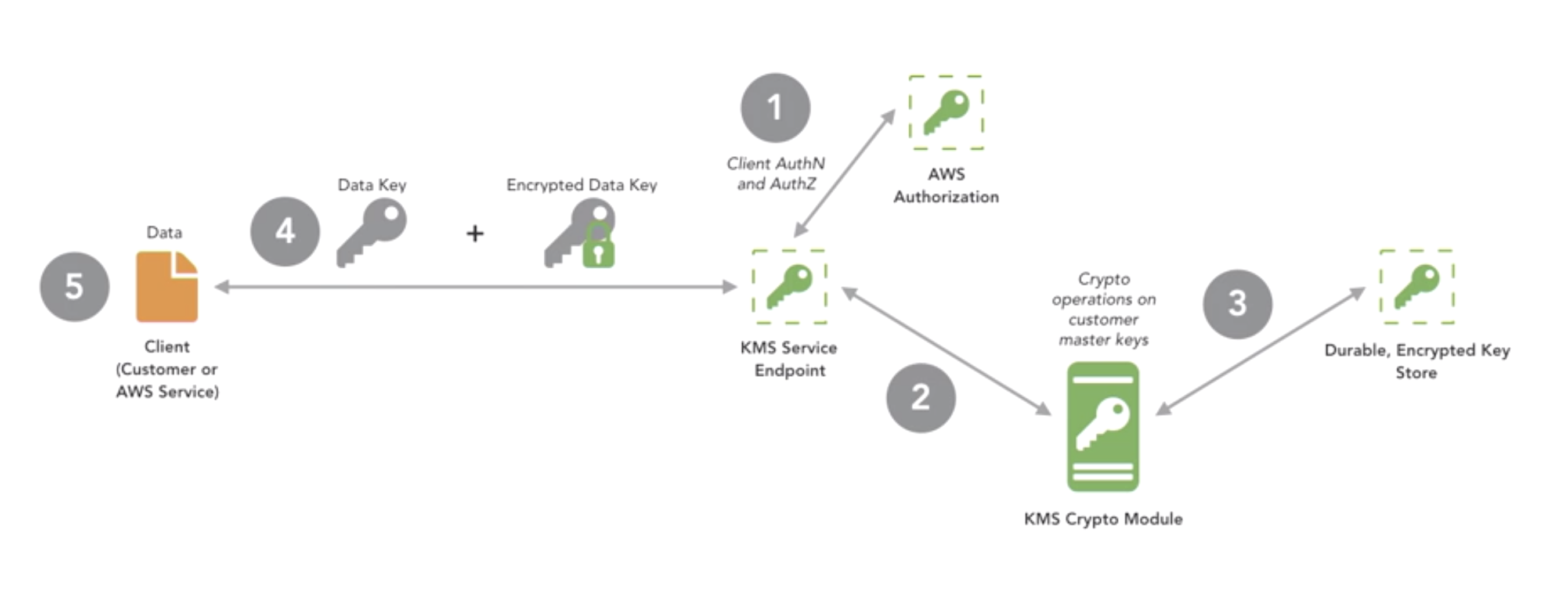
- How AWS services integrate with KMS?
- KMS Polices
- IAM policies are attached to IAM users, groups and roles
- KMS key policies are attached to CMKs
- Use IAM polices in combination with CMK policy
- set the CMK key policy to include policy statement that enables IAM polices
-

- use IAM policies to control use of encryption keys
-

- LC
- HSM (hardware security module)
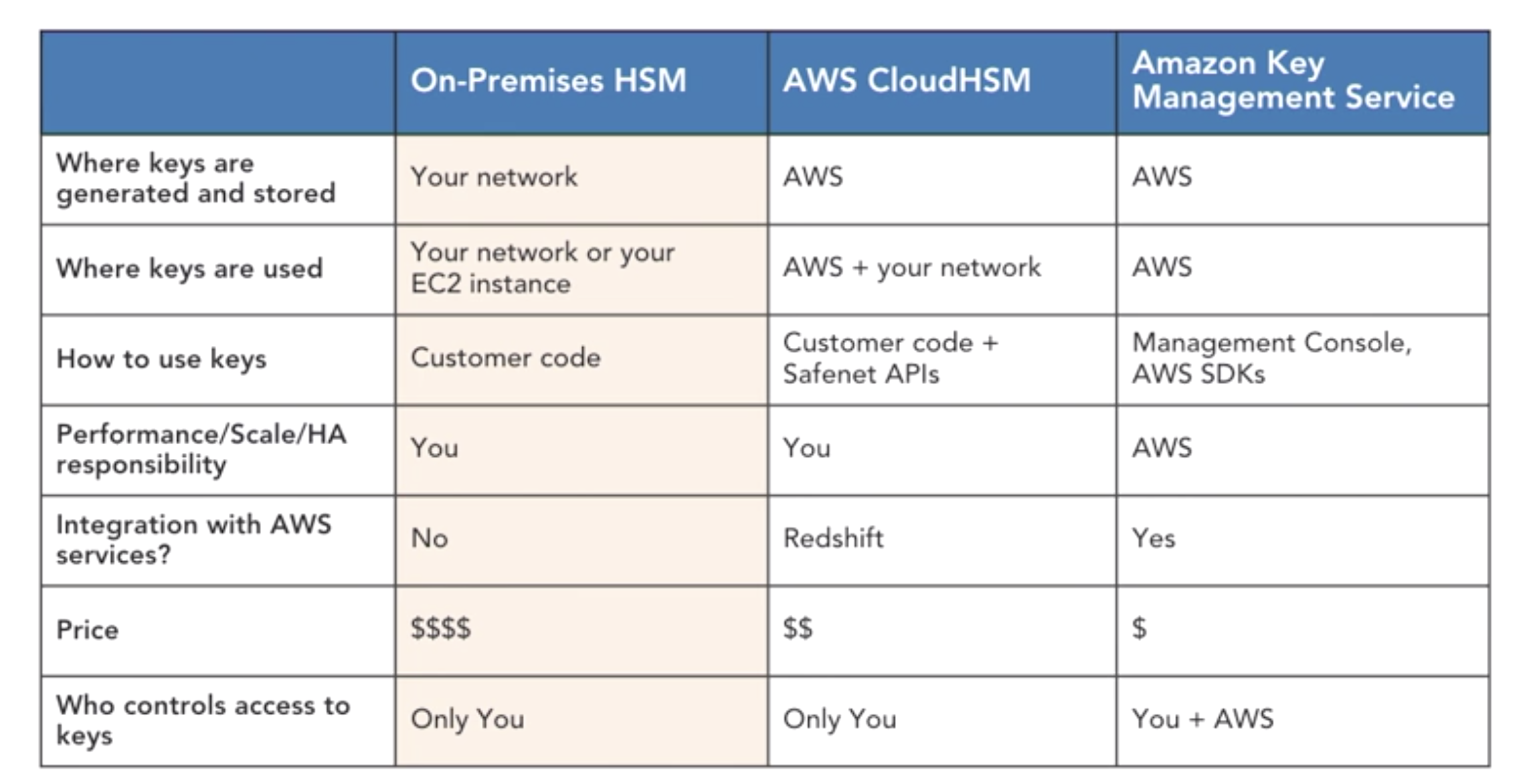
- hardware devices for crypto ops and key storage
- What’s Macie?
- It’s a serucity service that use ML to automatically discover, classify and protect sensitive data in AWS.
- Design Encryption for S3:
- client side
-
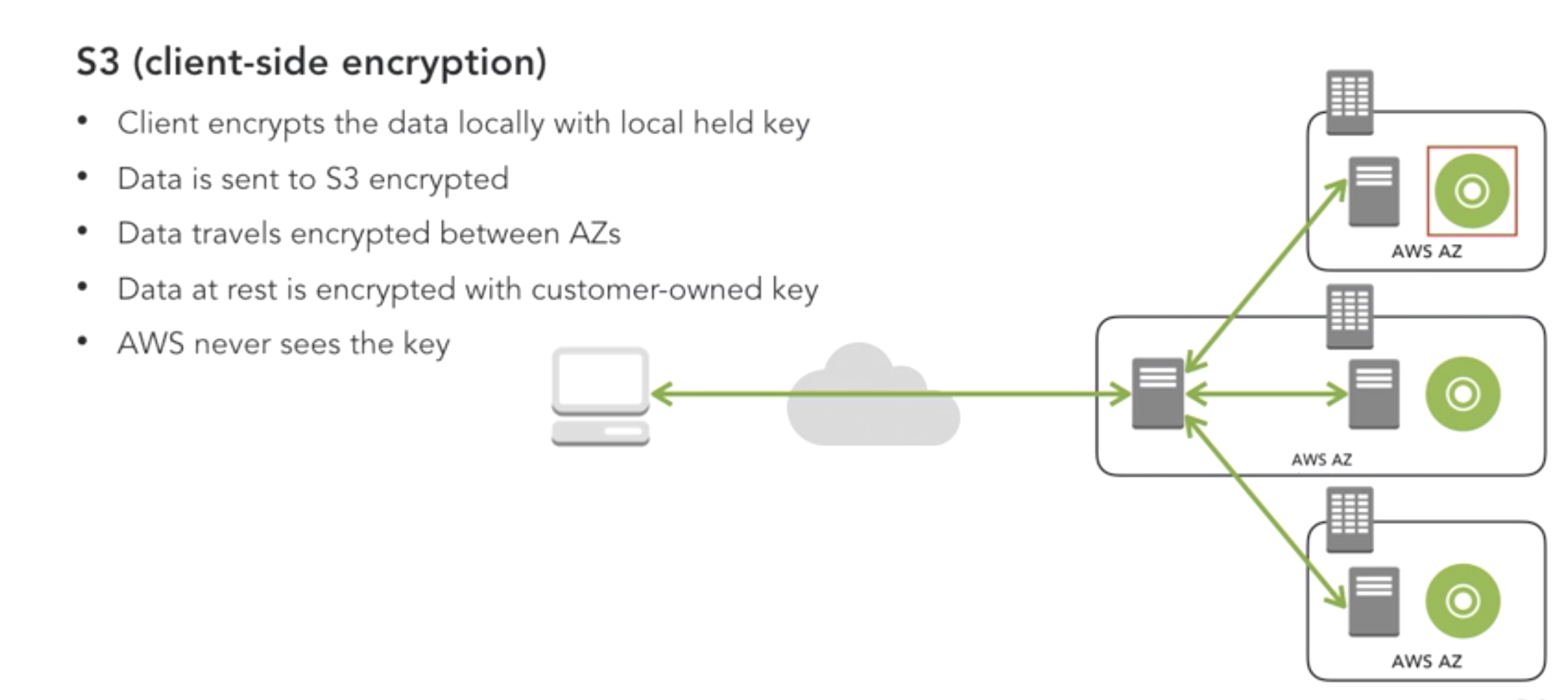
- server side
-
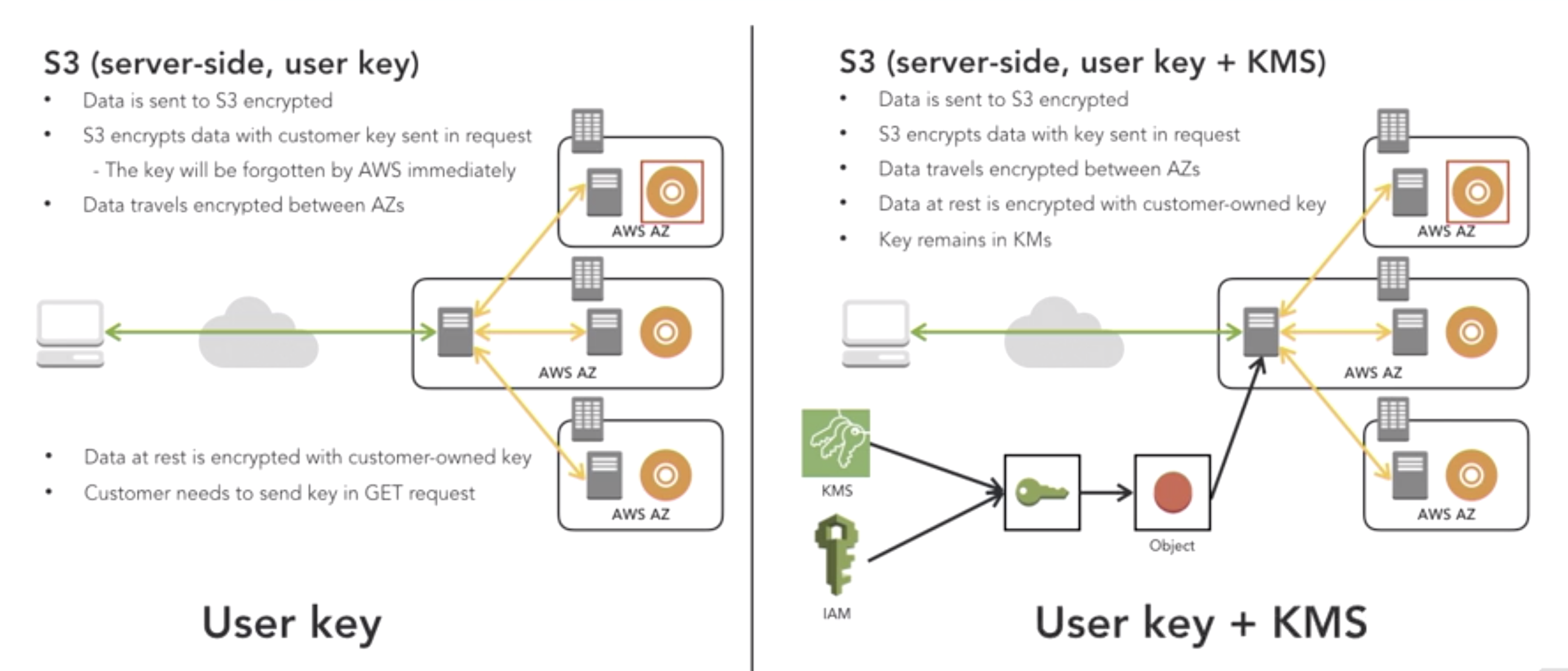
- Design Encryption for RedShift:
- Design Encryption for EC2 EBS volumes:
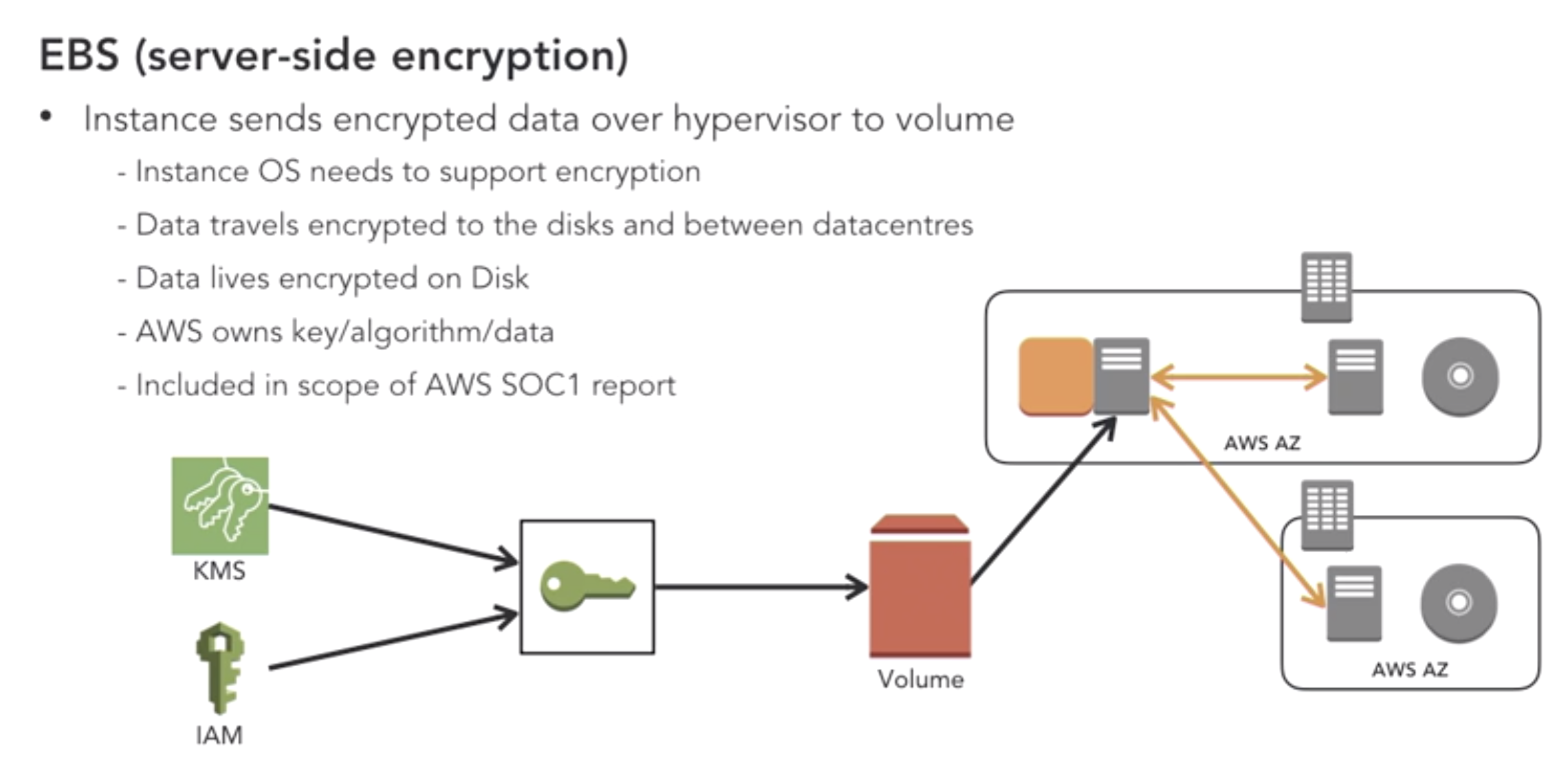
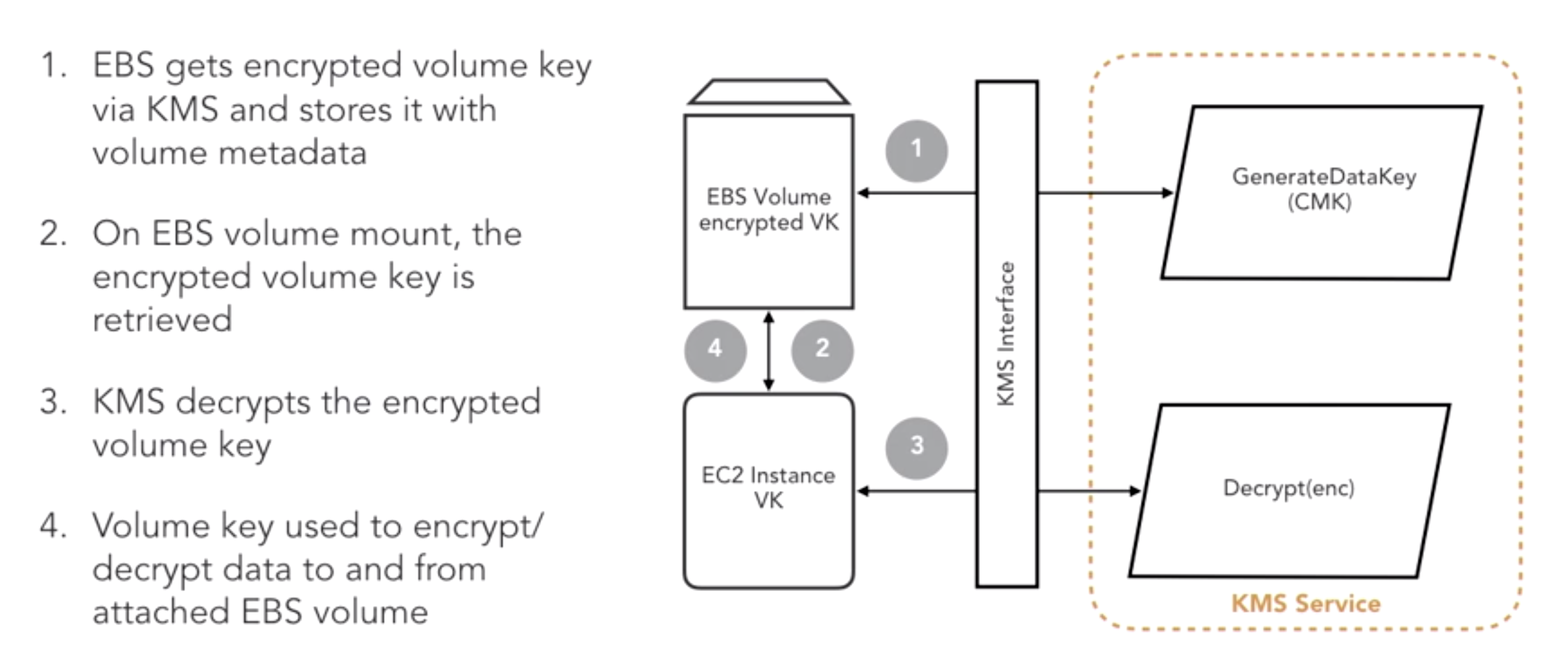
- Design Encryption for IOT:
- AWS IoT objects
- things (devices)
- certificaes (keys)
- IoT policies (permissions)
- All AWS IoT objects operate OUTSIDE of the other AWS security services, including IAM policies, Certificate Manager certificates, etc.
- AWS IoT objects
- Encryption with Certificate Manager
- make it easy to provision, manage and deploy, renew, SSL and TLS certificates on the AWS platform
Security Scenarios and Tradeoffs
- Third-party data security tool
- AWS marketplace for security
- vendor eg: SoftNAS
- AWS cloud compliance
- eg HIPAA
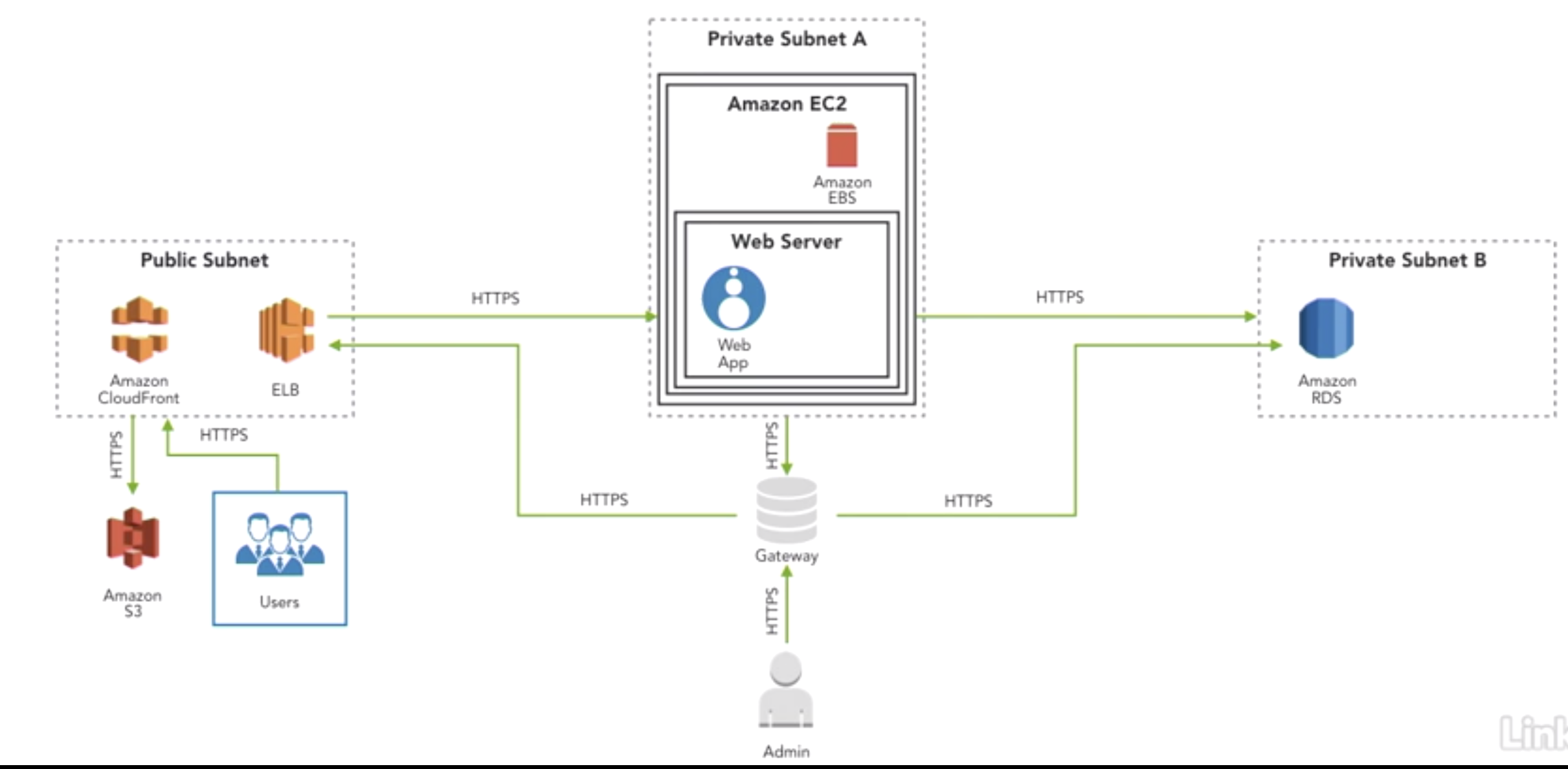
- Scenario1: Public website security
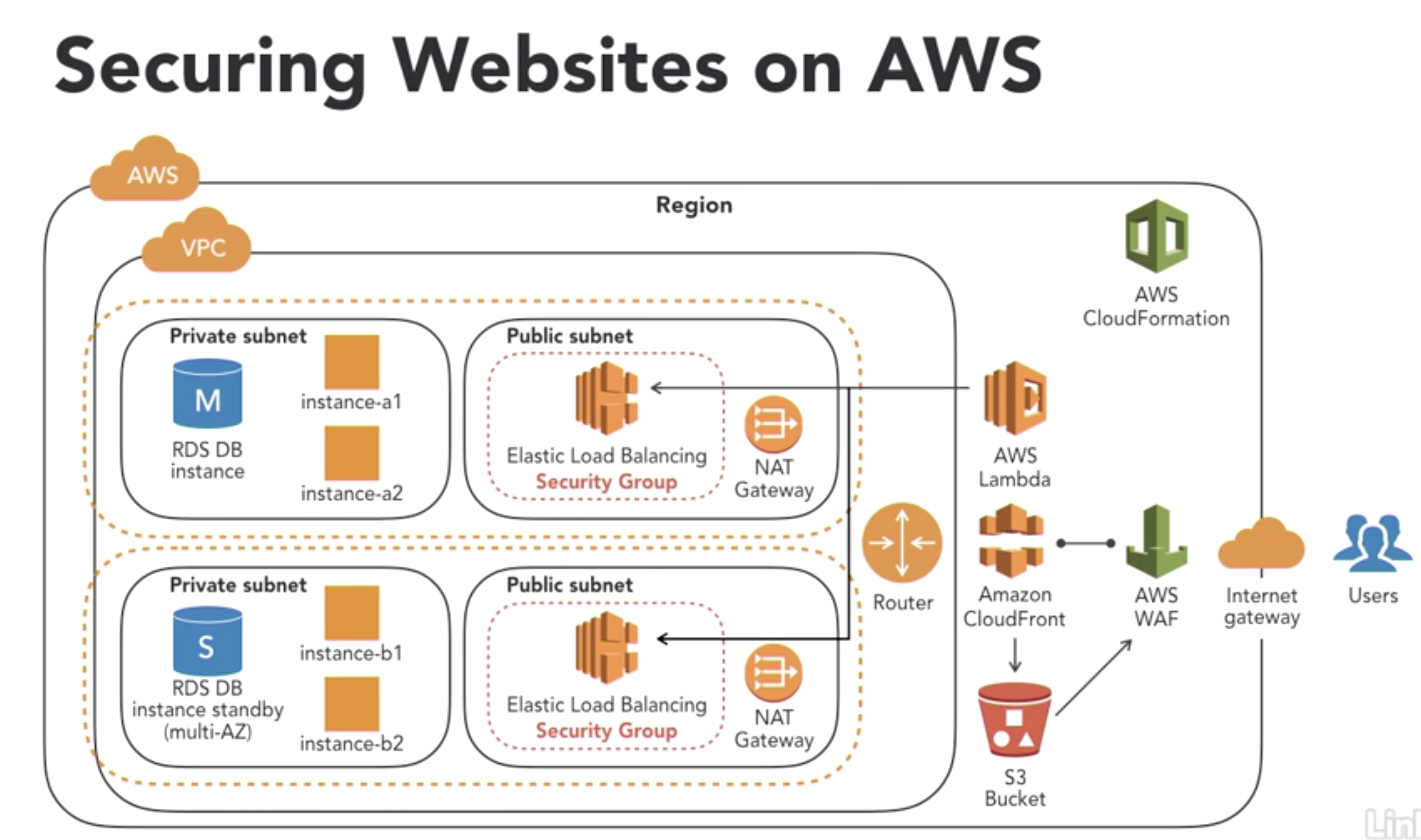
- Data Questions:
- where is the date at rest?
- which data is sensitive and needs further encryption?
- which path does the data travel through?
- which points in transit pose risks that requrie further security mitigation?
- Data Questions:
- Scenario2: Data pipeline security
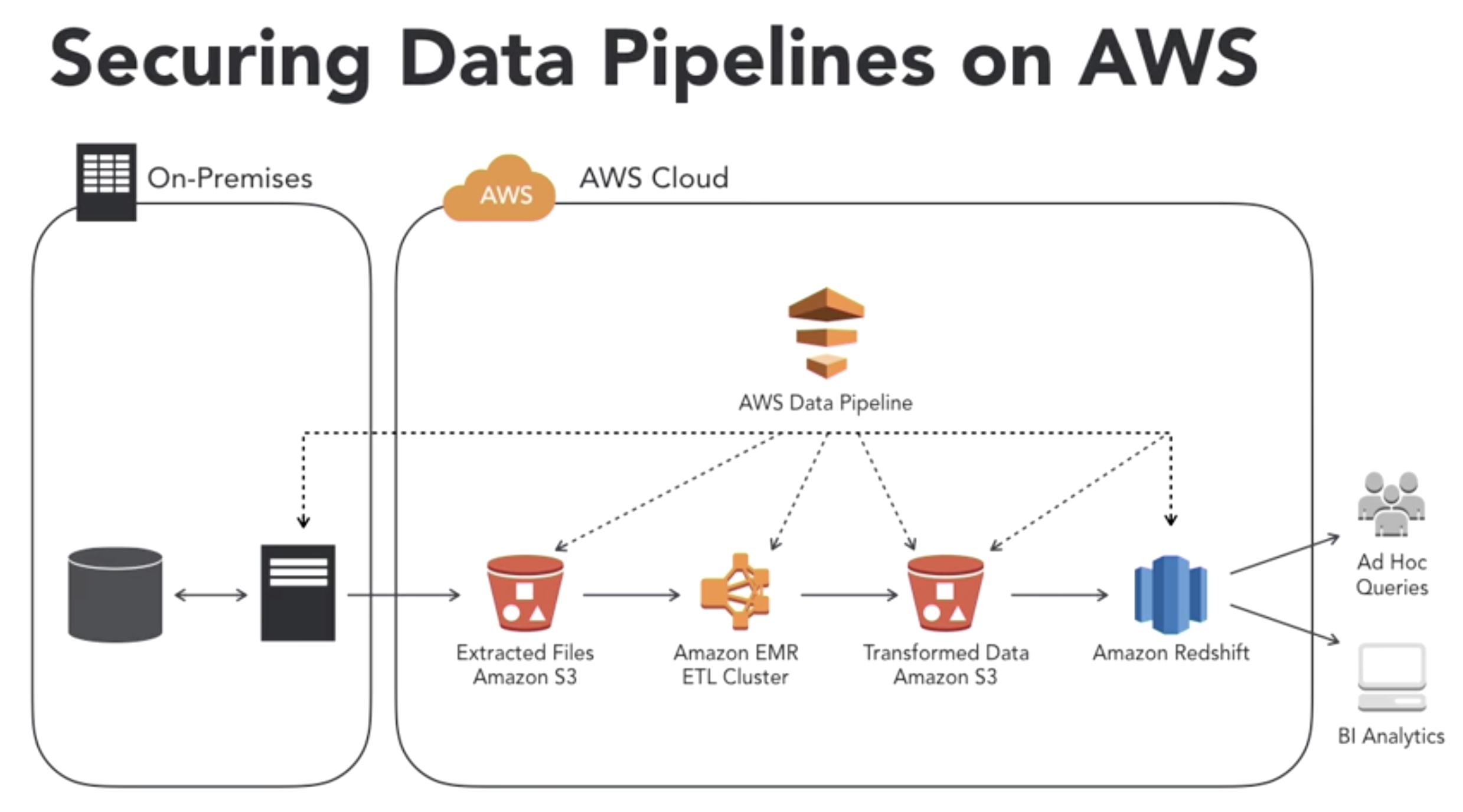
- Securing Data:
- Data transfer from on-premises storage to AWS cloud often done incorrectly
- 3rd party solutions often used to securely move data from on premises storage to AWS cloud
- reducing the amount of data transferred from on-prmises storage to AWS cloud improves security
- on-premises storage is typically the most unsecure piece of the data pilieline
- lack of security between produce and end-user apps
- Securing Data:
- Scenario3: Data lake security (serverless)
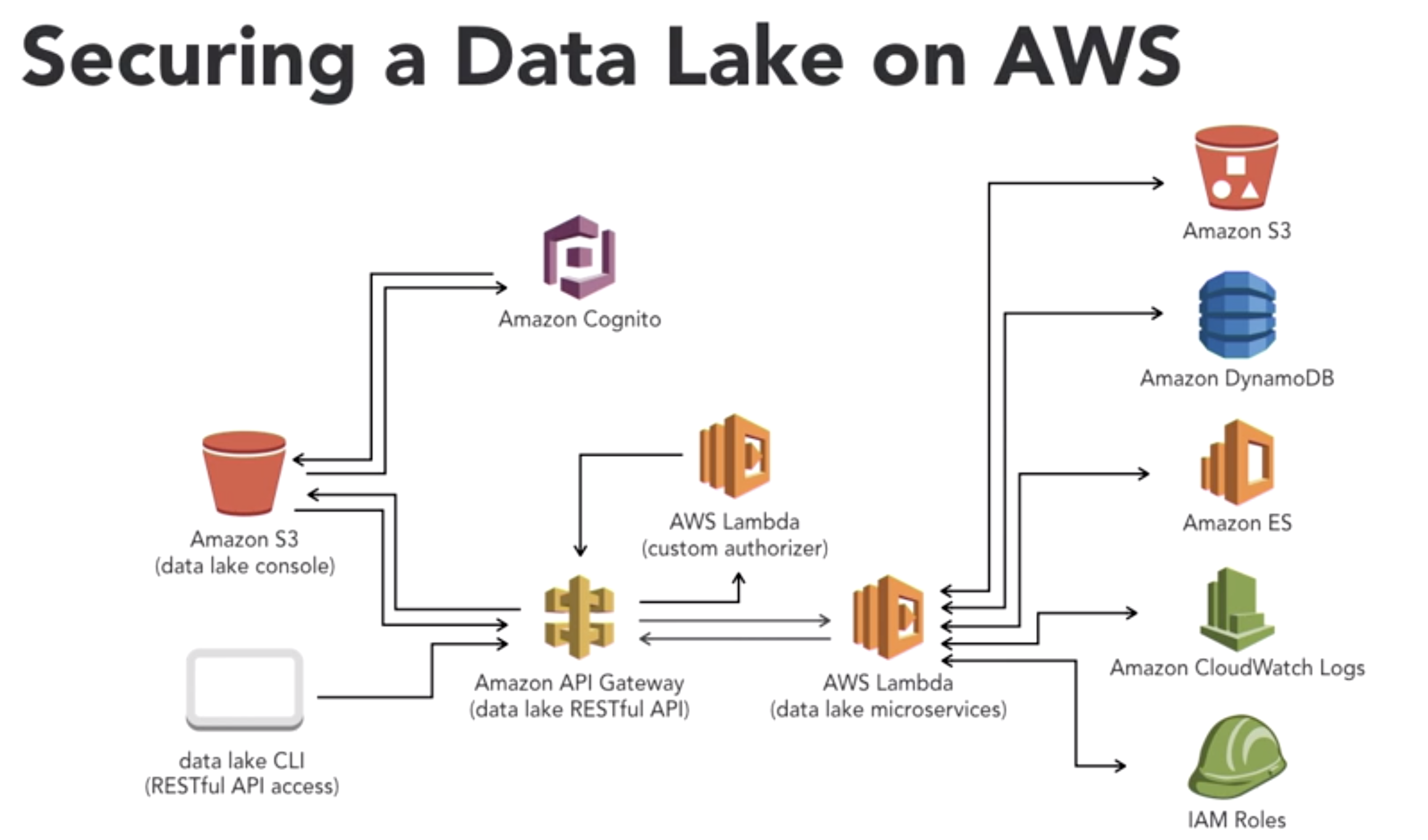
- Securing Data:
- within AWS cloud with sercice instances in a particurlar region
- Need to secure data, both at rest and in transit, with encryption
- S3 offers client-side or server-side encryption with different key management options
- import to encrypt both customer and configration data
- AWS handles all encryption and configuation for Lambda
- Amazon is taking on more and more of the responsibilit to secure the compute layer of serverless implementations
- Securing Data:
- Scenario4: IoT app security
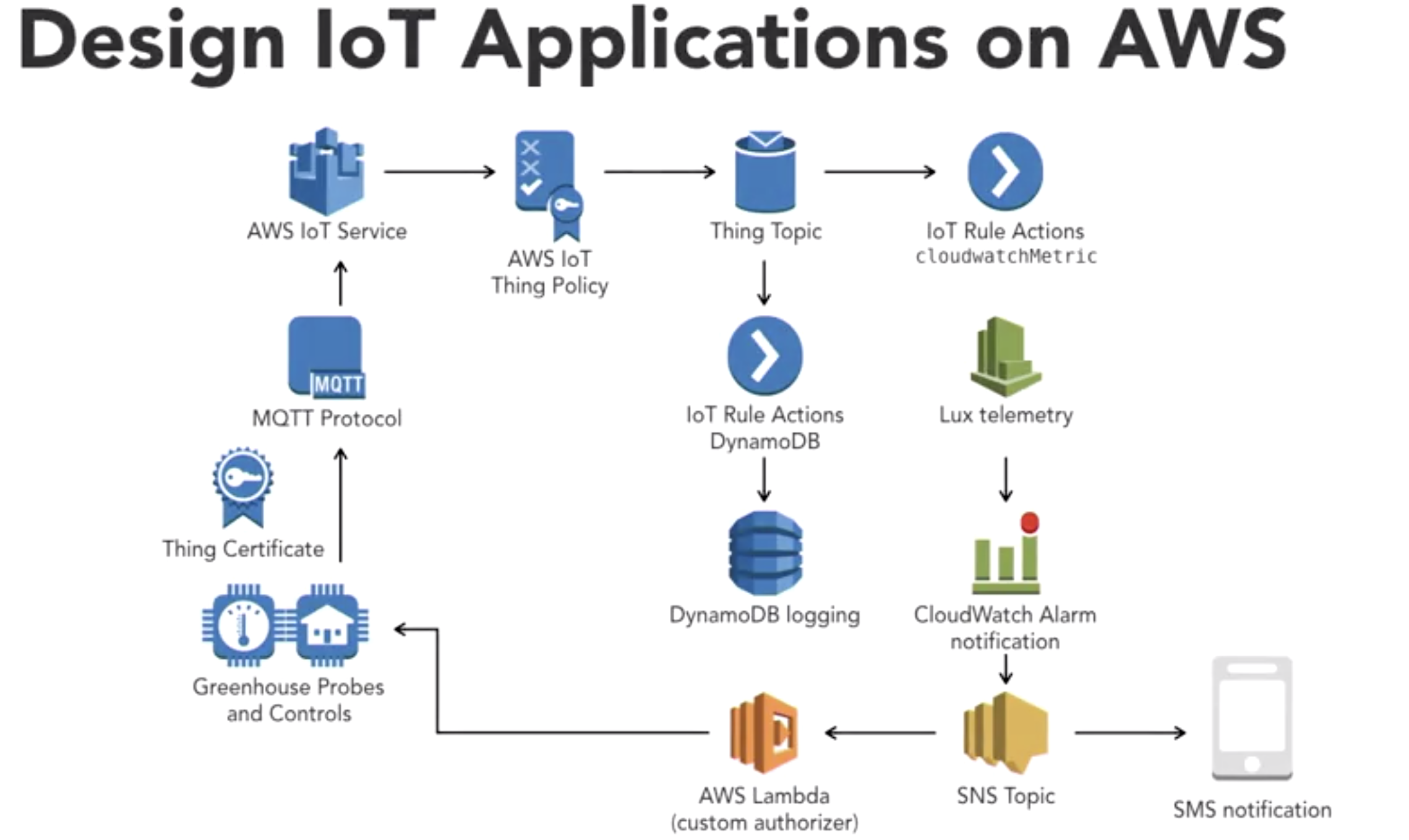
- Securing Data:
- default, Lambda does not sit in VPCs
- whether or not to use VPC boundary should be a design consideration
- PUB/SUB
- event driven
- Securing Data:
Design for DR
- DR areas and metrics
- what’s measured matters
- recover files and data
- recover compute
- recover services (DNS, etc.)
- RTO: recover time objective
- how long can you be down?
- RPO: recover point objective
- how much data can you lose?
- Recovered data verification
- how will you verify the correctness of recovered data?
- what’s measured matters
- DR patterns for data
- Files
- S3
- Glacier
- DB
- RDS and Redshift
- DynamoDB
- EMR
- Files
- Recover EC2 with EBS and more
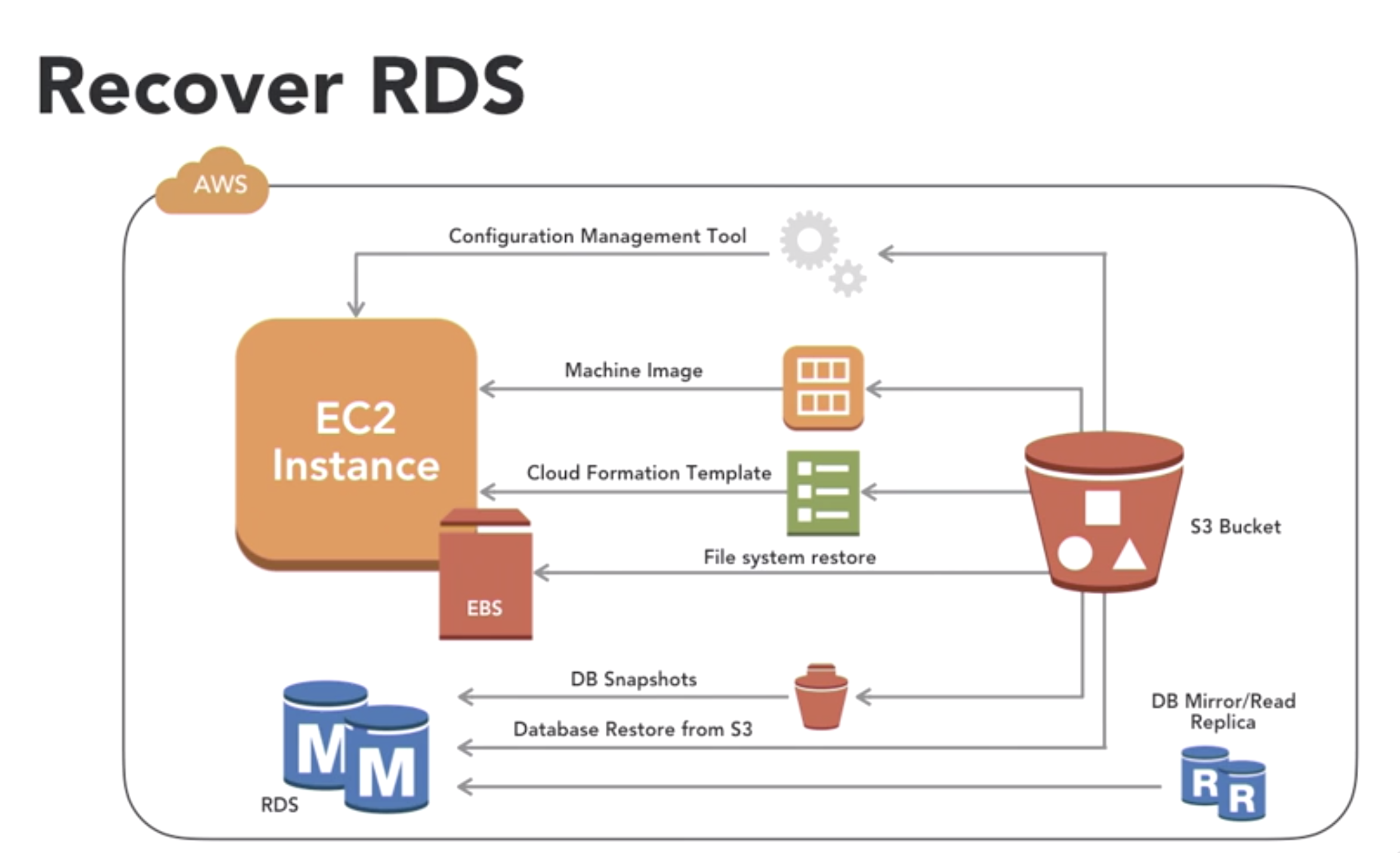
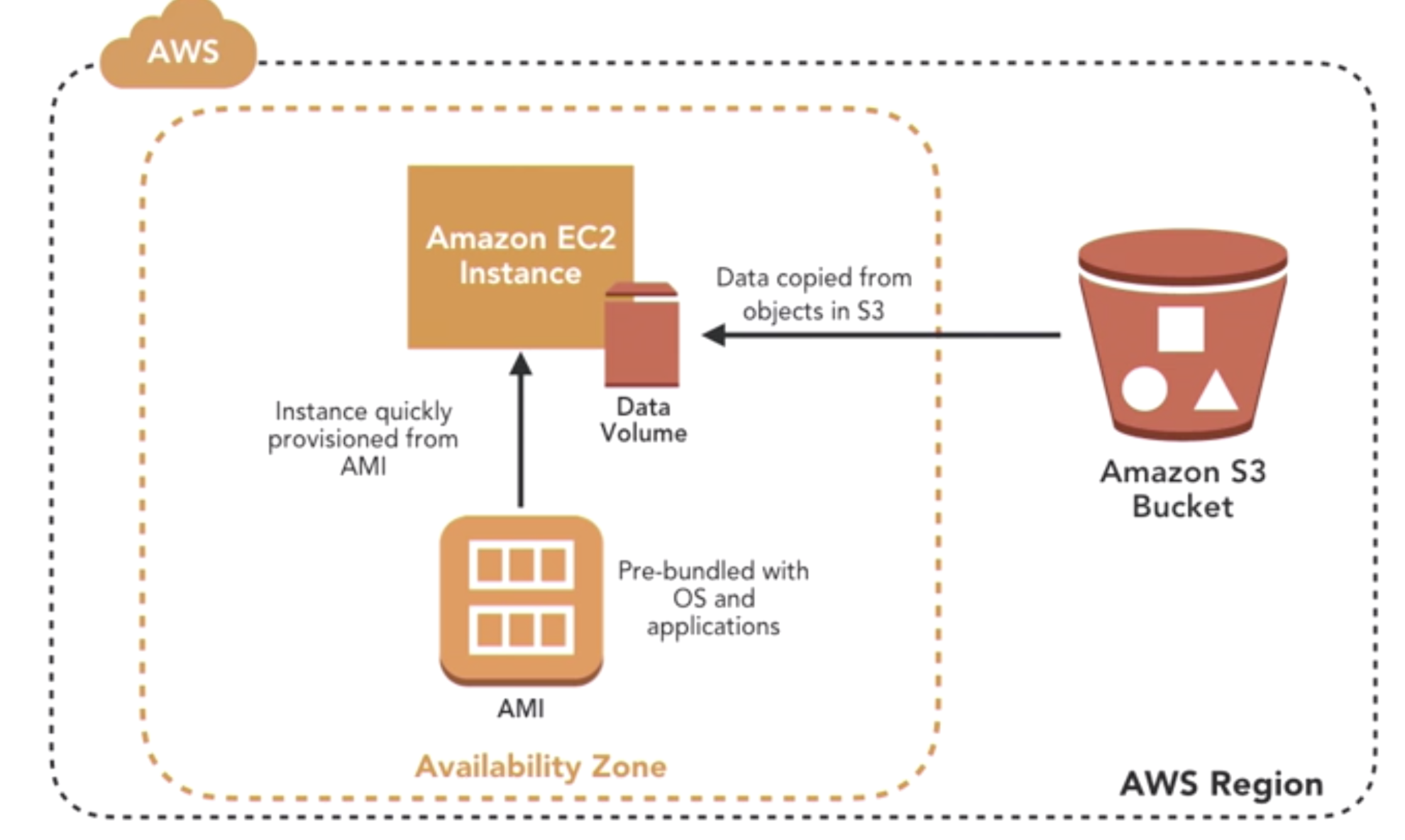
- AMI (amazon Machine Image)
- EBS (elastic block storae)
- Snapshot (can be the basis for AMIs)
- Recover data with AWS Import/Export
- snowball: 50T storage, 10G network …
- a physical device that you request from Amazon through the console or programmacitcally
- API
- snowball: 50T storage, 10G network …
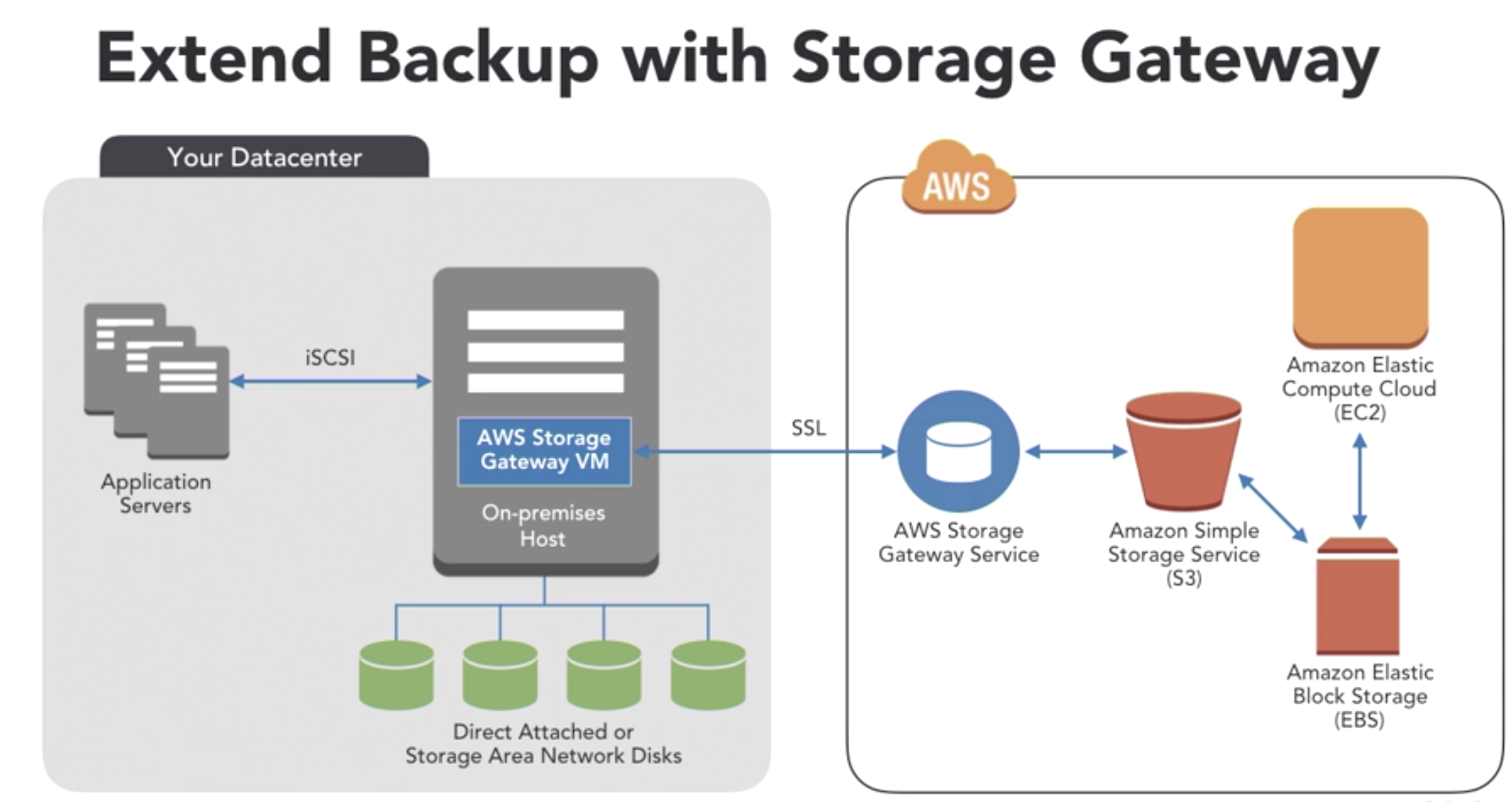
- Extend backups via Storage Gateway
- Recover DNS with Route 53
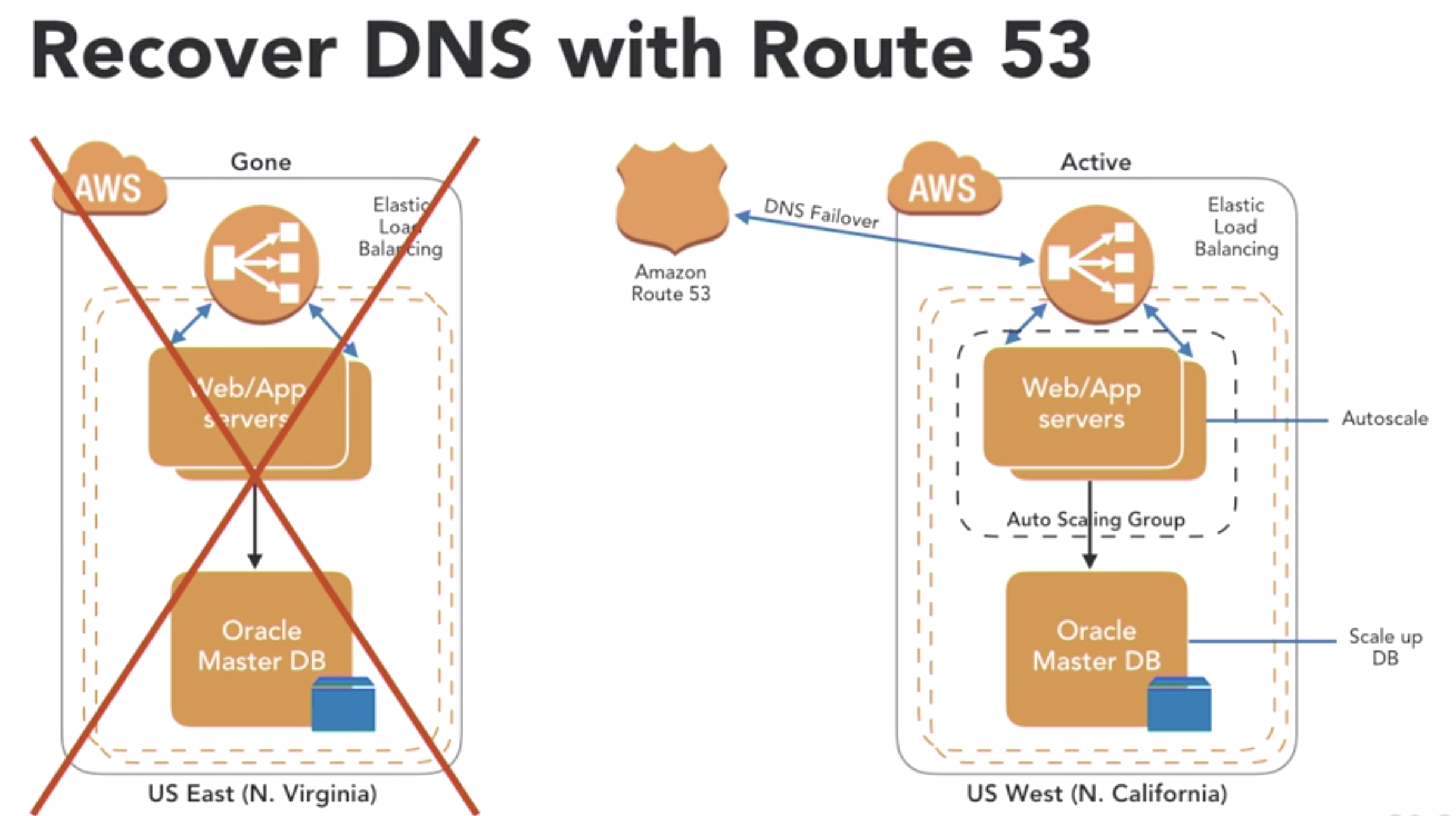
- define Health Checks
- DR recovery practices
- perform regular DR test (scheduled or un scheduled)
- follow written recovery procedures (runbooks)
- aws white papere: aws_disaster_recovery
- Other resources:
- CIS
- AWS Community Heroes
- Lynn Langit
