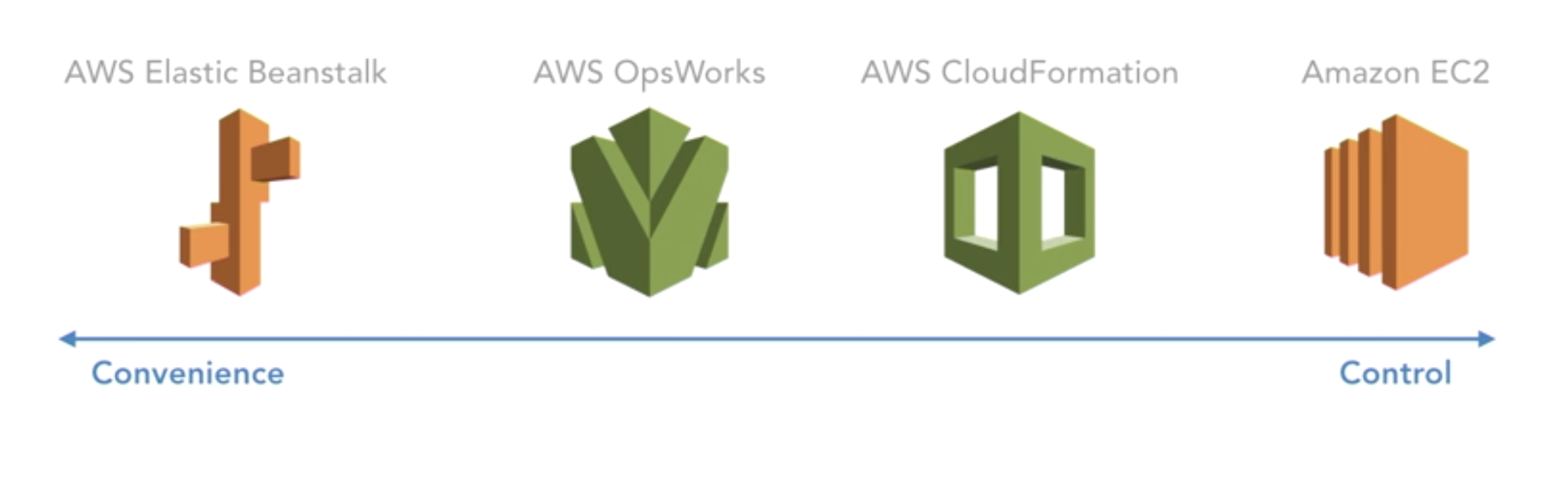
AWS Solutions Architect Associate3 - Implementing and Troubleshooting PaaS Products
IAM
- What’s IAM?
- AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting)
- Authentication: allows you to get in
- define users, groups access to your AWS resources
- Authorization: what you’re allowed to do
- grant and deny permissions to objects for specific individuals, groups or roles
- Accounting: determine what you did
- track who logs in to AWS, as well as the actions they perform
- Features of IAM:
- Identity federation
- PCI DSS compliance
- Integrated with most AWS services
- Shared access
- Free to use
- Multi-factor authentication
- IAM Users
- root account
- create an IAM user as regular account
- IAM groups
- a user can belong to multiple groups
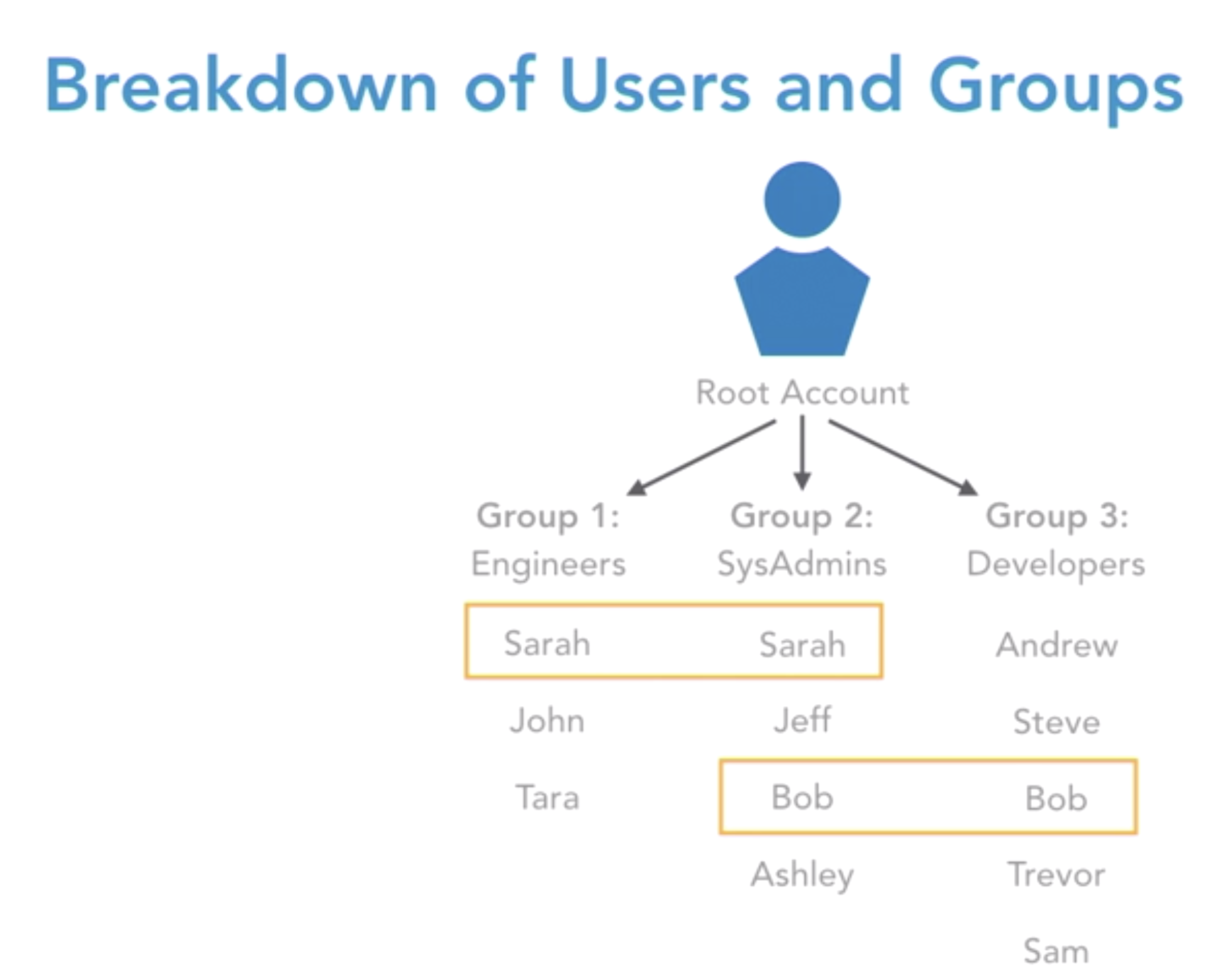
- a user can belong to multiple groups
- IAM roles
- eg: allow an external contractor temporary access to perform an audit on your AWS account logs
- can’t assume more than one role at a time
- can’t login as a role
- IAM policies
- Identity-based inline policies: assigned to IAM users and groups
- Managed policies: policy objects that may be applied to multiple resources, users and groups
- AWS managed policies (curated policies)
- Customer managed policies (user defined)
- Resource-Based Policies: must be attached to resources, can’t IAM indentity
- Json format
-

- IAM policy simulator
- test the effect of your IAM policies, roles
- help determine if your acess policies are too restrictive or lax before putting your app into production
- IAM Best Practices
- Follow the principle of “least privilege”
- Do NOT use the root user for day-to-day administration
- Use groups to assign permission to IAM users
- Create and enforce a strong password policy
- Make sure MFA(Multi-factor authentication) is enabled for all privileged users
- Use AWS managed policies wherever possible to assign permissions
CloudFormation
- What’s AWS CloudFormation?
- Management tool
- Helps you provision your infra resources
- Free to use; you only pay for the resources you deploy
- Template in a JSON or YAML format
- Version control/track changes
- Greate for DR
- Greate for mass production
- Sections of CloudFormation Template


- resource section: only required
- format version
- description
- metadata
- parameters
- mapptings
- conditions
- transform: serverless
- Components of CloudFormation
- Templates
- declaration of AWS resources that make up a stack
- JSON or YAML format
- Engine
- interpreter for the JSON or YAML template files
- read the input template, then create the output resources in a stack
- Stack
- collection of AWS resources managed as one unit
- Templates
- Explore CloudFormation
- Operate a stack
- depoloy
- update
- delete
Elastic Beanstalk
What’s Beanstalk?
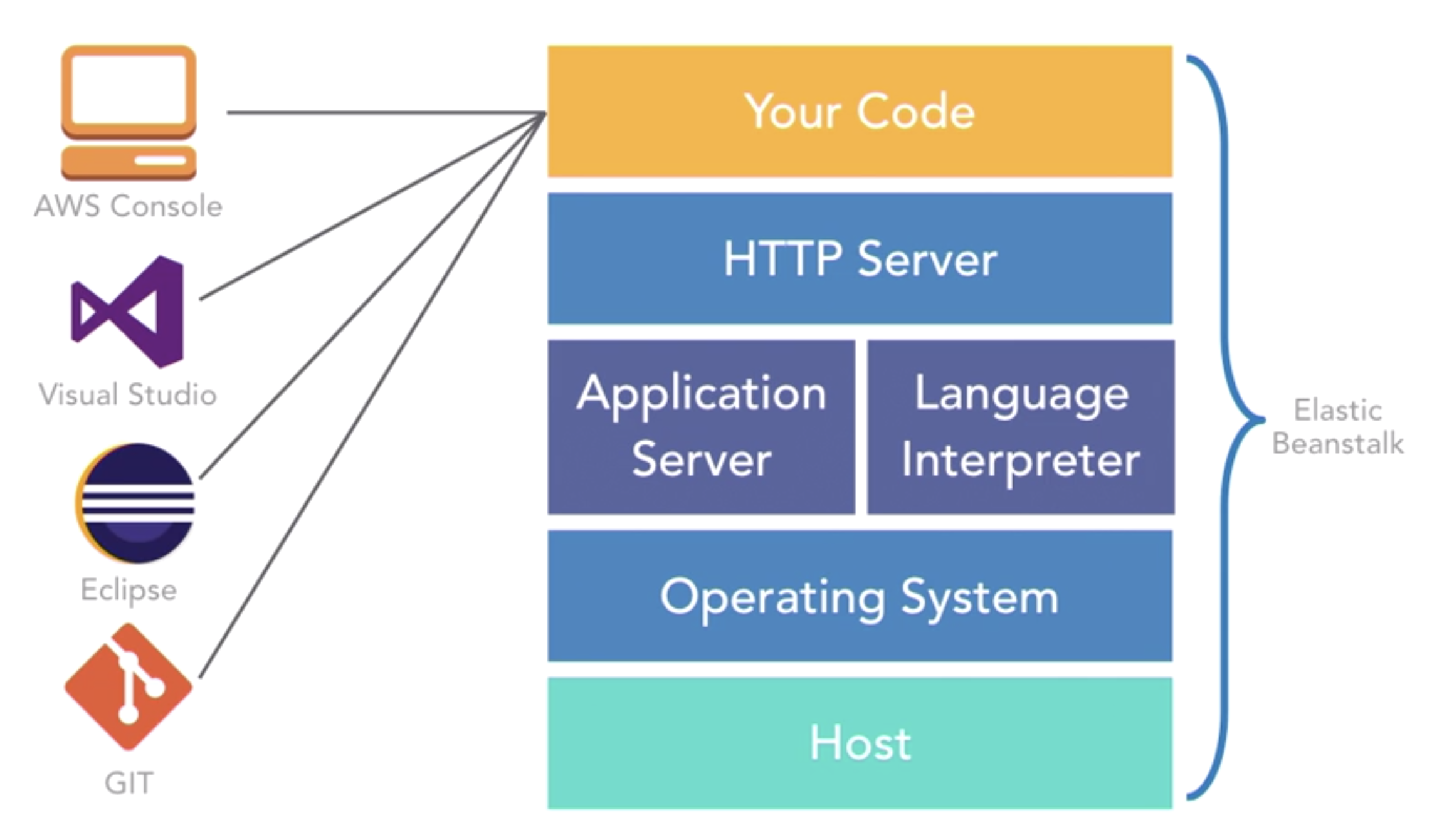
- help to deploy and test our apps quickly with less work
- an easy-to-use service for deploying and manageing web apps and services within minutes
Concepts?
- app:
- a logical collection of Beanstalk components
- basically a folder containing:
- app versions
- env
- env configurations
- app version
-
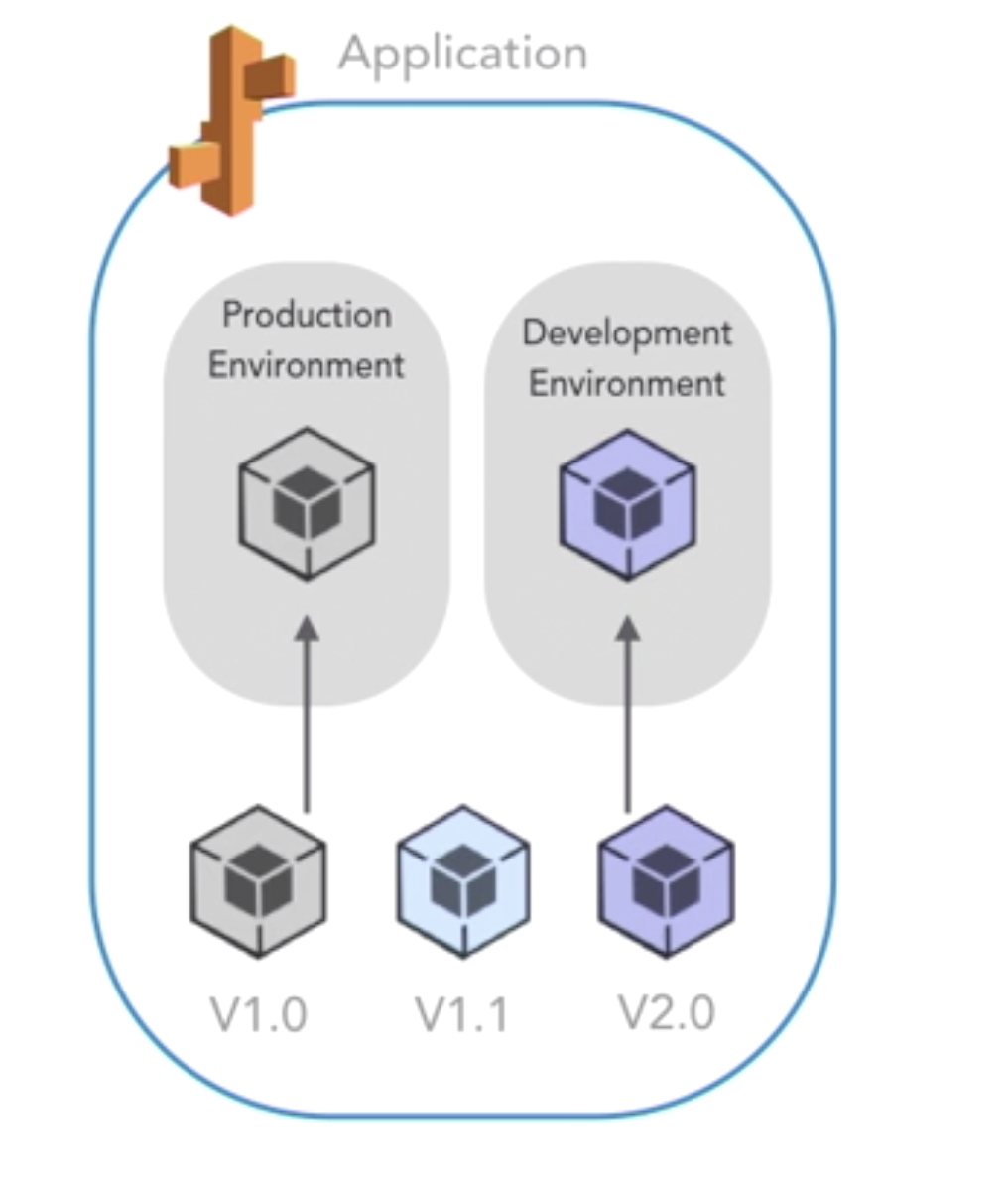
- a specific release of deployable code for an app
- each version is unique
- deploy multi versions to multi envs
- onp app per per env
- stored in Amazon S3 bucket
- env
- an infra (a set of AWS resource) provisioned to run an app version
- one app version per env
- env tier
-
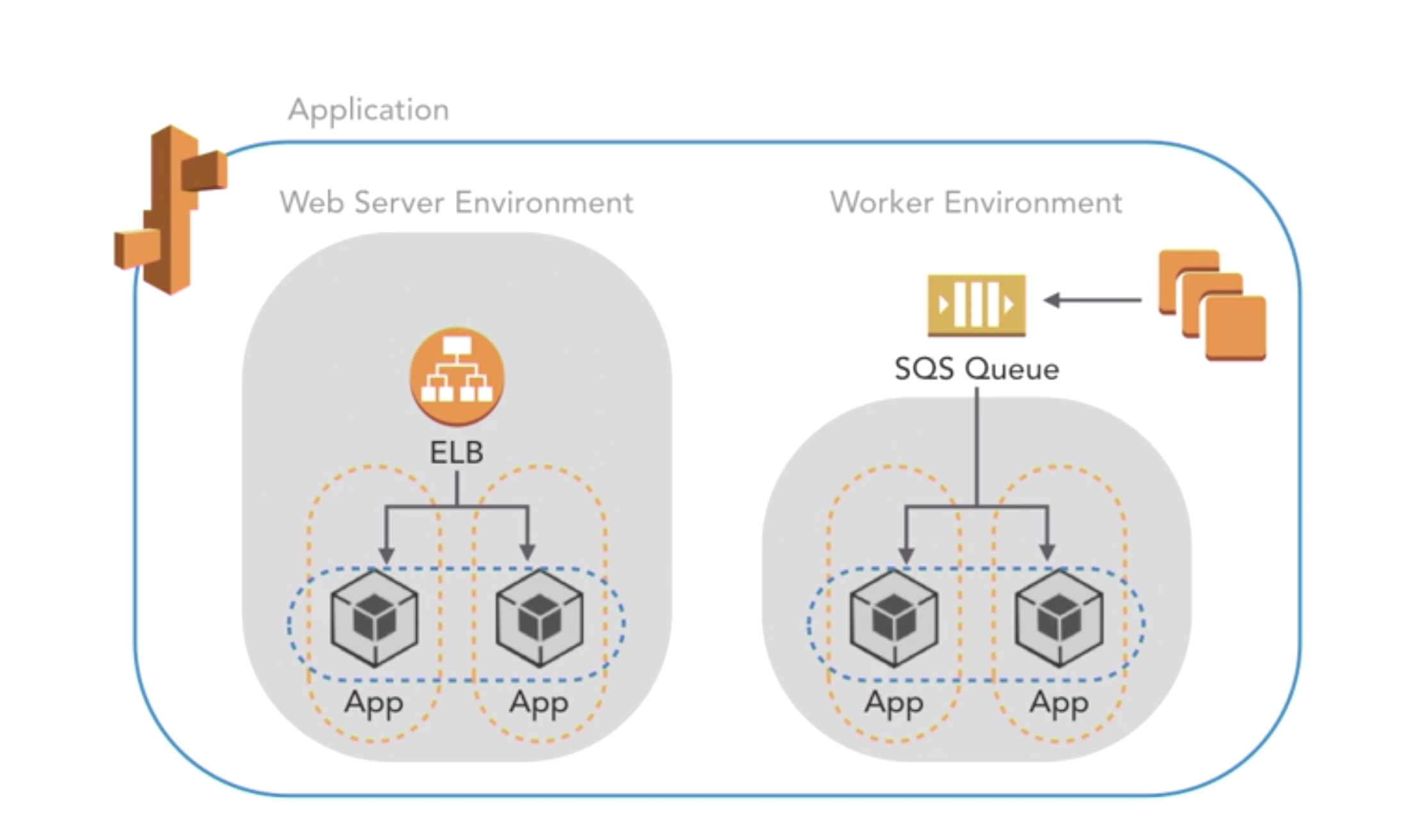
- front end: web server env
- run a website, we bapp, or web API that serves HTTP requests
- back end: worker env
- run a worker app taht processes long-running workloads based on queues
- front end: web server env
- env type
-
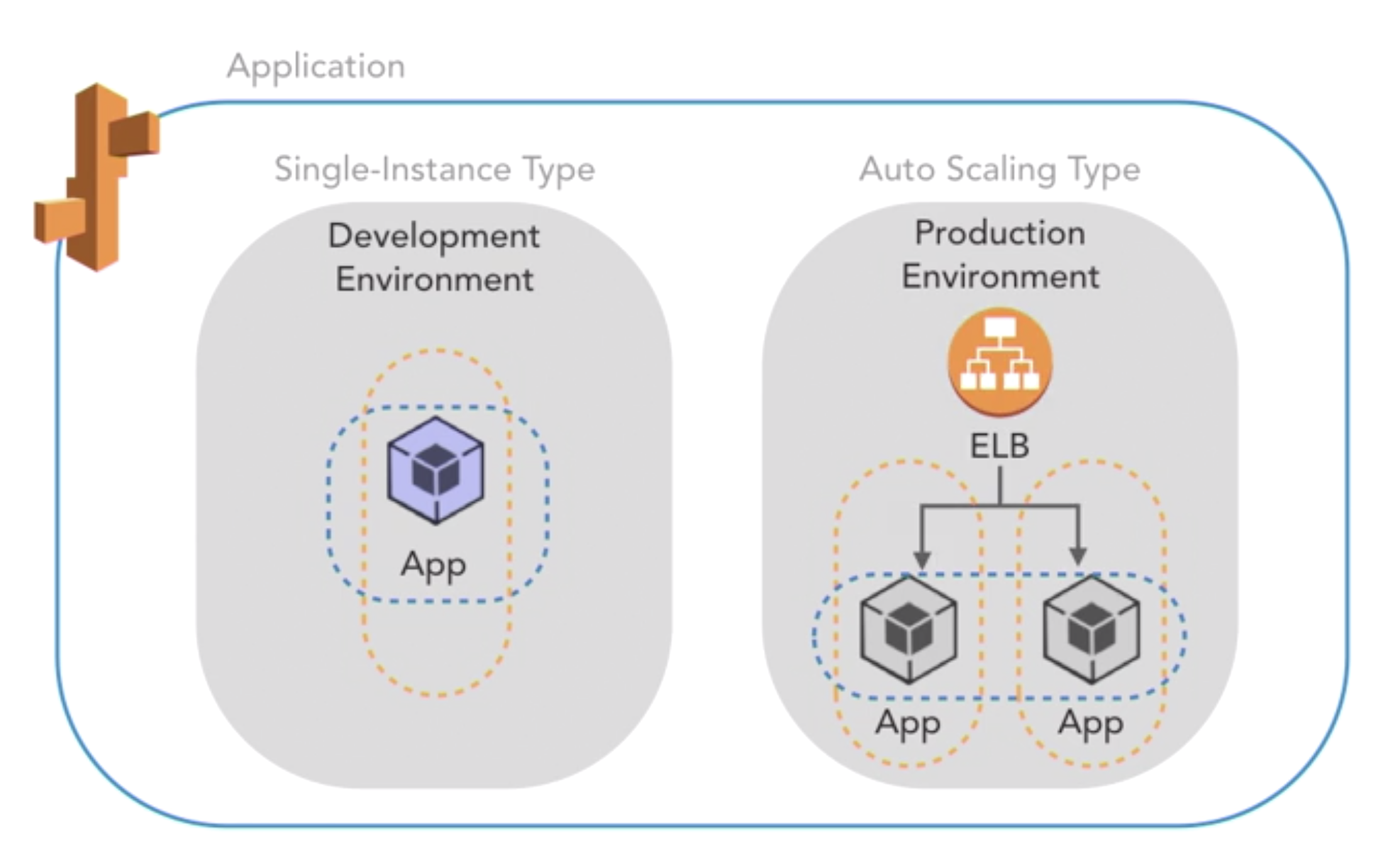
- single instance
- auto scaling: multi single instance
- app:
Modify an app
- rolling updates and monitoring
Troubleshoot modification
- by event check
Managing env
- dashboard and configuration
- health and logs
- monitoring and alarms
- updates, events and actions
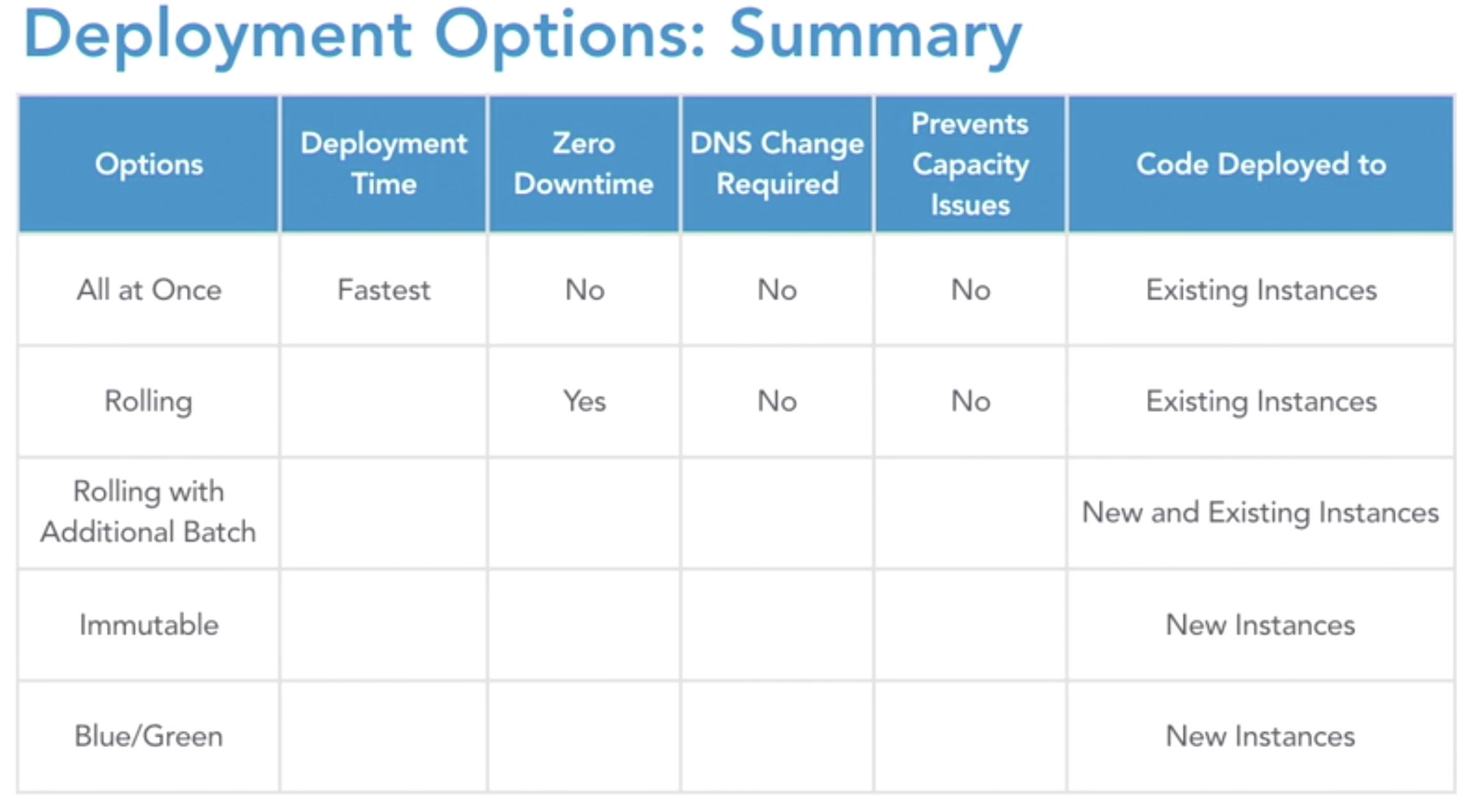
Deployment options when new version comming
- all at once
-

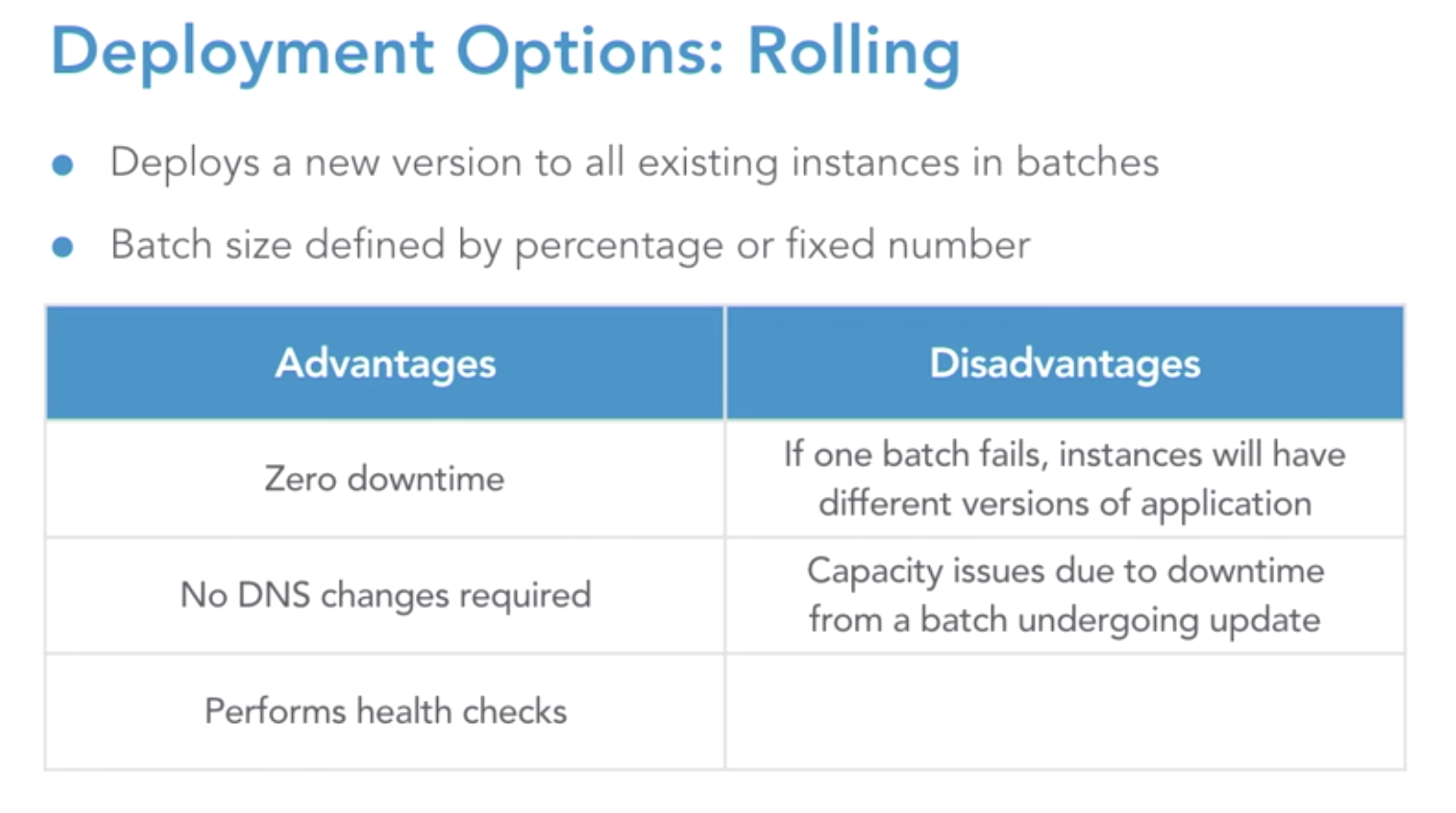
- rolling
-
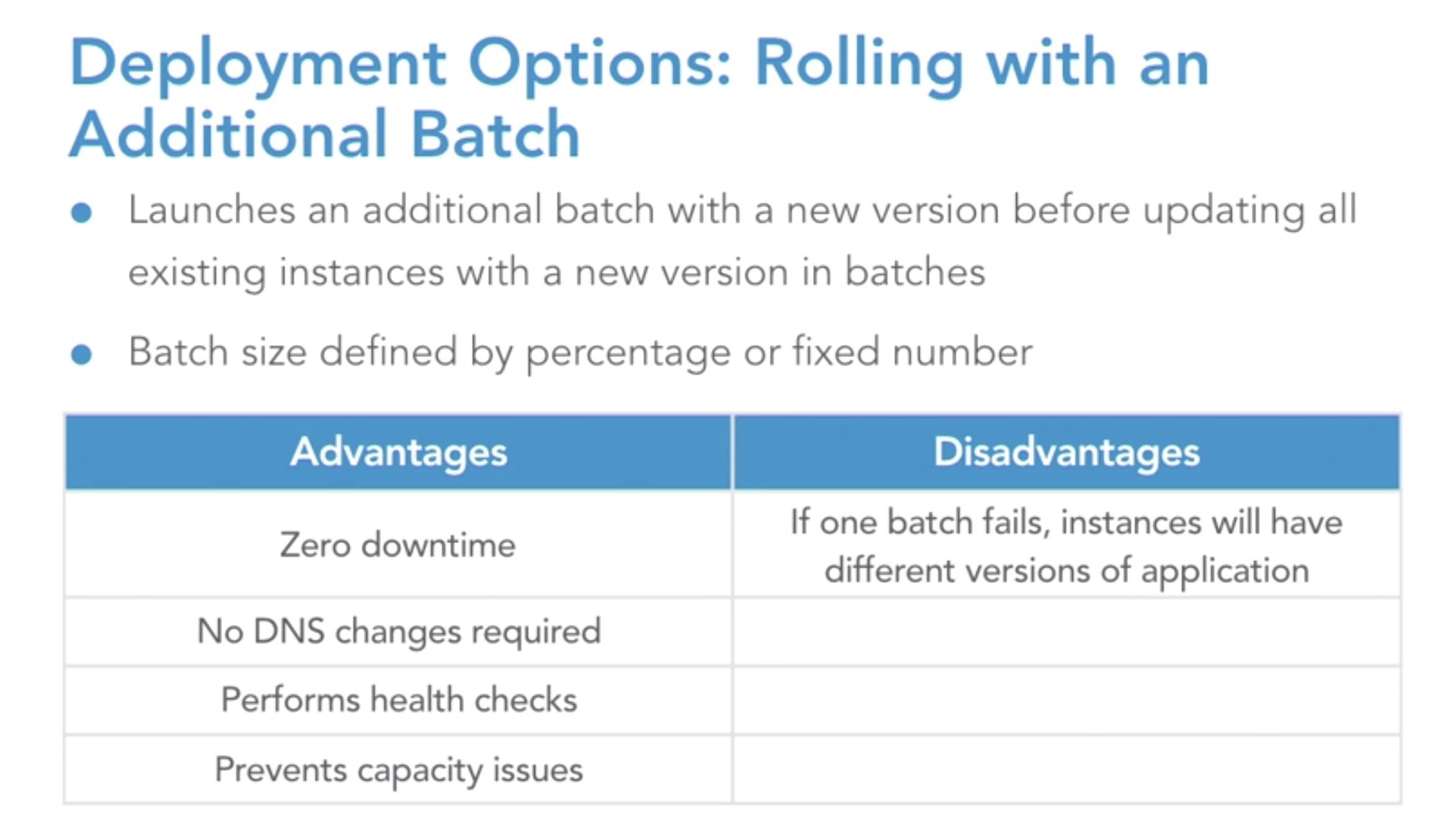
- rolling with and additional batch
-
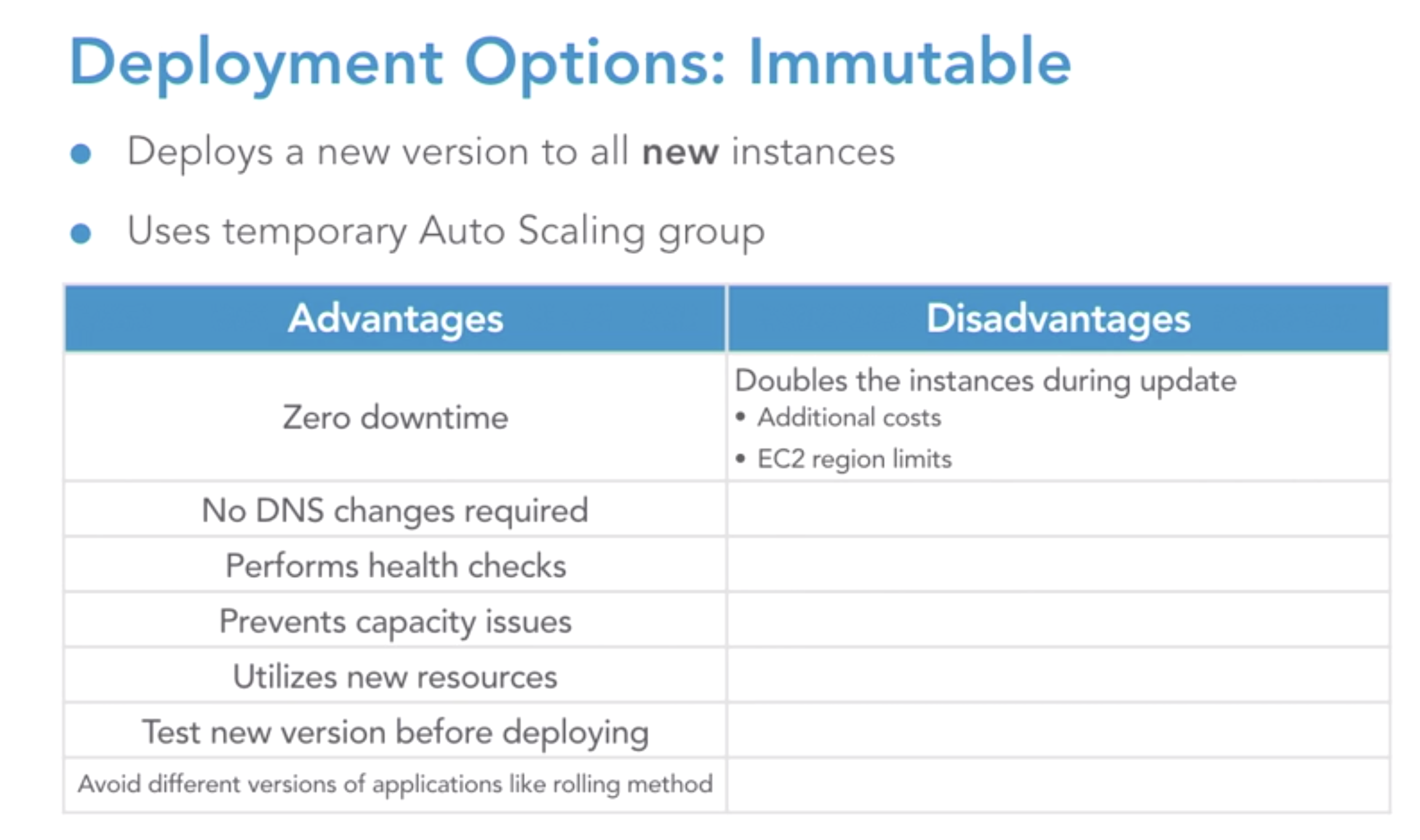
- immutable
-
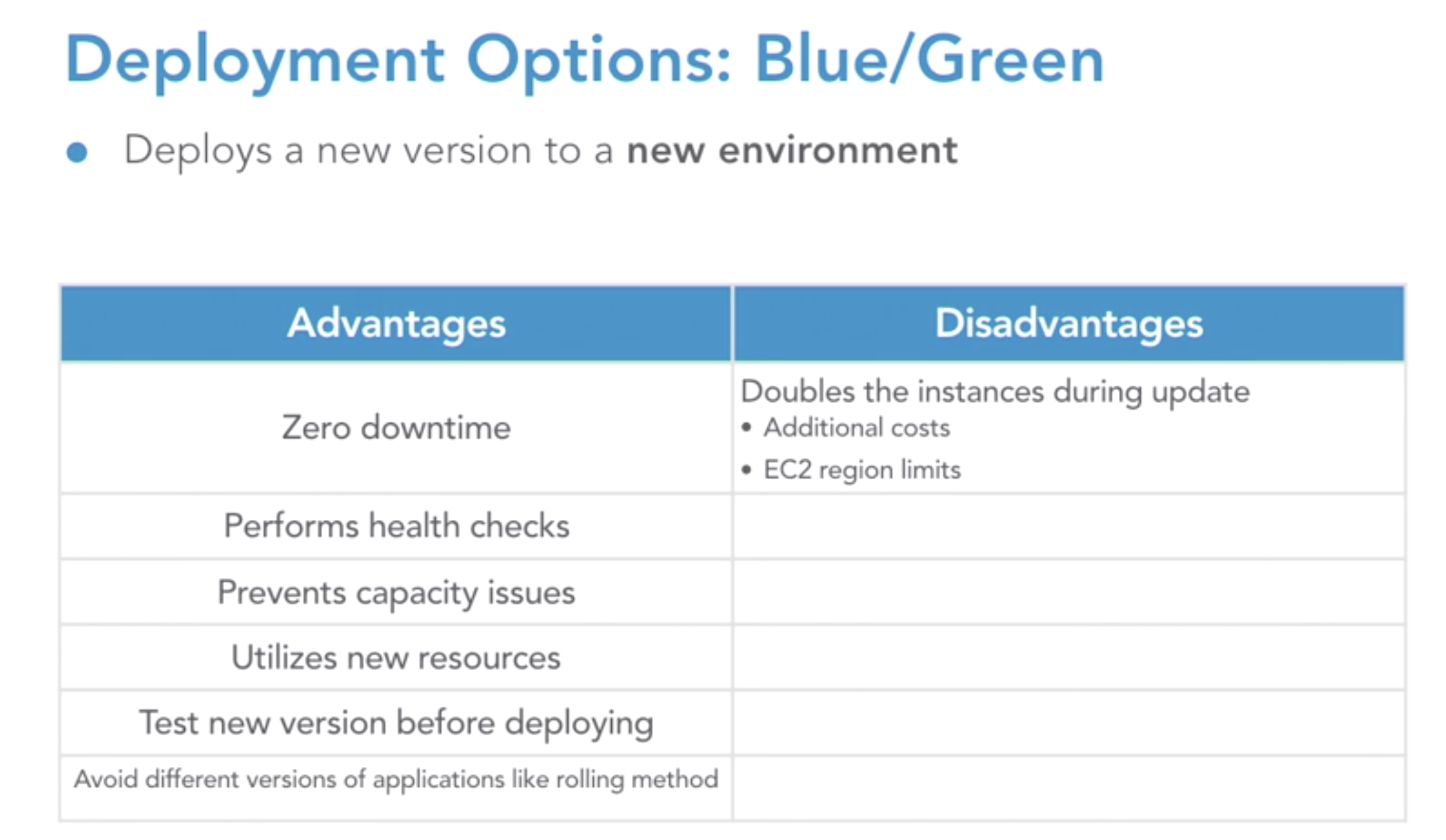
- blue/green
-
- summary
-
Deploy app versions
Advanced configuration
Additional considerations
OpsWorks ???
- A configuration management service that allows you to configure and manage server and apps using automation platforms like Chef or Puppet
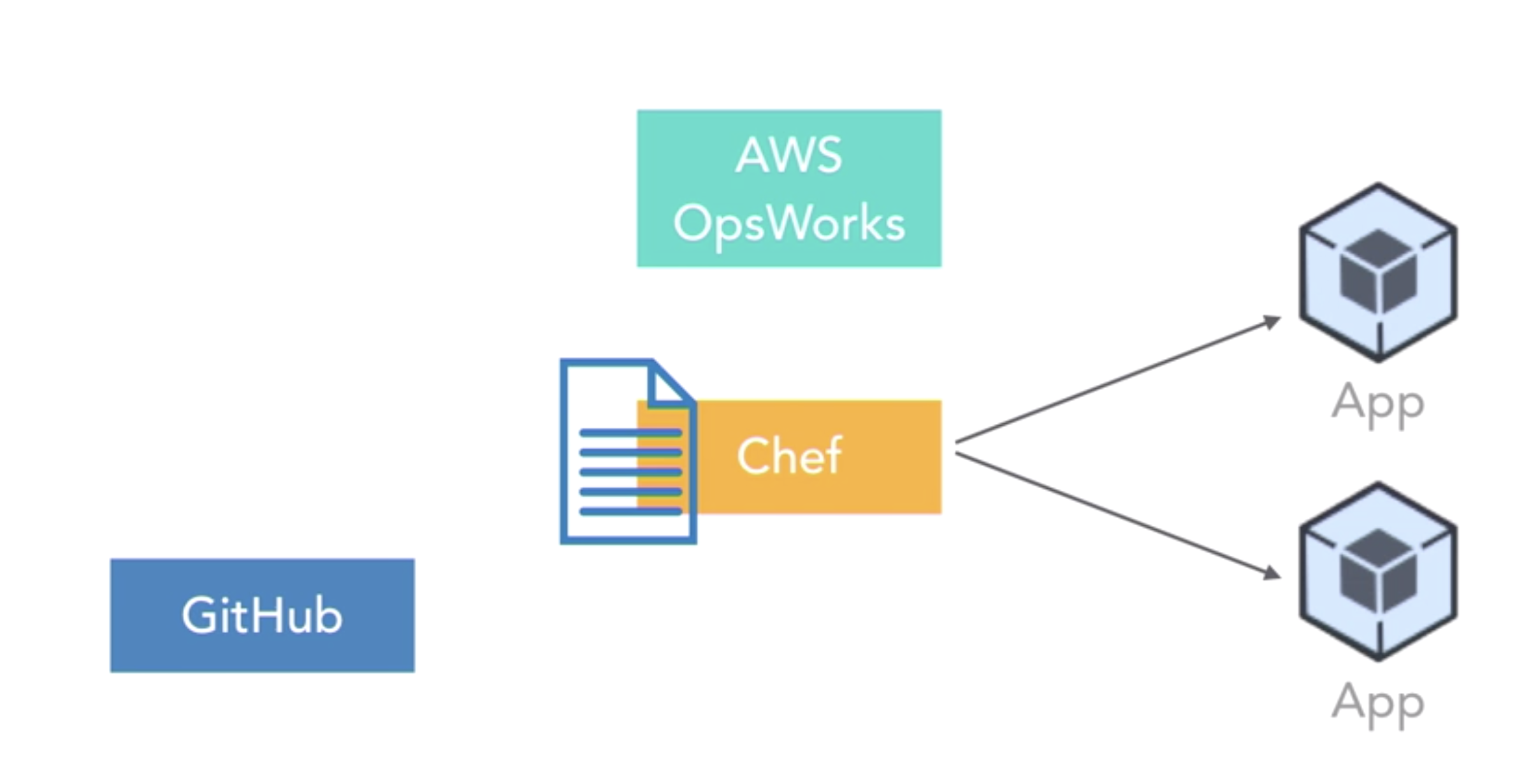
- aws opsworks stacks
-
- aws opsworks for puppet enterprise
- aws opsworks for chef automate
- concetps:
- cookbooks:
- recipes:
- client-server architecture
- setup process:
- step1: setup chef server with cookbooks and recipe roles
- step2: install chef client on instance
- step3: register instnces as chef node with check server
- step4: assign chef node with a role
- step5: chef client on chef node pulls recipes from chef server based on role
- step6: chef client applies recipes on chef onde by executing chef run
- if someone manually changes configuration on the node
- step7: chef client pulls recipes periodically (default: 30mins)
- step8: chef client checks for configuration changes and reapplies recipes
- consistent configuration restored
- concetps:
- Deploy OpsWorks
- Create Chef Automate server
- Configure Chef
- Add Node
- Remove Node
- Delete Chef Automate server
Beanstalk vs OpsWorks