Object-Oriented Fundamentals
- What’s object?
- 真实世界中的对象
- 对象有各种attributes属性 (名词)
- 对象有各种behaviors方法 (动词)
- What’s class?
- 将现实世界中的对象抽象
- code-template for creating program objects
- Four foundation ideas
- Abstraction抽象
- Polymorphism多态
- use the same interface for methods on different types of objects
- overriding (重写)
- method overloading (重载)
- Inheritance继承
- Encapsulation封装
- Three steps for OO
- Analysis
- Design
- Programming
- UML
Requirements
- Functional requirements:
- Non-Functional requirements:
- FURPS
- Functionality
- Usability
- Reliablility
- Performance
- Supportability
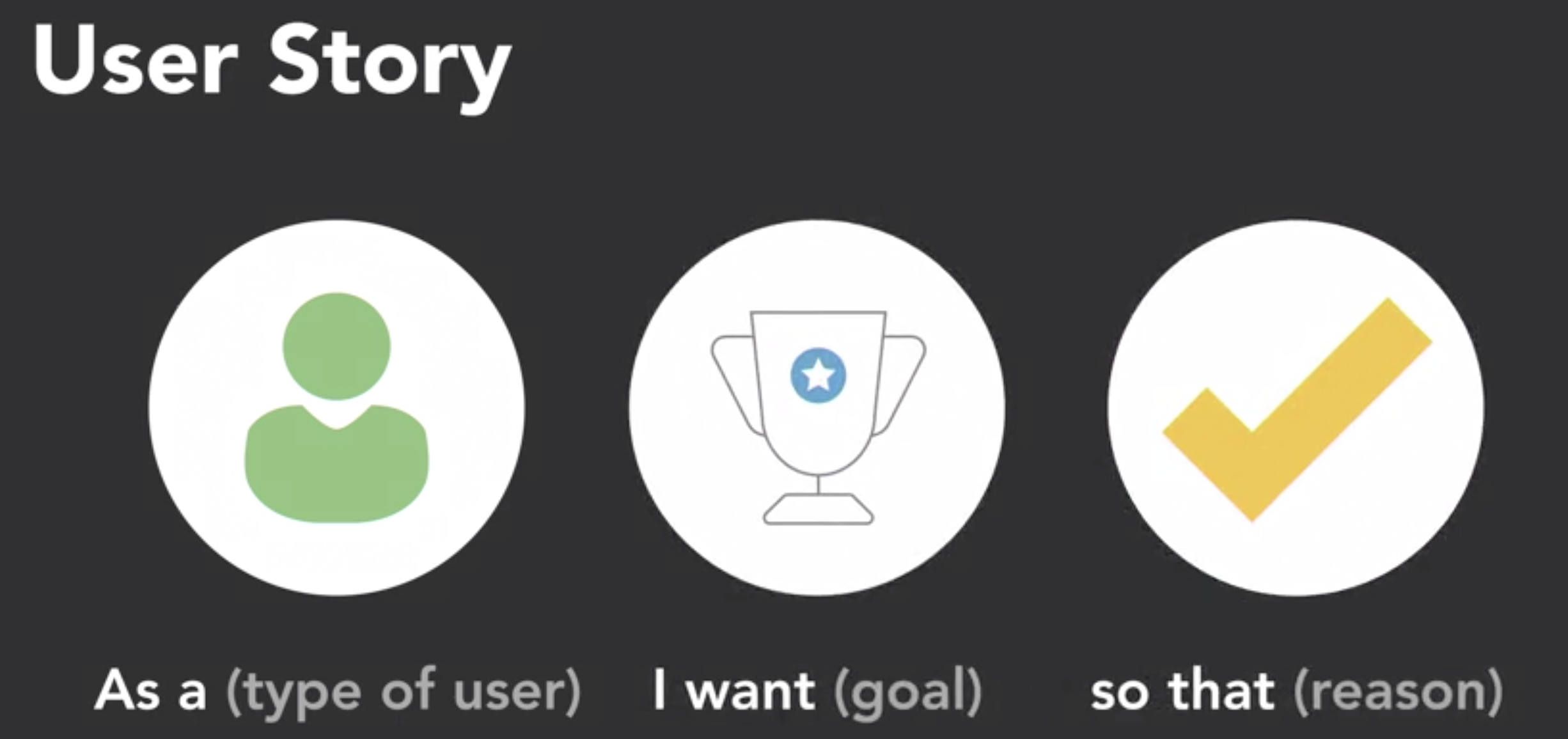
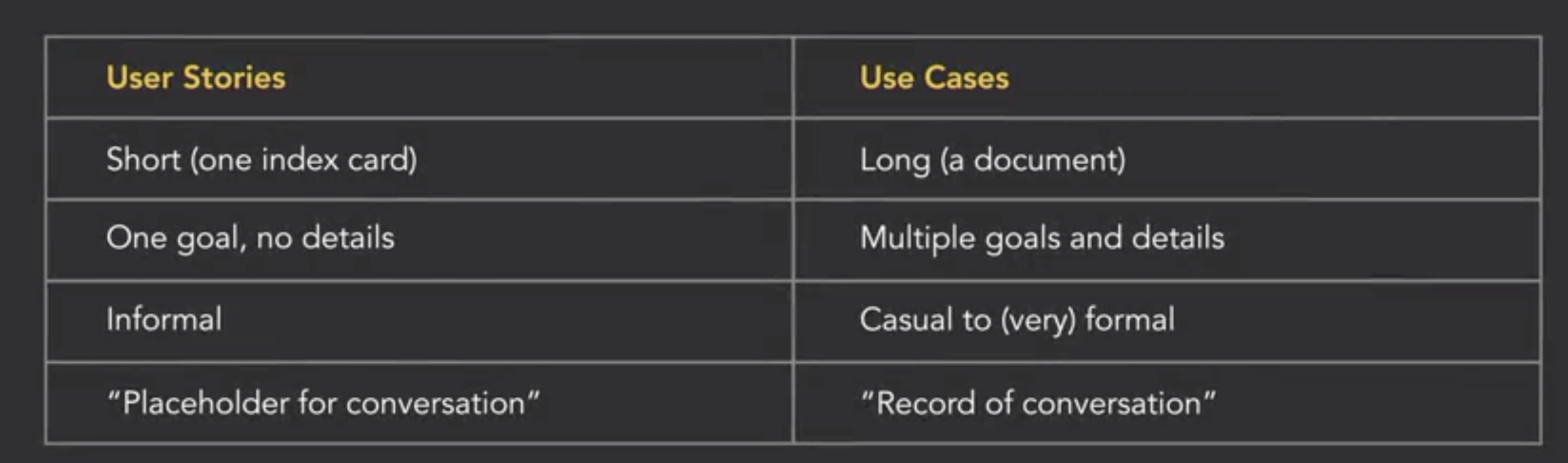
Use Cases and User Stories
- Use Cases
- title
- actor
- how to identiy?
- 交互对象
- primary actor is user for the application initialtion
- success scenario
- how to identiy
- 确认用户目标
- focus on the typical situation that would occur
- active voice, easy to read, short and concise
- Diagram use case
- make actor connect with scenario
- Use Stories
Domain Modeling
- Indentify objects
- Indentiy class relationships
- Indentiy class responsibilities
- CRC cards
- class, responsibility and collaboration
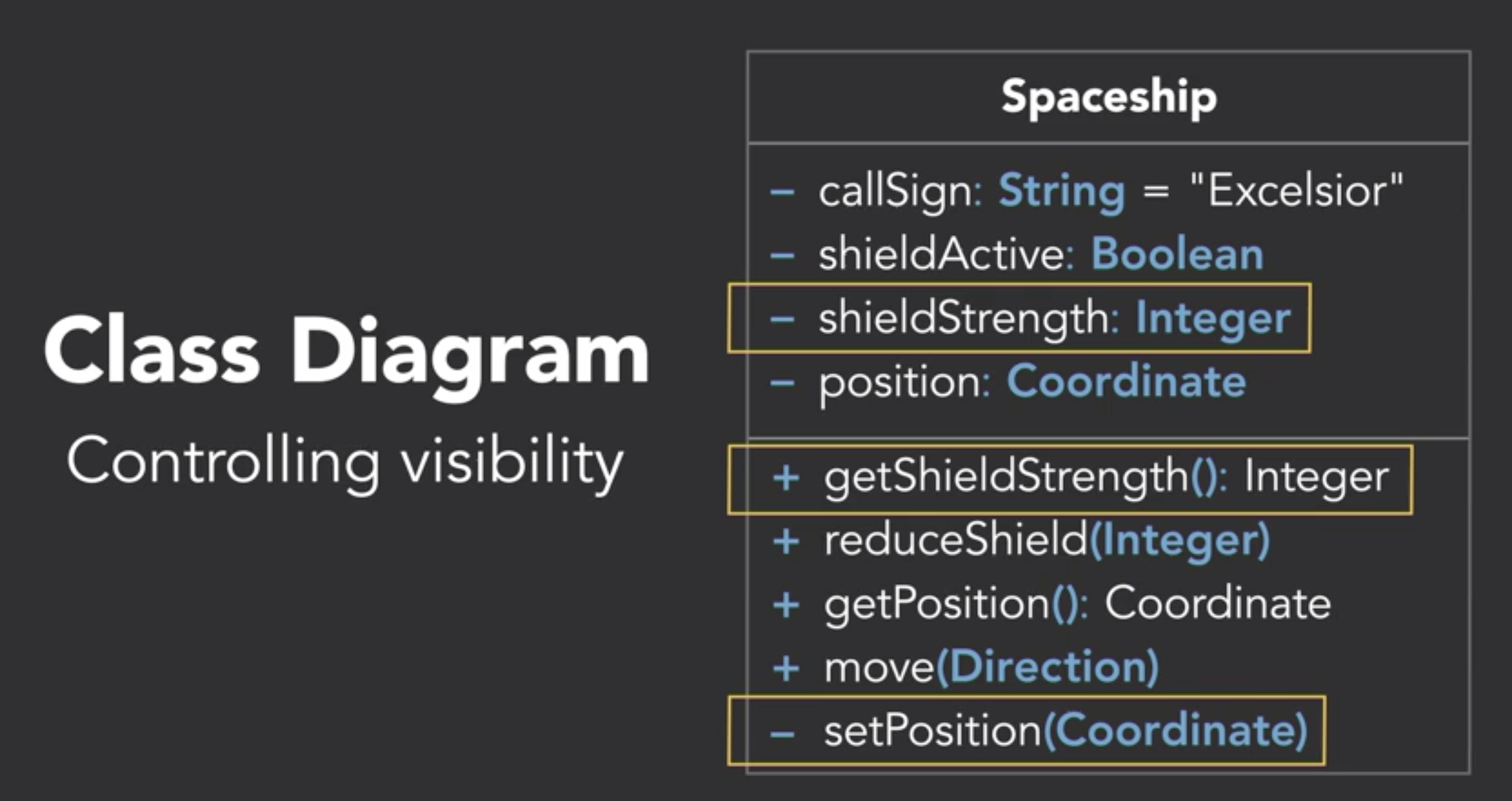
Class Diagrams
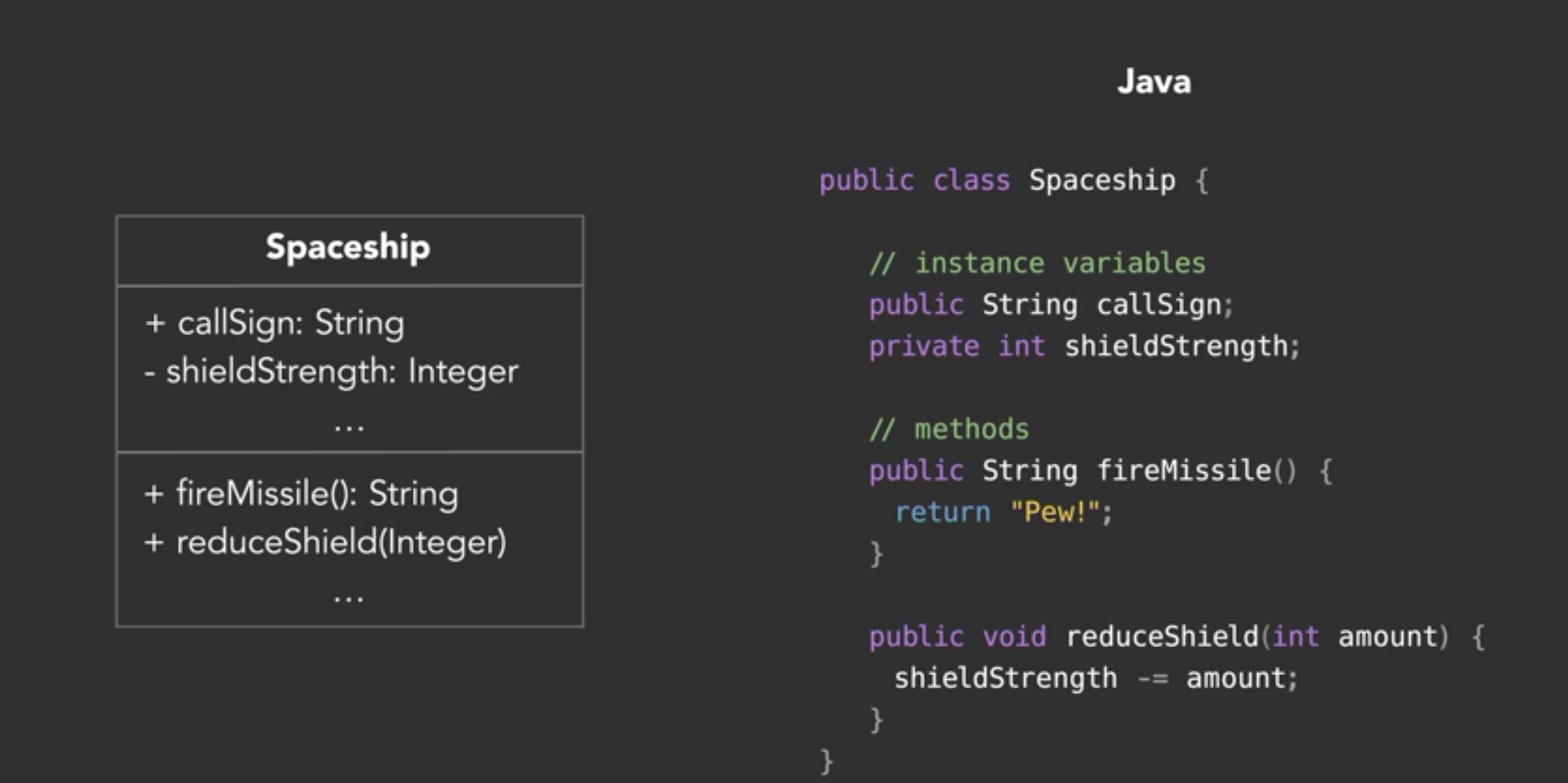
- UML diagram for class
- Convert class diagram into code
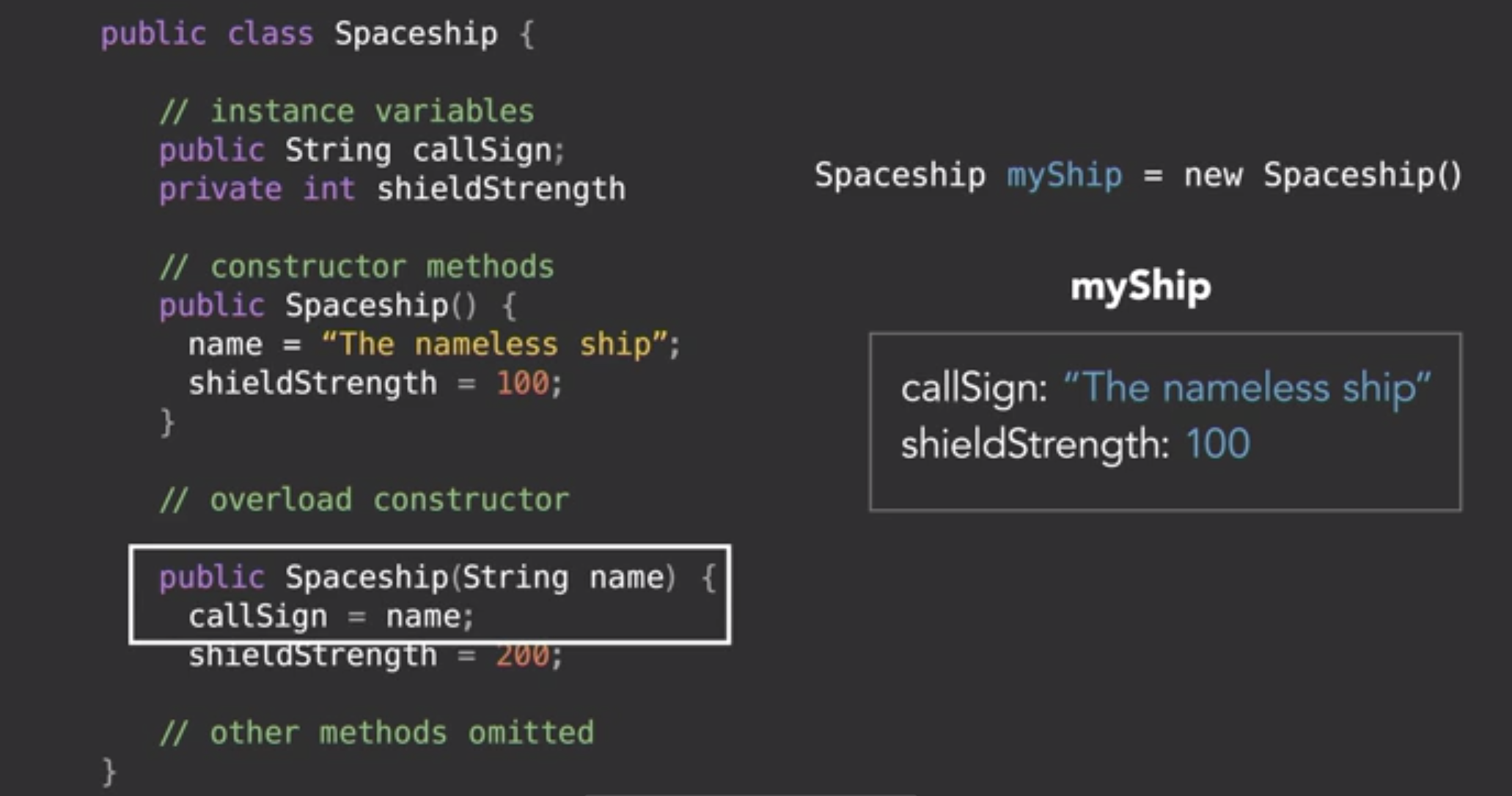
- Instantiation
- Constructor
- 初始化attribute
- 通过overloading, 可以有多个构造函数
-
- Destructoer
- Static attribues and methods
-
- classname.静态属性/方法,非静态对象,使用实例名称,eg:Instantiation.name
-
- static in UML
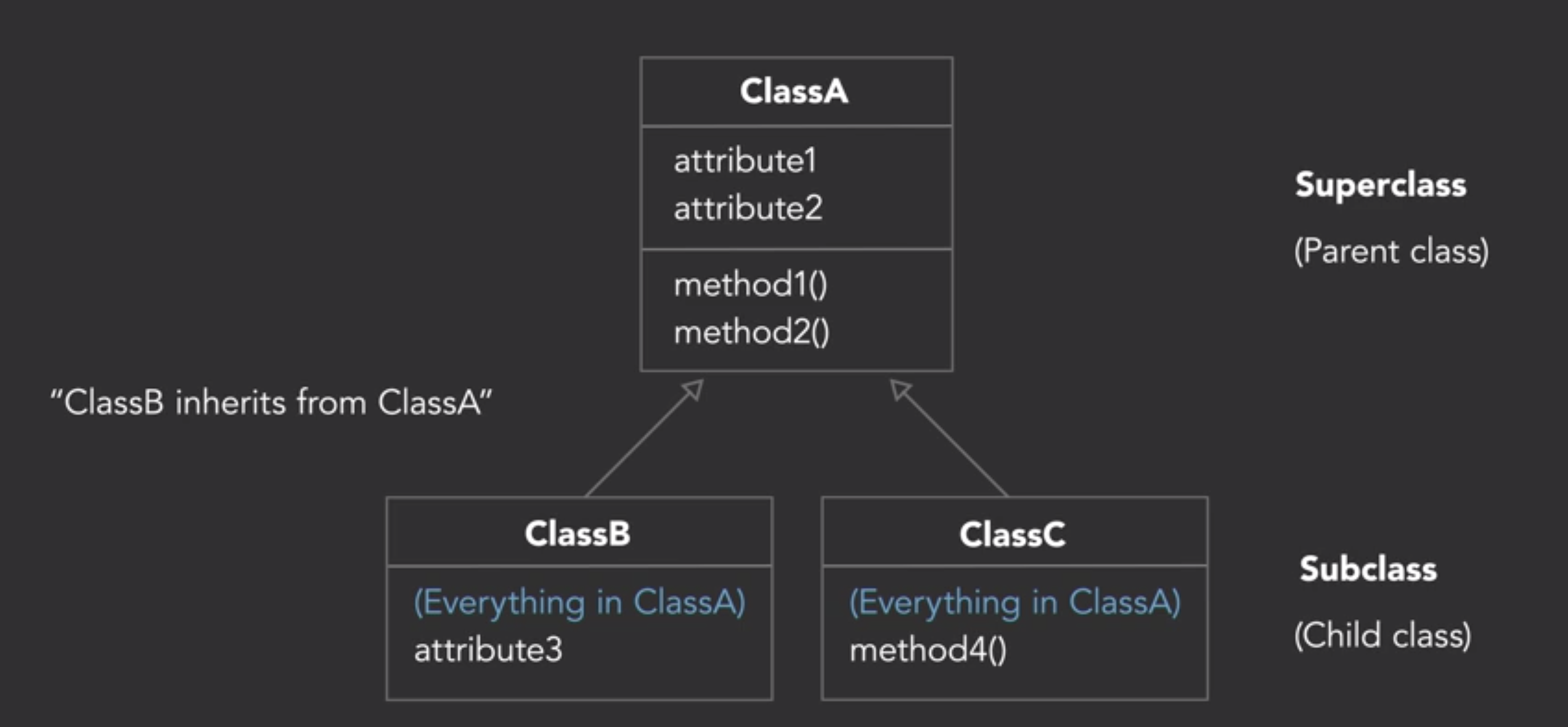
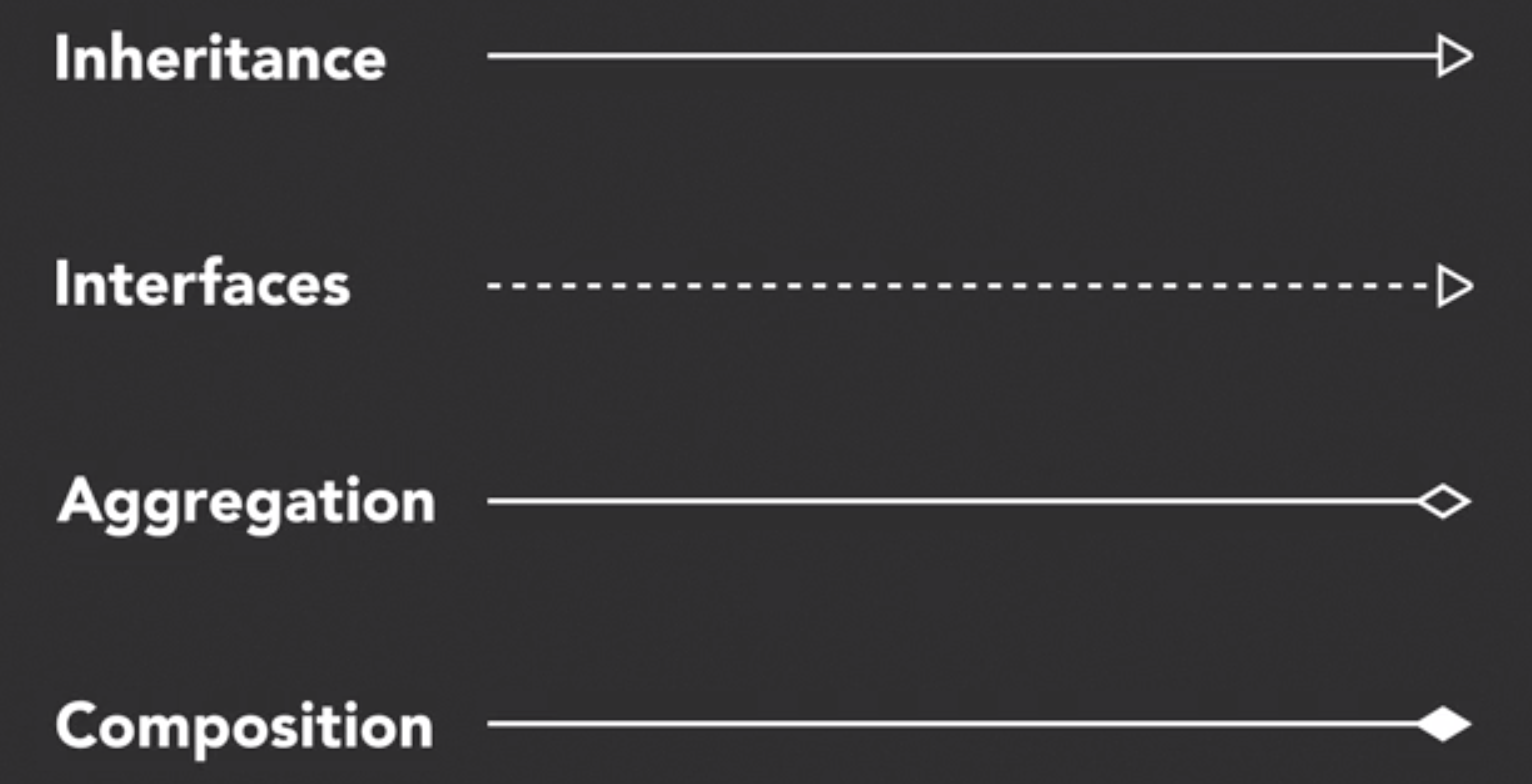
Inheritance and Composition
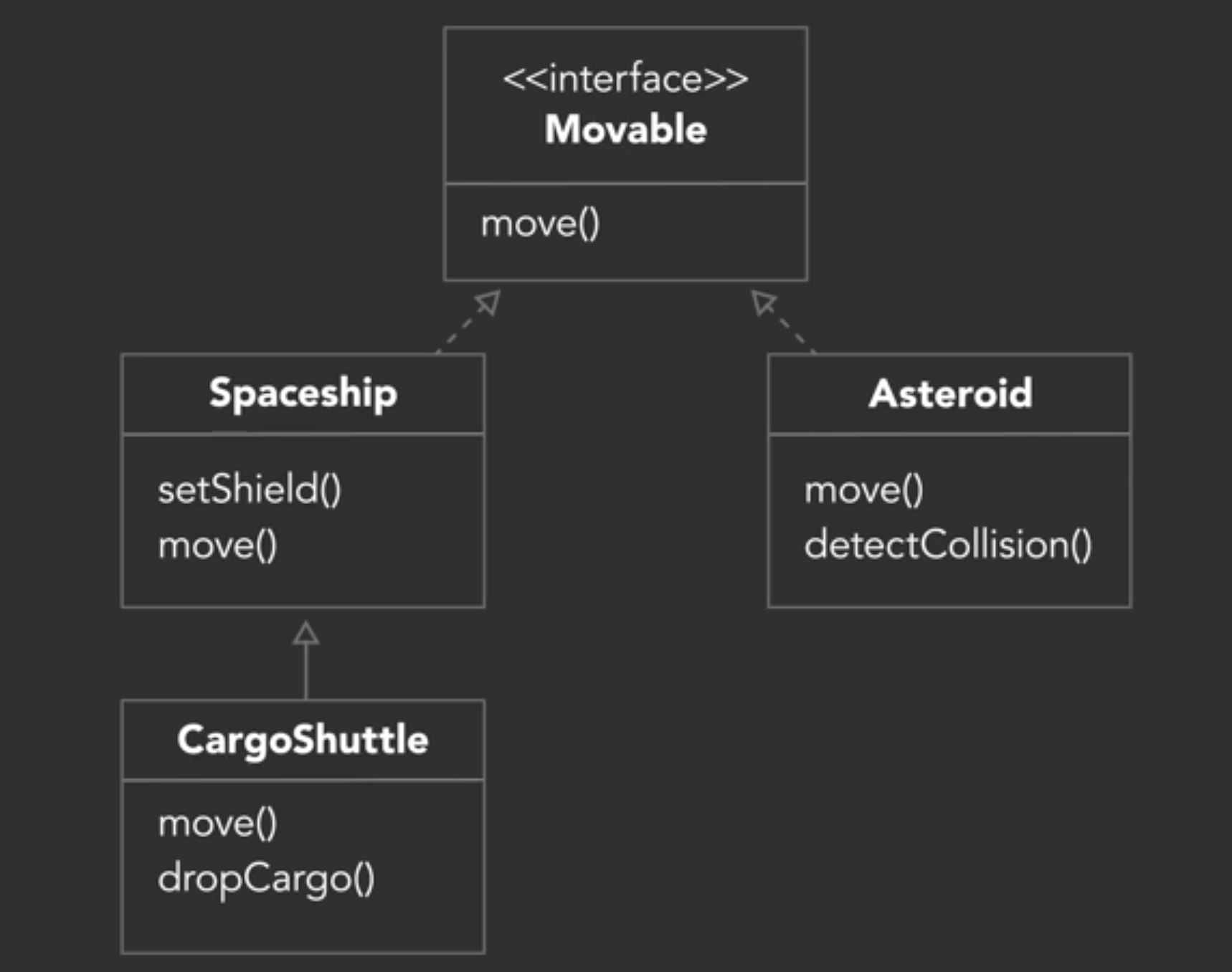
1. 继承 (is a)
-
- 在子类Overriding重写父类的方法
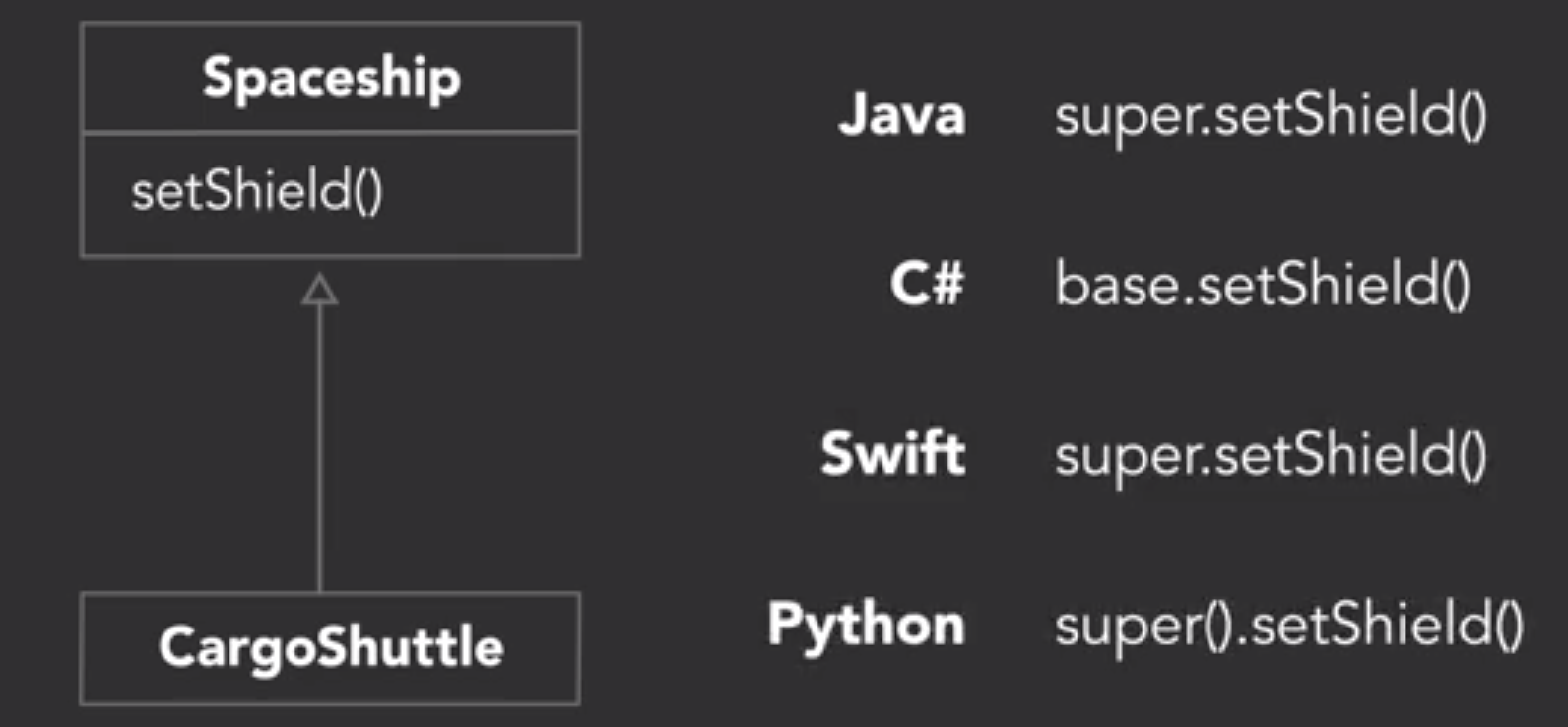
- 引用父类的方法
-
4. 抽象类 abstract class (UML中类名斜体)
+ exists for other classes to inherit
+ can’t be instantiated
+ contains at least one abstract method
5. 接口(interface)
+
+
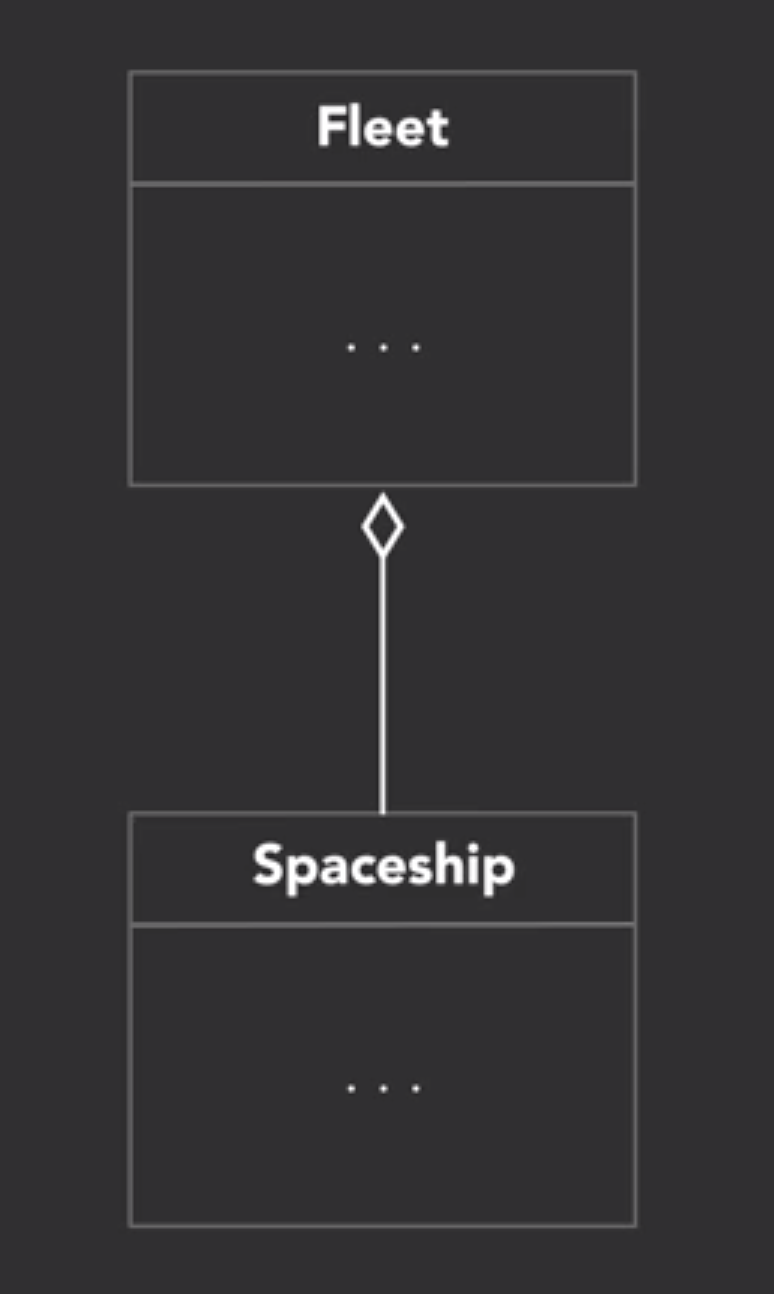
6. Aggregaton (has/uses many)
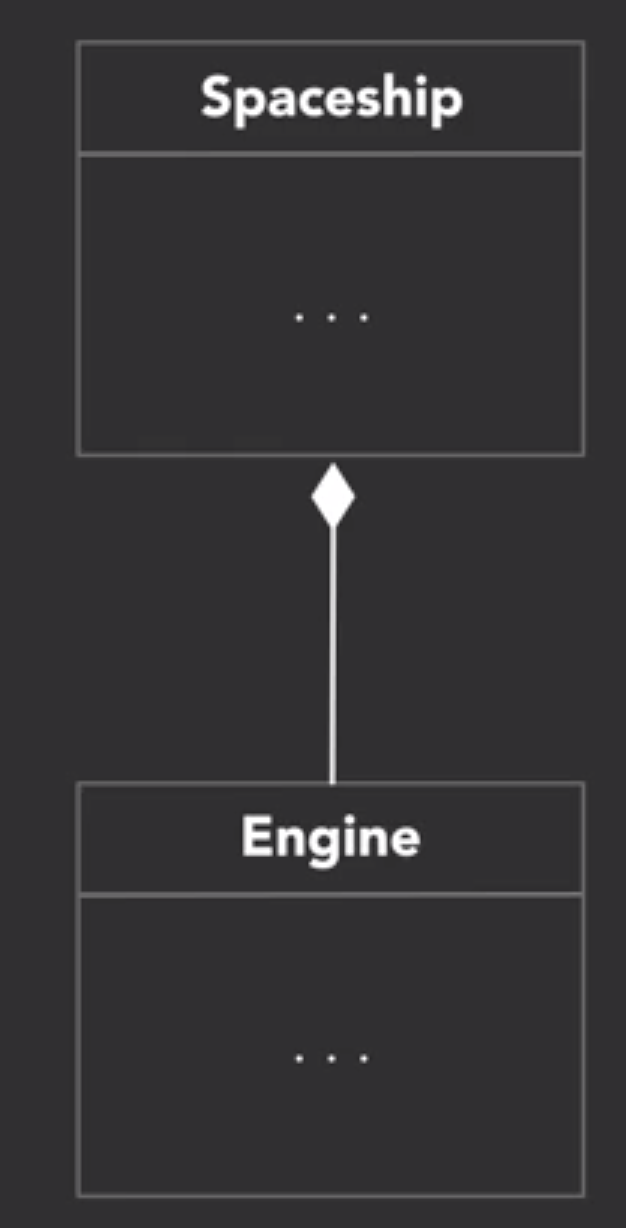
7. Composition (owns a)
8. UML
Software Development
- 面向对象语言对比
- Dev principle
- Single responsibility principle
- a class should have only a single reponsibility
- DRY
- YAGNI
- Code Smell
- Software testing
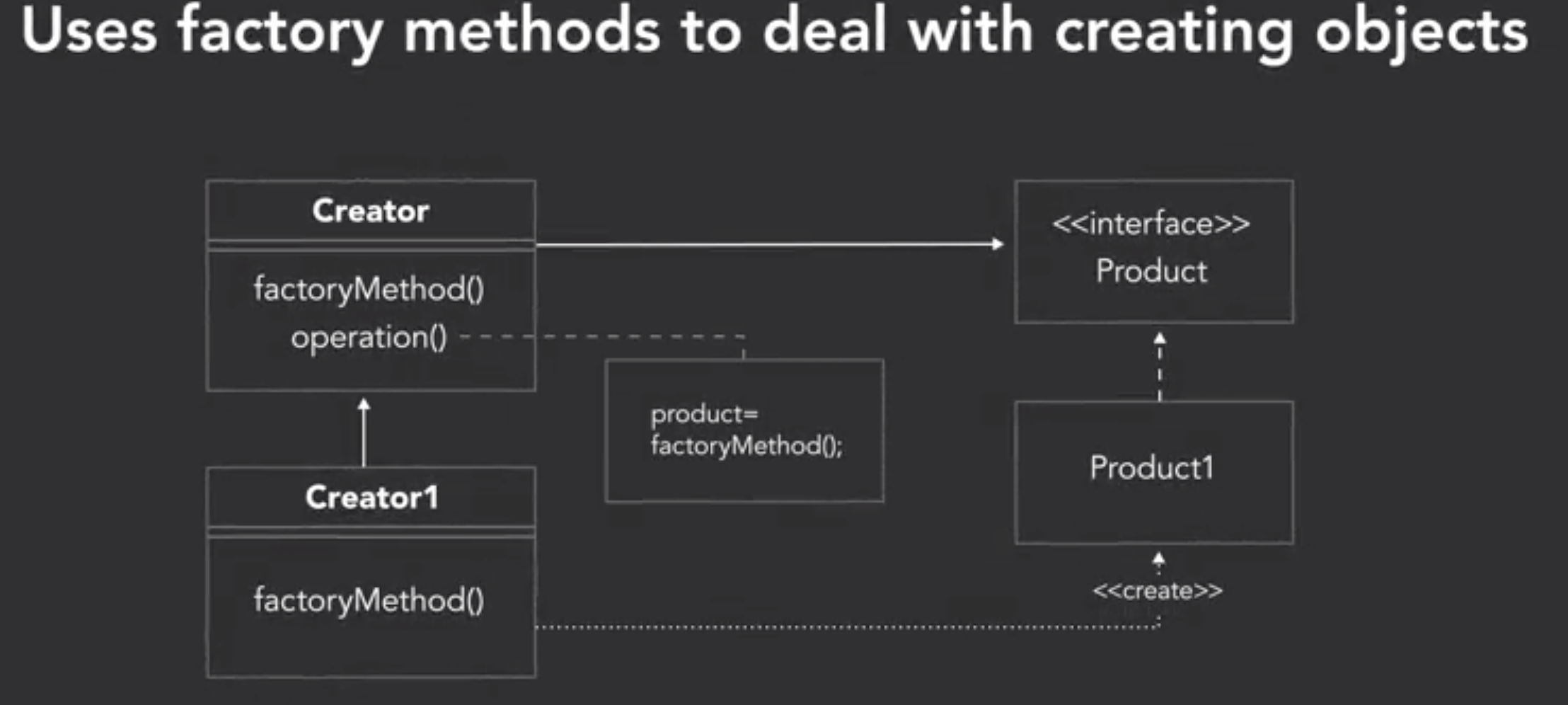
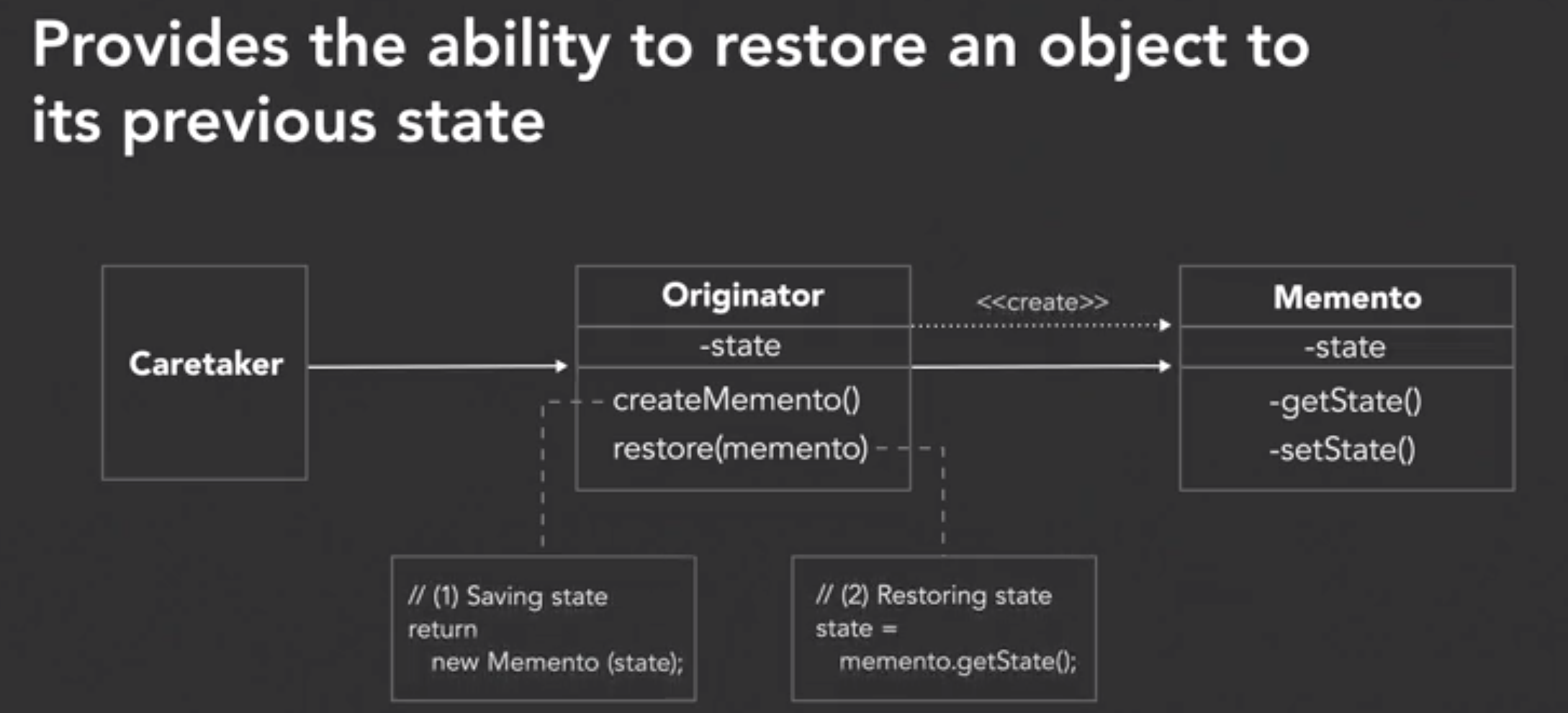
- Design patterns
- factory method pattern
- memento pattern
-
- 参考书
- “Design Patterns” by Gang of Four book
- “Head First Design Patterns”