Python - Algorithms
Overview
Algorithm complexity
- space: how much memory does it require?
- time: how much time does it take to complete?
Classification
- serial/parallel
- exact/approximate
- deterministic/non-deterministic
Common Algorithms
- search
- find specific data in structure
- sorting
- take a dataset and apply a sort order to it
- computational
- give one set of data, calculate another
- collection
- work with collecions of data
eg: 求最大公约数
def gcd(a,b): while(b!=a): t=a a=b b=t%b return a
- search
Algorithms Performance
- Measure how an algorithm responds to dataset size
- Big-O notation
- classifies performance as the input size grows
- “O” indicates the order of operation:
- time scale to perform an operation
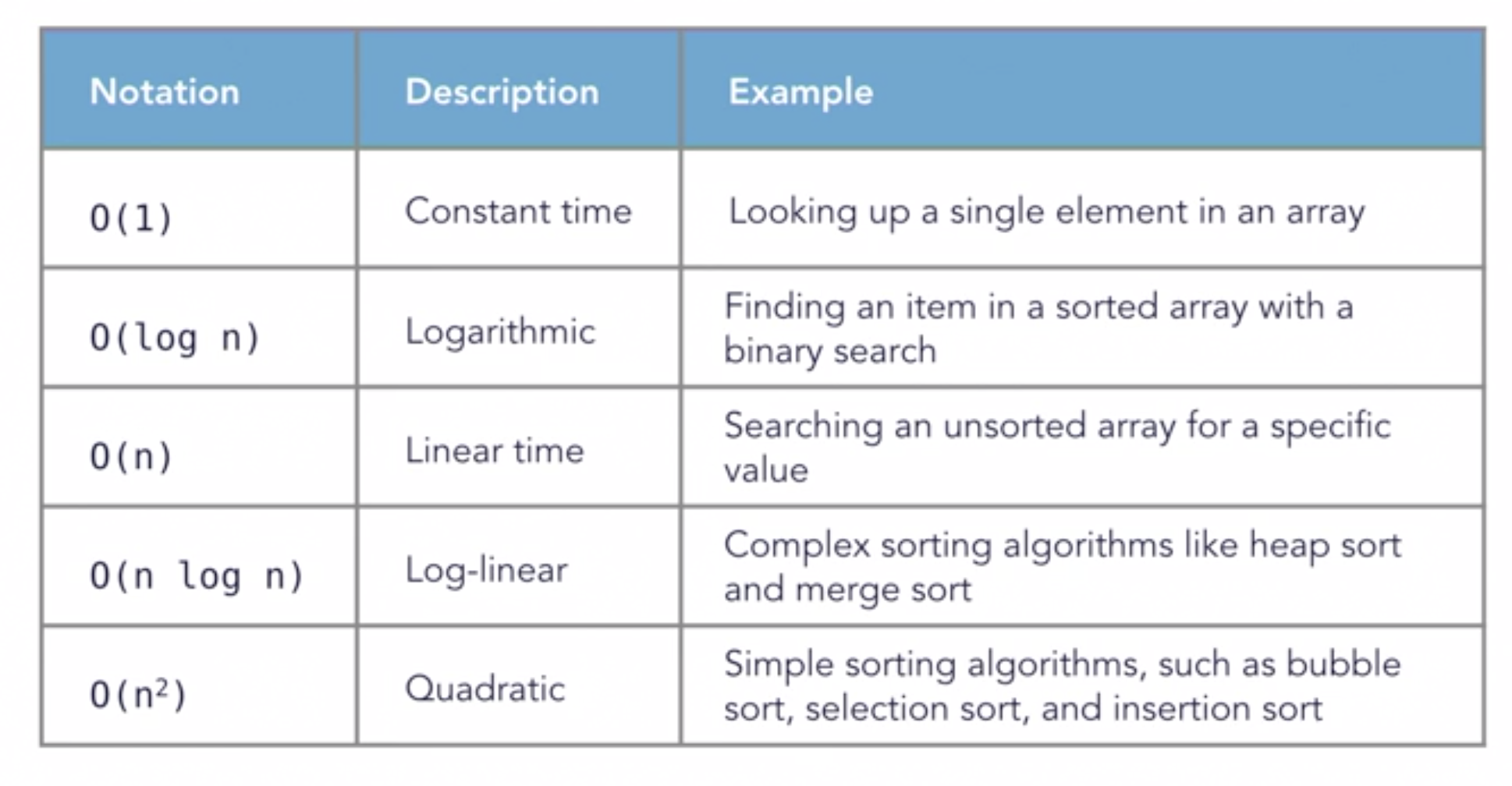
- Common Big-O terms
-
Common Data Structure in algorithms
- arrays
- linked lists
- stacks and queues
- trees
- has tables
Recursion
eg:
def countdown(x): if x==0: print ('done') else: print (x, '...') countdown(x-1) print ('foo')乘方eg:
def power(num, pwr): if pwr == 0: return 1 else: return num * power(num, pwr - 1)乘积eg:
def factorial(num): if num == 0: return 1 else: return num * factorial(num-1)
Sorting data
The bubble sort
def bubblesort(dataset): for i in range(len(dataset) - 1, 0, -1): print(i) for j in range(i): print("j="+str(j)) if dataset[j] > dataset[j+1]: temp = dataset[j] dataset[j] = dataset[j+1] dataset[j+1] = temp print(dataset)The merge sort
The quick sort
Searching data
Search in unordered list search
def find_item(item, itemlist): for i in range(len(itemlist)): if item == itemlist[i]: return i return NoneSearch in ordered list search (二分查找)
def binarysearch(item, itemlist): listsize = len(itemlist) - 1 lowerIdx = 0 upperIdx = listsize while lowerIdx <= upperIdx: midPt = (lowerIdx + upperIdx) //2 if itemlist[midPt] == item: return midPt if item > itemlist[midPt]: lowerIdx = midPt+1 else: upperIdx = miPt-1 if lowerIdx > upperIdx: return NoneDetermine if a list is sorted
def is_sorted(item, itemlist): for i in range(len(itemlist)-1): if(itemlist[i] > itemlist[i+1]): return Falsedef is_sorted(item, itemlist): return all(itemlist[i] <= itemlist[i+1] for i in range(len(itemlist)-1))
Other Algorithms
Unique filtering with hash table
filter = dict() for key in items: filter[key] = 0 result = set(filter.keys()) print(result)Value counting with hash table
counter = dict() for item in items: if(item in counter.keys()): counter[item] += 1 else: counter[item] = 1 print(counter)Find max value recursively
def find_max(items): if len(items) == 1: return itms[0] op1 = item [0] op2 = find_max(itms[1:]) if op1 >op2: return op1 else: return op2
